Ready to take control of your financial life? Whether you are an experienced investor or just starting, asset management is the key to making your money do the work for you. In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about managing your assets—think of it as your guide to better investing.
From maximising returns to minimising risk, let’s get into asset management!
What is Asset Management?
An asset management strategy is the plan that governs how your investments are managed to achieve specific financial goals. Think of it as the plan outlining where, when and how you will allocate your assets—whether shares, bonds, property or other investment vehicles.
A good strategy considers your risk tolerance, time frame and overall financial objectives. It’s not just about growing wealth but managing risk and ensuring your assets are diversified to ride out market ups and downs.
The strategy should be tailored to personal or organisational financial needs for long-term success. To understand how this is positioned, go for a CFO course.
Why Is It Important?
Here’s why having a strategy is key to your financial success:
- Maximises returns: An asset liability management strategy helps you allocate your investments to achieve the best growth. Instead of just picking stocks or assets, you have a plan in place that focuses on maximising returns over time by taking advantage of the right opportunities.
- Manages risk: Every investment carries some level of risk. A good management strategy ensures you’re not taking on unnecessary risk. It provides a balanced approach so you can weigh up potential gains against risk and not put all your eggs in one basket, minimising the impact of market volatility.
- Customised to your financial goals: One size doesn’t fit all in investing. A bespoke asset management strategy is aligned with your personal or organisational financial goals—whether you want to build wealth, a retirement plan, generate a regular income stream or preserve capital for future generations.
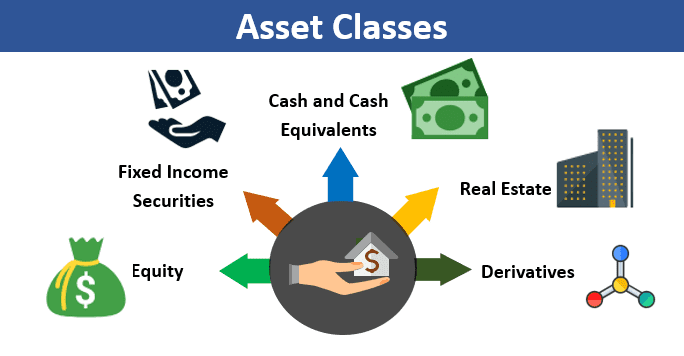
- Diversification: One of the key principles is diversification, or spreading your investments across different asset classes (shares, bonds, property etc.). This means no one bad investment can hurt your overall portfolio.
- Adapts to market conditions: The markets are always changing and a good strategy is flexible enough to adapt to changes. Whether it’s responding to downturns or new growth opportunities, your plan can be tweaked to stay relevant and keep your investments safe while capitalising on the latest trends.
- Long-term financial stability: With a solid strategy, you’re better equipped to achieve long-term financial stability. Rather than chasing short-term gains or making rash decisions, this strategy is focused on steady long-term growth and helps you build wealth gradually while protecting your assets.
- Better decision-making: Management for oneself is as important as asset liability management in banks. Rather than reacting emotionally or impulsively to market movements, you can make timely and thought-through investment decisions based on logic, data and your financial plan.
- More confidence and control: With a solid strategy for investments, you’ll have more control and confidence in your financial journey. Knowing each decision you make is part of a bigger plan gives you peace of mind even in times of market volatility.
Key Components of Asset Liability Management
Here are the primary components of asset management. Note that these are different from the types of asset management.
- Liquidity management: Has sufficient liquid assets to meet short-term liabilities and avoid cash flow issues.
- Interest rate risk management: Balances fixed and variable rates to reduce interest rate exposure.
- Currency risk management: Protects against foreign exchange risks for organisations with global operations.’
- Capital adequacy management: Has a strong capital base to absorb losses and comply with regulations.
- Gap analysis: Identifies mismatches in asset and liability maturities to reduce risk.
- Stress testing: Prepares for worst-case scenarios.
- Regulatory compliance: Meets financial regulations and guidelines.
How to Create a Strategic Asset Management Plan
Follow these steps to create a well-planned asset management system.
- Define objectives: Start by setting clear goals for what you want to achieve with your assets.
- Assess current assets: Do a full inventory of your current assets. Review their performance, condition and relevance to your overall strategy.
- Analyse market conditions: Research current market trends, economic factors and potential risks that could impact your assets.
- Create a strategy: Based on your objectives and analysis create a solid plan that outlines how to deploy, maintain and manage your assets. Consider diversification to reduce risk and increase returns.
- Implement and review: Put the plan in place and review asset performance and market conditions. Adjust the strategy as needed to respond to changes.
- Review and refresh: Review your management strategy regularly to ensure it’s still on track with your goals and market conditions.
Takeaway
A strategic asset management plan is the key to optimising your investments, managing risk and achieving long-term financial stability. By setting clear goals, reviewing your current assets and adapting to market changes, you can create a successful plan that will succeed.
If you want to go deeper into this process and improve your decision-making skills, Imarticus’s Chief Financial Officer course could be the next step in your career. Don’t give it a second thought! Opt today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is asset management?
Asset management is the process of planning and investing to grow wealth, reduce risk and achieve goals. It is generally used in the strategic allocation of assets like stocks, bonds or real estate.
What is asset liability management (ALM)?
ALM is about balancing an organisation’s assets and liabilities to manage risk, including liquidity and interest rate risk, to be stable.
What is asset liability management in banks?
In banks, ALM deals with liquidity, interest rate risk management and matching of asset and liability duration to be profitable and compliant with regulations.
Why is asset management important?
Asset management optimises returns, manages risk, diversifies investments and adapts to market conditions to help individuals and companies achieve long-term financial success.