Introduction: Why Consider a Career in Financial Markets?
Finance is shifting at a faster rate than ever, and with it comes a wave of new opportunity. If you’re a critical thinker who enjoys analysing economic patterns or calculating how money flows through networks, then a career in financial markets might be your calling.
This is not just a high-stakes trading floor business. It involves a broad range of jobs, from finance sales roles and market analysis to investment advisory and wealth management. And with India’s financial services industry growing at a phenomenal pace, it’s the perfect time to step forward and start building your own future.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know—job roles, required skills, market trading careers, finance sales jobs, careers in investment products, qualifications, and even salary expectations—so that you can make an informed decision about your next step.
The Financial Sector in India: Why It’s a Smart Bet
India’s banking and finance sector has been developing rapidly. Indeed, the sector experienced a growth of 9.6% during FY 2021–22, which was more than 5.6% in the previous year. The growth was facilitated by greater financial awareness, digitisation, and an escalating amount of youth investors entering markets. (Source)
The growth has also created a boom in demand for professionals possessing expertise in the sales of financial services, the distribution of products, and advice.
According to a report by Statista, the Indian financial sector is expected to continue expanding rapidly in the coming years, providing a solid foundation for those seeking a finance career path.
Careers in Financial Markets: What Are Your Choices?
The field provides various entry points based on your education and interests. Here are some typical job functions:
1. Product Sales Executive
- Specialises in the sale of financial products like mutual funds, insurance, and investment-linked products.
- Services individual and institutional clients directly.
2. Relationship Manager
- Maintains long-term client relationships.
- Offers money-management advice commensurate with clients’ life goals and risk appetite.
3. Equity Dealer or Trader
- Executes buy/sell orders on clients’ behalf or proprietary trading desks.
- Tracks real-time movement of markets.
4. Investment Advisor
- Makes suitable investment portfolio recommendations.
- Generally certified through NISM or any other regulatory body.
5. Portfolio Analyst
- Analyses and tracks investment portfolios.
- Helps fund managers make intelligent decisions.
- They are not only in demand but also offer good career growth and exposure to new technologies, such as robo-advisory, AI trading, and data analytics.
Why Product Sales in Finance Is a Fast-Growing Field
If you’re proficient in communication, familiar with financial products, and enjoy helping people achieve their goals, then product sales in finance may be the best career choice for you.
Principal Benefits:
- Very lucrative commissions over a guaranteed salary.
- Sapid career growth, especially in banks and AMCs.
- Establish a strong network in the investment division.
- Acquire the real-time practical application of finance concepts.
With Groww, Zerodha, HDFC AMC, and Paytm Money making financial products easily accessible, talented professionals with the necessary skills and an understanding of investor needs are being sought in large numbers.
Key Skills for a Financial Markets Career
Key Skills Across Functions:
- Communication and negotiation
- Market sensitivity
- Analytical mindset
- Basic understanding of financial instruments
- CRM tool skills (e.g., Salesforce, Zoho)
- Knowledge of risk management and compliance
Skill vs. Role Mapping Table
| Skill | Relevant Role(s) | Why It’s Important |
| Sales & Communication | Product Sales Executive, RM | To make complex products simple and build trust |
| Market Research & Analysis | Analyst, Trader | For data-driven decisions |
| Compliance & Regulatory Knowledge | All roles | For legal and ethical financial activities |
| Tech Savviness | Trader, Portfolio Analyst | Tools such as Excel, Bloomberg, and TradingView are essential |
| Interpersonal Skills | Relationship Manager, Advisor | The key to building long-term relationships with clients |
Where to Learn These Skills
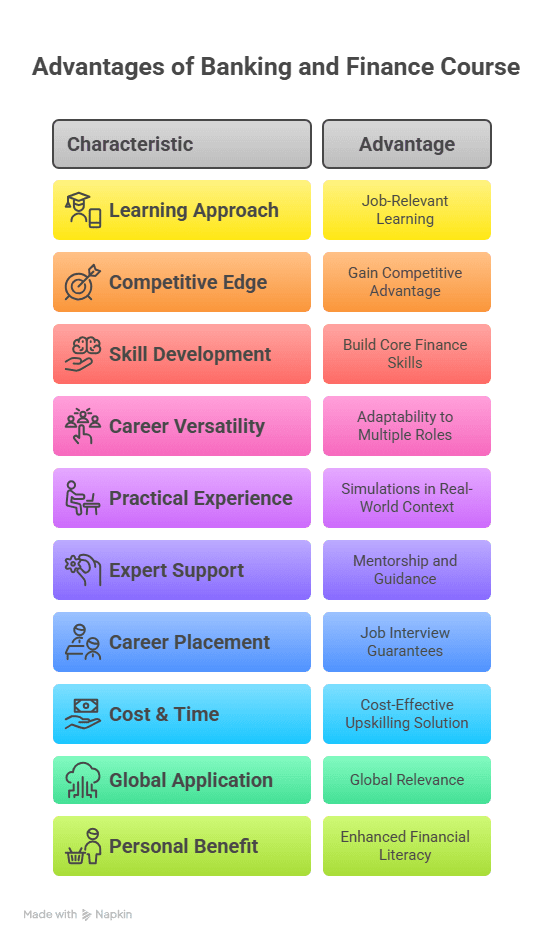
If you are a fresher or want to upskill, the Postgraduate Program in Banking and Finance by Imarticus Learning is one of the most industry-focused programmes present.
Program Highlights:
- Comprises retail banking, financial products, risk management, and compliance
- Role-playing simulations to acquire practical skills
- Mock interviews and placement assistance
- Over 100+ hours of live training by industry experts
- Access to 500+ hiring partners for placement assistance
Career Outcomes Upon Completion of a Banking Certification Course
Completion of a well-designed banking certification course like Imarticus Learning can lead to:
- Immediate offers of bank and NBFC jobs
- Eligibility for sales & relationship management roles
- Adequate interview preparation is due to mentoring
- Placement salary ranging between ₹3.5–5.5 LPA
- Ability to reach ₹8–12 LPA in 3–5 years
Examples of Real Growth and Market Insights
India possesses mutual fund assets under management valued at more than $1.6 trillion, according to IBEF.
NASSCOM’s report also indicates a 28% increase in fintech and private bank employment in 2022.
Investment product careers are likely to grow with Tier II and Tier III cities joining the financial stage.
Learn Financial Markets A to Z in 2024 | Investment Banking Masterclass | CIBOP
Top FAQs: Answering What You’re Wondering
1. What is my background for a job in financial services sales?
Most employers prefer candidates with degrees in commerce, finance, or business. But engineering or arts graduates with adequate training can also succeed.
2. Do I need an MBA to start working in this industry?
No. Hands-on skills and certifications matter more. An MBA is welcome but not necessary.
3. What is the average salary in finance product sales?
₹3–6 LPA as a starting salary. Leaders earn ₹10–12 LPA in two years.
4. What are the proper certifications?
NISM-Series V-A (mutual funds), NISM-Series X-A/B (investment advisory) add credibility.
5. How is this different from regular sales?
It’s less about selling and more about solutions. You match products with client needs and long-term goals.
6. Can I switch over to portfolio management down the road?
Yes. Experience and skill result in vertical movement being extremely prevalent.
7. Which sectors hire for financial markets jobs?
Banks, AMCs, broking firms, fintechs, NBFCs, and wealth management firms.
8. Is the job stressful?
It’s goal-driven, but also provides excellent rewards and appreciation.
9. Can it be a long-term profession?
Most certainly. Some start as sales professionals and then rise to be heads of wealth, zonal managers, or investment strategists.
10. What are some entry-level job titles?
Sales Officer, Financial Product Executive, RM Trainee, Investment Advisor – Associate.
Conclusion: Charting Your Finance Career Path
A career in financial markets can be wonderfully rewarding, financially and mentally. If you crave stability, high rates of growth, or the opportunity to work hand-in-hand with real-world financial choices, this is a field full of possibility.
And with good training, you don’t need to know it all from Day One. What matters most is your inquisitiveness, your enthusiasm to learn, and your ability to connect financial solutions with real human needs.
Key Takeaways
- India’s financial sector is on fire—now’s the perfect time to get on board.
- Financial services sales certification gets your career moving faster.
- Product sales jobs in finance offer great earning potential and long-term future opportunities.
Discover more about the Imarticus Learning Banking and Finance Postgraduate Program and start building the career you’re worth.