Introduction
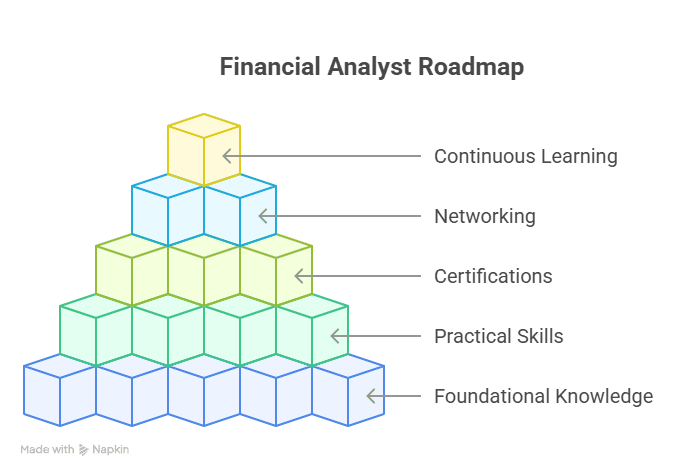
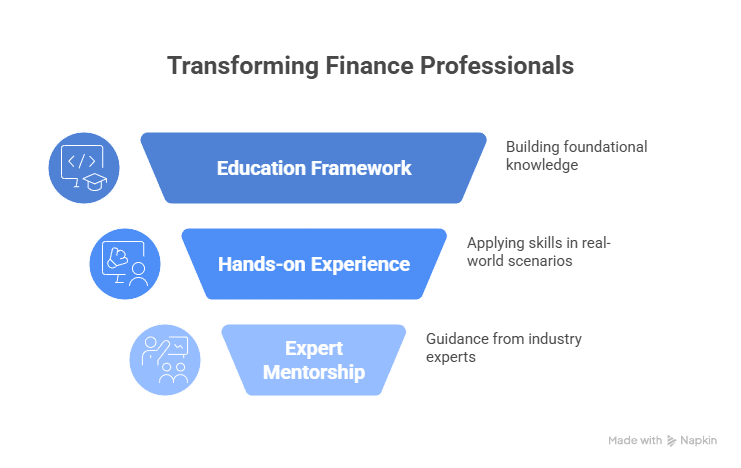
Let’s face it-spreadsheets have their limits. As you move through your finance career in India, you may have felt as if the demands of the job were asking for you to go beyond basics and speak the language of actual deals. Transitioning to that level is not just a matter of learning more Excel functionalities or finding the hottest templates to download. What you need is a shift in thinking, based on a framework of education, hands-on experience, and expert mentorship. This is the power of a financial modelling and valuation course.
This blog breaks down how the right course doesn’t just upskill you but rewires your thinking for high-stakes environments like investment banking, private equity, or corporate finance. It delves into how such programs, built around real-world finance projects and advanced valuation strategies, empower Indian professionals and students to evolve from spreadsheet users into deal-making pros.
Why Finance Career Transformation Requires More Than Excel
Ask a hiring manager in finance, and they’ll say the same as the last 20 they spoke with – basic proficiency in spreadsheets is given, but not enough. If you’re building a discounted cash flow model or evaluating a leveraged buyout, decision-makers want talent who can model uncertainty, think about risks, and link numbers back to a strategy. This is where a financial modelling and valuation course closes the gap.
A career transformation in finance does not take place in a bubble. It requires the right mix of applied case studies, simulations, and the right curriculum designed for industry ramp-up and performance. Programs designed for Indian students and professionals often come integrated with tools like Excel, PowerPoint, and even Python—all essential to modern finance roles.
Here’s what you need beyond Excel:
- Deep understanding of valuation frameworks
- Clear communication of insights through dashboards and presentations
- Scenario building and stress-testing assumptions
- Modelling for real transactions like IPOs, mergers, and capital raises
- Interpreting industry trends through structured financial storytelling
Advanced Valuation Strategies: Beyond the Basics
Valuation is more art than science. Sure, you can compute a fair value using DCF or comparable company analysis. But are you skilled enough to challenge assumptions, adjust for market anomalies, or understand intangible asset valuation? That’s what advanced valuation strategies are all about.
Courses that focus on financial modelling and valuation don’t just spoon-feed you formulas. They teach you how to build flexible, dynamic models from scratch. And more importantly, they help you interpret the story those numbers tell.
Comparison Table: Basic vs. Advanced Valuation Techniques
| Parameter | Basic Approach | Advanced Valuation Strategies |
| Method Used | DCF, Relative Valuation | Sum-of-the-parts, Contingent Claims |
| Adjustments Considered | Limited to common ratios | Minority discounts, Control premiums |
| Industry Application | General | Sector-specific (Tech, Real Estate, etc) |
| Risk Analysis | Single variable sensitivity | Monte Carlo simulation, scenario testing |
For a deeper dive into advanced valuation thinking, check out this Harvard Business Review article on measuring company value beyond financials.
The Role of M&A Financial Modelling Training
Mergers and acquisitions aren’t just flashy headlines in the Economic Times; they are complex, multilayered transactions that require razor-sharp modelling skills. This is where M&A financial modelling training takes centre stage in any serious financial modelling and valuation course.
Learning how to construct models for M&A includes everything from target screening and synergy analysis to post-deal integration and scenario building. It’s the kind of learning that not only helps you in interviews but prepares you for deal rooms and boardroom discussions.
What You Learn in M&A Modules:
- Modelling accretion/dilution
- Financing mix: debt vs. equity
- Sensitivity to synergies and cost savings
- Pre- and post-deal valuation
- Due diligence modelling techniques
- Risk-adjusted return analysis
According to PwC’s Global M&A Industry Trends, global M&A volume is projected to remain strong into 2025. That means demand for M&A-ready professionals is only increasing.
Real-World Finance Projects: Learning That Sticks
Reading textbooks is fine. But nothing prepares you for the real world like actual project work. A robust financial modelling and valuation course always includes real-world finance projects that replicate industry scenarios.
These capstone projects are designed to mimic IPO valuations, LBO models, sector-specific valuation models, or even private equity case studies. You don’t just learn; you do.
Real-World Finance Project Examples:
- IPO Valuation for a FinTech startup
- LBO Model for a Private Equity transaction
- DCF valuation of a large-cap listed company
- Sector analysis of banking or pharmaceuticals
- Simulation of a buy-side investment pitch
This experience becomes especially valuable for Indian students aiming for high-performance finance roles in investment banking, equity research, or corporate strategy.
Investment Analyst Upskilling: Tools and Techniques That Matter
As a budding or mid-career analyst, the transition from reporting historical data to forecasting future growth is essential. That’s where investment analyst upskilling through a financial modelling and valuation course really shines.
From learning Excel hacks for model speed to mastering databases like Bloomberg or Capital IQ, this upskilling prepares analysts to function as strategic advisors rather than mere data handlers.
Must-Have Tools for Investment Analysts:
- Microsoft Excel (advanced functions, macros)
- PowerPoint (investment decks)
- Capital IQ, Bloomberg, Refinitiv
- Python/R for quantitative models
- Tableau for financial dashboards
- Scenario and risk modelling templates
Upskilling like this not only helps in job interviews but makes you better at articulating insights, pricing deals, and evaluating investment opportunities.
The Course That Delivers: Financial Analysis Prodegree
If you’re ready to take the leap, Imarticus Learning’s Financial Analysis Prodegree is a top choice. Co-created with industry experts, this course offers intensive training in financial modelling and valuation, complete with real-world finance projects, live mentorship, and placement assistance.
It’s designed for Indian learners seeking genuine finance career transformation. Whether you’re just out of college or have a few years in the field, the program adapts to your pace, giving you access to tools, techniques, and case-based learning.
FAQs
Q1: Who should take a financial modelling and valuation course?
This course is well suited to finance graduates, MBAs, working professionals in banking or investment roles, and career changers trying to get into finance. It is also suitable for entrepreneurs looking to better understand valuation metrics.
Q2: How long does it take to finish such a course?
Whereas some part time or online options allow for more flexible pacing especially for working professionals, most programs can be completed in 3 to 6 months depending on the intensity and structure of the course.
Q3: Do I need to have prior finance knowledge to enrol?
Having some base level of knowledge is useful but many courses start with fundamental building blocks and develop to such complex modelling that they are accessible to beginners.
Q4: Are the tools I will learn in the course relevant to the job market?
Absolutely! Most programs focus on Excel, PowerPoint and sometimes even Bloomberg or Python. You won’t be able to avoid these programs in corporate finance, investment banking and equity research.
Q5: Will I complete hands-on project work with the course materials?
Yes, particularly with the better courses. You will work on IPOs, M&A cases, LBO models and then you can present the finished products in your job interviews.
Q6: How does this course help in job placement?
Many programs have industry tie-ups, career services, and placement support. Real-world projects and strong portfolios often give candidates an edge in interviews.
Q7: Can I learn this course online?
Definitely. In fact, online learning offers flexibility. Look for programs with live classes, mentor support, and real-time feedback for the best outcomes.
Q8: What salary boost can I expect post-certification?
While it varies, many professionals report salary jumps of 20-40% post-certification, especially when transitioning into high-value roles.
Q9: Is certification important in finance hiring?
Yes. A recognised certification acts as a signal to recruiters about your skills and commitment. It also helps you stand out in competitive applicant pools.
Q10: What makes the Imarticus Prodegree different?
The mix of practical training, expert faculty, and career services sets it apart. It’s structured around outcomes, not just content.
Key Takeaways
- A financial modelling and valuation course is more than a skill upgrade—it’s a mindset transformation.
- Learning advanced valuation strategies helps you value companies beyond simple ratios.
- M&A financial modelling training is crucial for understanding complex transactions.
- Real-world finance projects make learning stick and build your portfolio.
- Investment analyst upskilling includes hands-on tools that align with modern job requirements.
- Courses like the Financial Analysis Prodegree offer industry-driven content and career support.
Conclusion
In today’s hy-per-competitive world of finance, to become a deal-making superstar requires way beyond Excel skills. You need a structured learning plan, quality coaching and real life experiential learning. A quality financial modelling and valuation program doesn’t just prepare you for jobs, it prepares you for deals.
So if you are serious about advancing your career in finance, the time to act is now. Sign up for a program like the Financial Analysis Prodegree and step into the world of true finance, real skills and real results.