A guide to understanding Tableau concepts
When you analyze data in Tableau, you have a choice. You can either choose to display the data continuously or discretely.
Continuous – A continuous chart is easy to read. The bars or lines in the chart never indicate a break in the data. If you’re comparing two or more sets of data, the continuous manner of displaying the data is the best choice. If you want to see how one number affects another, this is the best way to do it.
Discrete – A discrete chart is one in which the data is broken into discrete bars or lines. This is the best choice when you want to compare two or more sets of data. It’s also a good choice when you want the viewer to know that there is a difference. This may be something like comparing the sales numbers of two stores.
What are row level, aggregate level, and table level in Tableau?
This is probably the most confusing aspect of Tableau for beginners.
By row level, we mean that the data is organized in rows.
By aggregate level, we mean that the data is organized at the level of aggregates.
For example, we have company names and numbers at the row level. At the aggregate level, we would group the numbers under one name.
Tables can add visual interest and can provide another layer of data that can be used to understand your data further.
At the table level, we would join all the data from the previous examples under one name, “Technology.” This name could be a column in the table or a filter on the view.
A quick overview of Tableau features
Decision Trees – A powerful tool you can use to see the relationship between different data sets. For example, let’s say you want to see what your customers like the most about your products. A decision tree will help you visualize this data. You can either use Tableau’s built-in decision tree tool or create your own.
Visual Crosstabs – This is a great way to create a table that shows the breakdown by category or by a specific value in a column. With this table, you can compare two columns or two columns and a value.
Heatmaps – This is a great way to visualize your data like the crosstabs. All you need to do is select a measure and create a bar chart. Then, you can add a visual pattern to the bars.
Time-Series Charting – This is great for visualizing a history of data. You can use an actual time series or create a visual that spans multiple data points.
Interactive Charts – This is the blending of interactive and visual data. You can use this feature to create dashboards that support complex queries and deliver dynamic visuals.
Advanced Reporting – Tableau’s reporting features are some of the best out there. You can create custom reports or use their built-in report templates.
Linking to Data Sources – Like many data visualization tools, Tableau allows you to connect to external data sources. You can access your SQL database, Excel spreadsheets, Amazon machine learning model, or Google Spreadsheets.
What are the Dimensions and measures in Tableau?
When you create a visual in Tableau, you are creating a visual using dimensions and measures. A dimension is a way to categorize your data. Let’s say you have a marketing team that tracks different metrics related to their work. You could create a dimension to store this information. Let’s say you create a dimension called “Metrics” that contains the following information:
Tableau features
You can integrate Tableau with many data sources, including SQL databases, Excel spreadsheets, Google Spreadsheets, Amazon Web Services, and more.
– Tableau has a free software product and a low-cost subscription product.
– Tableau’s subscription-based product has more functionality.
– Tableau can be used for data discovery, analysis, reporting, and visualization. – Data sources can be internal or external.
– Tableau can be used for self-service BI or for managing a BI project.
– Tableau can be used for data hygiene, wrangling, quality, modeling, and more.
– Tableau is available on all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
– Tableau is highly customizable and offers different charting and visualization styles.
With this knowledge, we know you can get an idea of data visualizations when using business intelligence software like Tableau. So what are you waiting for? Apply for an Imarticus Learning course today by visiting our training centers in Mumbai, Thane, Pune, Chennai, Bengaluru, Delhi, Gurgaon, or Ahmedabad or contact us through chat support.



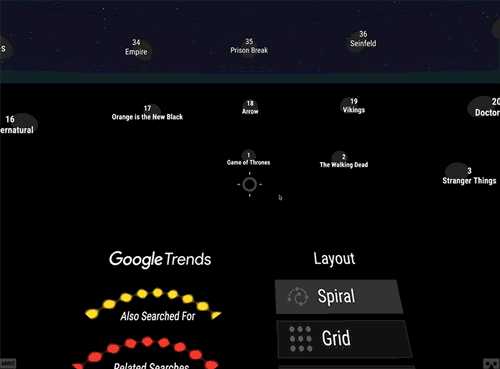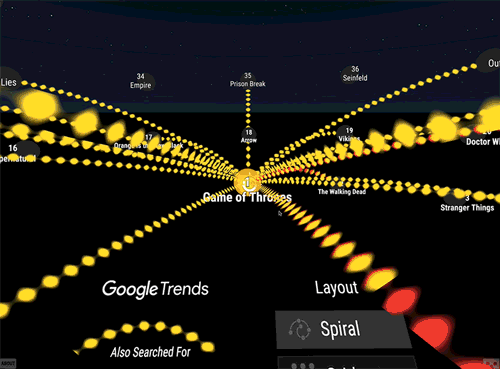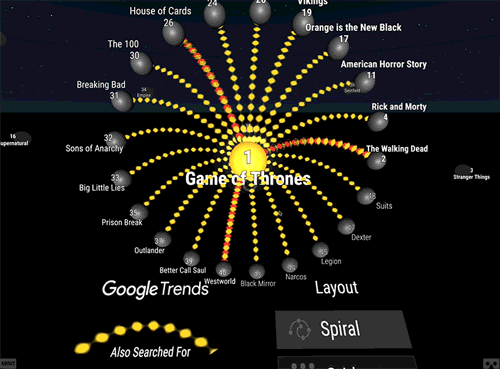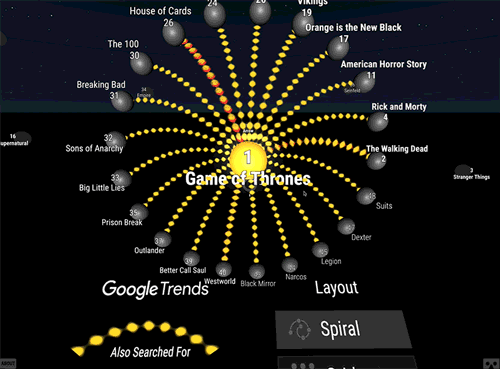
 Tableau opens a way for qualifying and quantifying the data while also identifying any particular pattern with the missing data. It is one of the robust tools that is required while implementing the machine learning models or solutions so that the business side can also understand and visualize the analysis or predictions.
Tableau opens a way for qualifying and quantifying the data while also identifying any particular pattern with the missing data. It is one of the robust tools that is required while implementing the machine learning models or solutions so that the business side can also understand and visualize the analysis or predictions.