Debt Capital Markets (DCM) is a dynamic market in which firms, governments, and organisations raise funds by selling debt securities to investors. It promotes large-scale economic growth, investment, and stability.
DCM refers to various financial products, including bonds, loans, and commercial paper serving a specific function. The process entails thorough preparation, review, and coordination among numerous parties, such as investment banks, underwriters, and legal consultants.
Individual and institutional investors alike carefully weigh risk and reward before engaging in DCM activity.
Explore deeper into the world of the Debt capital market in India and learn about its procedures, important stakeholders, regulatory frameworks, and vital role in defining the country’s financial environment.
If you are looking for a career in investment banking or take up an investment banking course, keep reading to learn what is debt capital markets and the varied frameworks of Debt Capital Markets.
What is Debt Capital Markets
The Debt Capital Market (DCM) is a crucial part of the financial market in which companies raise capital by selling debt securities to investors. Bonds, notes, and other fixed-income instruments are examples of debt securities. DCM promotes cash flow from investors seeking to lend money to issuers in need of capital to support their operations or projects, such as firms, governments, and financial institutions.
It issues the terms and conditions of the debt instrument in DCM, including maturity dates, repayment schedules and interest rates. These debt instruments are purchased by institutional investors and mutual funds in exchange for periodic interest payments.
DCM is crucial for the financial ecosystem as well as its importance in banking and finance courses as it allows firms to raise capital for governments to finance public initiatives. It enables investors to analyse and manage risks via debit instruments of various credit grades.
Key Terms for Understanding Debt Capital Markets
While establishing a career in banking and finance and looking for investment banking courses online, aspirants must have an understanding of what is debt capital markets and the key terms for debt capital markets. They are:
1) Bonds
Understanding the complexity of bonds is critical for participants in the debt capital market because it allows them to make informed investment decisions, manage their money effectively, and navigate the financial environment. Bonds are often classified depending on their issuer, credit rating, maturity date, and interest payment arrangements. Bonds can also be purchased and sold on the secondary market, where prices vary depending on market circumstances and investor mood.
2) Fixed Income Markets
Fixed-income markets are an essential component of debt capital markets. These marketplaces make trading various financial securities, such as bonds and treasury bills, possible. Investors buy these securities in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of principle when they mature. Fixed-income markets serve an essential role in funding governments, businesses, and other entities, allowing them to raise cash while providing investors with a stable income stream.
3) Interest Rates
Interest rates are crucial in debt capital markets as they are the agreed-upon interest rates at which borrowers agree to repay their loans over time. These rates are scrutinised by investors because they have a direct impact on the perceived value of debt instruments. Interest rate variations are significantly affected by central banks, economic circumstances, and reliability, making them a crucial driver in the dynamics of debt capital markets.
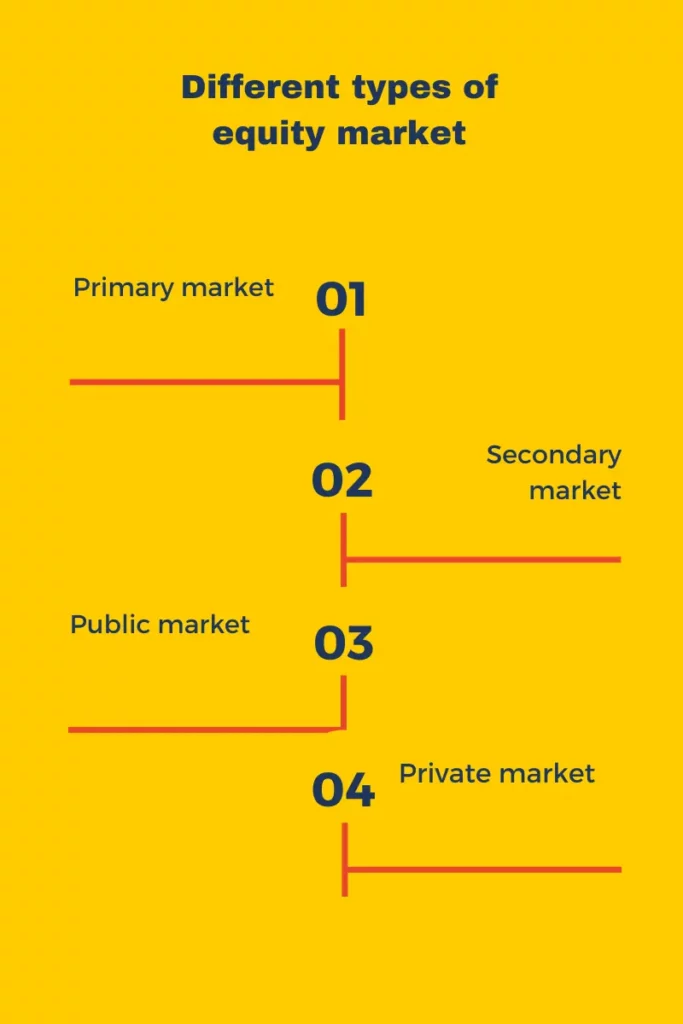
4) Primary Market
For organisations looking to raise money through debt instruments, the primary market is an essential environment in the overall structure of the debt capital markets. It serves as the initial point of issuance when debtors sell bonds or other debt securities to investors. This stage includes the underwriting and distribution methods that allow organisations to get the necessary money. The ability to navigate the primary market effectively is critical for successful borrowing endeavours
5) Secondary Market
The secondary market acts as a crucial platform for investors to buy and sell pre-existing debt instruments. Investors trade bonds and other debt instruments, resulting in liquidity and price discovery. The characteristics of this market have a substantial impact on the pricing and yield of debt instruments, making it an important component for both issuers and investors in the debt capital markets.
Debt Capital Markets Vs. Equity Capital Markets
While trying to understand what is debt capital markets, one must be clear about knowing the distinctions between debt capital markets and equity capital markets. These two important types of capital markets are two of the primal systems to study in a banking and finance course.
This is one of the primary principles to study in an investment banking course.
| Aspects | Debt Capital Markets | Equity Capital Markets |
| Purpose | To raise capital via debt securities. | To raise capital via equity shares. |
| Ownership | No requirement for ownership. | Ownership transfer required to shareholders. |
| Risks to Issuer | Fixed interest payment rates, hence low risks. | No fixed payments, higher risks. |
| Voting Rights | No voting rights. | Voting rights only for shareholders. |
| Liquidity | Higher priority. | Lower priority in case of bankruptcy. |
| Repayment | Periodic interest payments. | No mandatory repayment scheme. |
| Risk to Investors | Lower risks and predictable returns. | Higher risks for potential dividends. |
| Returns | Fixed payment rates on interest. | Dividends and capital gains. |
| Regulatory Environment | They are regulated by government agencies. | It is regulated by both government and stock exchange agencies. |
| Exist Strategy | Flexible for exit. | Flexible exit only through stock trading. |
Debt Capital Market in India
Let’s discuss about the role of the debt capital market in India’s economy. DCM plays a crucial role in the financial environment of India. Financial institutions like SEBI and RBI raise capital through debt securities, contributing to a substantial expansion of DCM over the years.
DCM provides a variety of investment options, including corporate, municipal and government bonds, resulting in transparency and accessibility among investors. This has further improved as a consequence of regulatory reforms and the development of electronic trading platforms. Furthermore, credit rating companies offer beneficial assessments of debt issuers, allowing for informed investment decisions.
Mutual funds, insurance firms, and individual investors seeking consistent returns and portfolio diversification are among those who invest in the debt capital market in India. The growth of the DCM illustrates India’s commitment to nurturing a vibrant financial ecosystem while serving the financial demands of its expanding economy.
Conclusion
Debt money Markets (DCM) are a significant financial platform for funding money via debt securities. DCM plays an important role in global finance, offering stability and opportunity for both issuers and investors, thanks to its extensive variety of products and expanding investor interest.
Check out Imarticus Learning’s Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional course or CIBOP course to learn what is debt capital markets and build your career in investment banking with 100% job assurance. You can have 0-3 years of work experience to take up this investment banking course. This banking and finance course will upscale you and place you in big companies.