Capital markets allow individuals, companies, and governments to trade financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. In investment banking, the importance of capital markets is enormous as they play an important role in facilitating the flow of funds between investors and entities in need of capital. Investment banks also assist in raising funds through initial public offerings (IPOs), bond issuances, and other securities transactions, contributing to economic growth and corporate expansion.
Let us move forward with an in-depth analysis of the crucial investment banking fundamentals. We aim to offer comprehensive insights while exploring a range of relevant investment banking courses suitable for prospective candidates seeking to pursue this field.
What is Capital Market?
In investment banking, capital markets are financial markets where long-term debt and equity-backed securities are traded. These markets act as essential pathways for funds to flow between banks, investors, businesses, governments, and individuals. The main purpose of capital markets is to facilitate the transfer of wealth from savers to entities that can use it for long-term investments or projects.
Let us learn more about the structure of the capital market:
Primary Market vs. Secondary Market
The primary market, (or the new issues market), is the platform where companies publicly offer new stocks or bonds for the first time, often through an initial public offering (IPO). To facilitate these transactions, companies enlist Investment banking firms to review the securities and create comprehensive prospectuses that outline important details, including price.
Strict regulations exist in the primary market to ensure transparency and investor protection. Companies need to file statements with regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and go through an approval process before becoming public. However, small investors may need more support to participate in the primary market. The primary focus is often on selling available securities quickly to meet volume requirements.
In contrast, the secondary market consists of regulated venues, such as the New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq, where previously issued securities are traded among investors. Issuing companies do not directly participate in secondary market transactions.
Within the secondary market, two categorisations exist auction and dealer markets. In auction markets, buyers and sellers congregate in a centralised location and publicly declare the prices at which they are willing to buy or sell securities. The New York Stock Exchange operates based on this method. On the other hand, dealer markets rely on electronic networks for trading. This is where most small investors typically participate.
To proceed with investment banking, financial modelling, it is crucial to analyse the important elements of capital marketing.
Types of Capital Markets
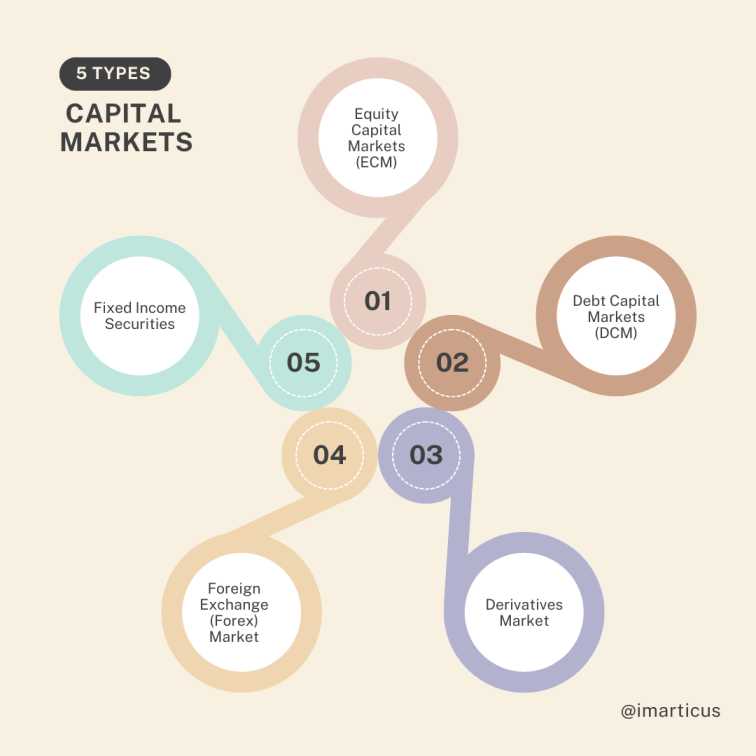
Let us learn about the different features of the capital market as well as the important types of capital markets that investors, organisations and governments deal with.
Equity Capital Markets (ECM)
Equity Capital Markets (ECM) cover a range of financial activities related to the insurance and secure trading of equity securities.
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs): Initial public offerings occur when a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time, becoming a publicly traded entity. Through an IPO, the company raises capital by selling shares to investors, who can then trade them on the secondary market.
Follow-on Offerings: These arise when an already publicly traded company issues additional shares to increase its capital. These offerings can take diverse forms, such as a seasoned equity offering (SEO) or a rights issue.
Rights Issues: The company provides current shareholders the chance to buy more shares at a lower price. This helps the company raise capital from its existing shareholders while allowing them to keep their ownership stake in the company.
Private Placements: These involve the sale of securities to a selected group of investors, usually institutional investors or accredited individuals, bypassing the general public. Private placements allow companies to raise capital without undergoing a public offering.
Equity-linked Securities: These hybrid financial instruments combine characteristics of both debt and equity. Equity-linked securities offer investors the potential for equity-like returns while possessing certain debt-like traits. For example – convertible bonds, exchangeable bonds, and warrants.
Investment banking services work closely with companies, offering advice on the optimal timing and structure of IPOs, managing follow-on offerings, structuring rights issues, arranging private placements, and overseeing the issuance of equity-linked securities.
Debt Capital Markets (DCM)
Debt Capital Markets (DCM) involve raising debt capital through various financial instruments and activities. Here’s an overview:
Bonds: Debt securities issued by entities to raise capital, representing a loan made by investors. Bonds have different features such as fixed or variable interest rates, varying maturity dates, and credit risk levels.
Commercial Paper: Short-term debt instruments used for meeting funding needs, typically issued at a discount by corporations, with a maturity of less than a year.
Syndicated Loans: Large loans provided by a group of lenders (syndicate) to finance projects or acquisitions. Risk and administration are shared among lenders, with loan terms structured by investment banks or financial institutions.
Convertible Bonds: Bonds that grant bondholders the option to convert them into the issuer’s common stock at a predetermined price. They offer the potential for equity participation while receiving fixed-interest payments.
High-Yield Debt (Junk Bonds): Bonds issued by companies with lower credit ratings carry higher default risks but also higher yields.
In Debt Capital Markets (DCM), investment banking firms assist companies in raising debt capital, providing advisory services, underwriting, structuring, and distributing debt securities to investors.
Derivatives Market
Derivatives offer opportunities for risk management, speculation, and portfolio diversification. Investors, corporations, and financial institutions use them to manage exposure, protect against losses, or exploit market opportunities. However, proper investment banking training can aid in a successful transition and mitigate possible market risks.
Options: Derivative contracts that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified period. Options offer flexibility for hedging, speculation, or generating income.
Futures: Agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a future date. Unlike options, futures contracts require both parties to fulfil the agreement. Futures are commonly used for hedging in commodities and financial markets to manage price risks.
Swaps: Contractual agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows or financial instruments based on predetermined terms. Interest rate swaps, the most common type, involve parties exchanging fixed and floating interest rate payments to manage exposure. Currency swaps and commodity swaps are other types.
Forward Contracts: Agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified price on a future date. These contracts are customised and traded over-the-counter (OTC). Forward contracts provide flexibility in terms of contract terms and settlement.
Hedging Strategies: Using financial instruments such as options, futures, or swaps is a way to protect against potential losses caused by unfavourable price movements in an underlying asset. Hedging helps individuals or businesses reduce risks associated with changes in interest rates, exchange rates, commodity prices, or other market factors.
Foreign Exchange (Forex) Market
The Forex Market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally. Participants include banks, commercial companies, central banks, investment management firms, hedge funds, and retail forex dealers.
Important elements include:
Spot Market: It’s where immediate currency transactions take place at the current market price (spot rate). This is the most common form of foreign exchange trading.
Forward Market: Involves trading currencies for future delivery at a predetermined exchange rate through forward contracts. It helps manage currency risk and hedge against fluctuations.
Currency Swaps: These agreements involve exchanging interest payments and principal amounts on loans denominated in different currencies. Currency swaps help manage interest rate risk and obtain favourable borrowing terms.
Currency Options: Derivative contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a specific currency at a predetermined price within a specified period. Currency options provide flexibility for hedging or speculation.
Exchange Rate Risk Management: Strategies and techniques used to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on financial transactions. This includes hedging instruments like forward contracts, currency swaps, and currency options.
Fixed Income Securities
Fixed Income Securities are investment instruments representing loans made to issuers (governments, corporations, or municipalities). They pay fixed interest over a specific period and return the principal at maturity. Mitigating risks requires proper investment banking skills.
Treasury Bonds: These are long-term fixed-income securities provided by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. They have durations of 10 to 30 years and are secure investments supported by the U.S. government.
Corporate Bonds: Debt securities issued by corporations to raise capital. Investors lend money in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of principal at maturity. Corporate bonds carry varying levels of risk based on the issuer’s creditworthiness.
Municipal Bonds: Issued by state and local governments or agencies to fund public infrastructure projects. They can be tax-exempt and come in general obligation and revenue bond types.
Mortgage-Backed Securities: Represent ownership in a pool of residential mortgage loans. Investors receive cash flows from mortgage payments, providing exposure to the housing market.
Asset-Backed Securities: Backed by pools of assets like auto loans, credit card receivables, or student loans. Investors gain access to diversified income streams.
Difference Between Money Market and Capital Market
Here are the differences between the money market and the capital market:
Duration: Money market deals with short-term borrowing and lending, while capital market focuses on long-term investments.
Instruments: Money market involves instruments like commercial paper, while capital market includes assets like stocks and bonds.
Purpose: Money market addresses short-term liquidity needs, while capital market supports long-term funding and growth.
Risk and Return: Money market generally offers lower returns with lower risk, whereas capital market returns can be higher but with potentially higher risk.
Participants: Money market participants are often banks and financial institutions, while capital market involves investors, companies, and governments.
Market Maturity: Money market instruments have shorter maturity periods, while capital market securities have longer durations.
Regulation: Money market is closely regulated to maintain stability, while capital market has comprehensive regulations to protect investors and ensure transparency.
Example: Money market could involve trading short-term certificates of deposit, while capital market may include buying shares of a company’s stock.
Capital Market Functions and Real-world Examples
Let us learn about the important features of capital markets with the help of capital market examples.
Diversification Opportunities: Capital markets enable investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in a range of assets, like Google’s parent company Alphabet issuing bonds to raise capital.
Efficient Allocation of Resources: Companies can secure funding for growth projects, such as Amazon issuing stocks to finance expanding its distribution network.
Risk Management: Investors can hedge risks using derivatives like options contracts, exemplified when a farmer uses futures to lock in a price for their upcoming crop.
Access to Capital: Start-ups can raise funds for innovation, as seen with Uber going public to gain capital for its global expansion.
Global Connectivity: International companies can access funds globally, as demonstrated by Japanese automakers issuing bonds in the United States.
Transparency and Regulation: Capital markets are regulated, ensuring fair and transparent transactions, exemplified by the Securities and Exchange Commission overseeing companies’ financial reporting.
Long-Term Investment: Investors can engage in long-term strategies, like pension funds investing in government bonds to secure future retiree payments.
Price Efficiency: Efficient markets quickly reflect information, as seen when a company’s stock price adjusts rapidly to news about its earnings report.
Liquidity for Investors: Investors can sell shares in exchange for cash, illustrated when a retiree sells stocks to cover living expenses.
Funding Public Projects: Governments raise funds for public projects by issuing bonds, allowing citizens to invest in their country’s development.
Investment Banking in Capital Markets
Investment banking services play a prominent and vital role in the functioning of capital markets. Within investment banks, specialised divisions known as capital markets groups focus on offering a wide range of services revolving around the issuance and trading of securities in these markets. Such Investment banking skills are crucial for companies looking to raise capital and investors seeking opportunities to buy or sell securities in an efficient and regulated environment.
Here’s an overview of the components:
Underwriting Securities Offerings: Underwriting involves an investment bank assisting a company in raising capital by issuing stocks or bonds. Among the most sought investment banking careers, the underwriter commits to purchasing the securities from the issuer at a certain price and reselling them. This mitigates the risk of not selling directly to investors. The underwriter determines the offering price, assesses market demand, and ensures legal and regulatory compliance.
Pricing and Allocation Strategies: Pricing strategies determine the offering price based on market conditions, investor demand, and the issuer’s financials. Allocation strategies distribute securities fairly and efficiently, considering investor demand, regulatory requirements, and issuer preferences. Comprehensive investment banking training can help you learn the nitty-gritty of market price speculation.
Book Building Process: Underwriters determine the IPO price through book building. Institutional investors submit bids for shares and prices. The underwriter evaluates these bids to determine the final offering price. Book building is an efficient way to price securities.
Syndicate Management: In more extensive offerings, a syndicate is formed to share risk and responsibility. The lead underwriter or book runner leads the syndicate in marketing and distributing securities. Syndicate management includes structuring the offering, coordinating investor roadshows, managing the order book, and allocating shares to investors.
Capital Market Instruments
In investment banking, Capital market instruments are diverse financial instruments traded in capital markets. Here’s an overview:
Stocks: Represent ownership in a company, with potential capital appreciation and dividends. Traded on stock exchanges.
Bonds: Debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, etc. Investors lend money in exchange for interest payments and principal returns. Influenced by interest rates, credit ratings, and market conditions.
Derivatives: Financial contracts deriving value from an underlying asset or benchmark. Examples include options, futures, forwards, and swaps. Used for hedging, speculating, or gaining exposure. Can be complex and involve risk.
Mutual Funds: Investment vehicles pooling money from multiple investors, investing in a diversified portfolio managed by professionals. Offers diversification, professional management, and liquidity.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Similar to mutual funds, providing intra-day liquidity. Can track various indexes, sectors, commodities, or investment strategies. Offers flexibility, diversification, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional funds.
Capital Market Regulation and Compliance
Capital market regulation and compliance are crucial for maintaining the integrity and stability of financial markets. Key entities include:
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC is responsible for regulating and enforcing federal securities laws in the US. It aims to safeguard investors, ensure fair markets, and promote capital formation.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA): FINRA, authorised by Congress, regulates broker-dealers in the US. It establishes conduct standards, administers licensing exams, performs exams and surveillance, and resolves investor-broker disputes.
Dodd-Frank Act: The Dodd-Frank Act was enacted following the 2008 financial crisis with the goal of improving financial stability, transparency, and accountability, while also safeguarding consumers. It introduced regulatory changes including derivatives regulation, the establishment of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), and the Volcker Rule.
Basel III: Basel III refers to a set of global banking regulations developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS). The objective of Base III is to strengthen banks, enhance risk management, and promote stability in the global banking system through the implementation of stricter capital, liquidity, and leverage standards.
Market Abuse Regulations: These regulations aim to prevent market manipulation, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities. Investment banking services play a vital role in maintaining market integrity and investor confidence.
Capital Market Trends and Developments
Capital market trends and developments significantly shape the financial landscape. Key trends and developments include:
Sustainable and Green Financing: This involves financial products and services supporting eco-friendly and socially responsible initiatives. The growing focus on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in investment decisions drives the demand for sustainable investment opportunities. Green bonds and sustainability-linked loans are popular green financing instruments.
Fintech Innovations: Financial technology innovations are changing the financial services industry. Developments in areas such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and digital payments are transforming different parts of capital markets, making them more efficient, accessible, and transparent.
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs): SPACs garner substantial attention as publicly traded companies established to acquire or merge with other companies within a specified timeframe. They provide an alternative path to going public, bypassing the traditional IPO process. The SPAC market experienced some slowdown in 2022, with lower volume and underperformance of completed mergers.
Alternative Trading Systems: These platforms offer an alternative to traditional stock exchanges for securities trading. ATSs facilitate electronic trading outside of exchanges, promoting liquidity, broader access, and lower transaction costs. Buyers and sellers can connect directly through ATSs
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Cryptocurrency: Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are used to raise funds for projects that are based on blockchain technology. They allow the issuance and sale of digital tokens or cryptocurrencies in order to raise capital. Although ICOs have become popular in recent times, they have faced regulatory scrutiny due to concerns related to investor protection and fraudulent activities.
Alternatively, digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are continuously transforming, garnering attention from institutional investors and the establishment of regulations for their trading and safekeeping.
Conclusion
The capital markets are currently facing challenges and uncertainties, including economic slowdown, regulatory changes, and volatility. However, it’s important to acknowledge that there are opportunities for growth and investment. To navigate the capital markets effectively, individuals should adapt to regulatory changes, focus on quality investments, and stay informed about market trends.
Wandering how to get started with an investment banking course?
Well, Imarticus Learning is here to help!
With a Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional training program, Imarticus presents you with a great opportunity to learn or level up your investment banking skills.
Wait, there’s more! How about investment banking internships with the top recruiters?
Yes! Imarticus Learning makes sure that, along with honing up your skills with the robust investment banking course, you’re awarded an investment banking certification to make things a bit easier for your investment banking career journey.
What are you waiting for? Get in touch!
FAQs
Is capital markets a good career?
Capital markets offer a great career for professionals as well as freshers who are looking for opportunities in the domain of investment banking.
What are the benefits of the capital markets?
Capital markets provide opportunities for organisations to raise funds for growth and expansion, while offering individuals a platform to invest and potentially earn returns on their investments.
Who controls the capital market in India?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates and controls the capital market in India.