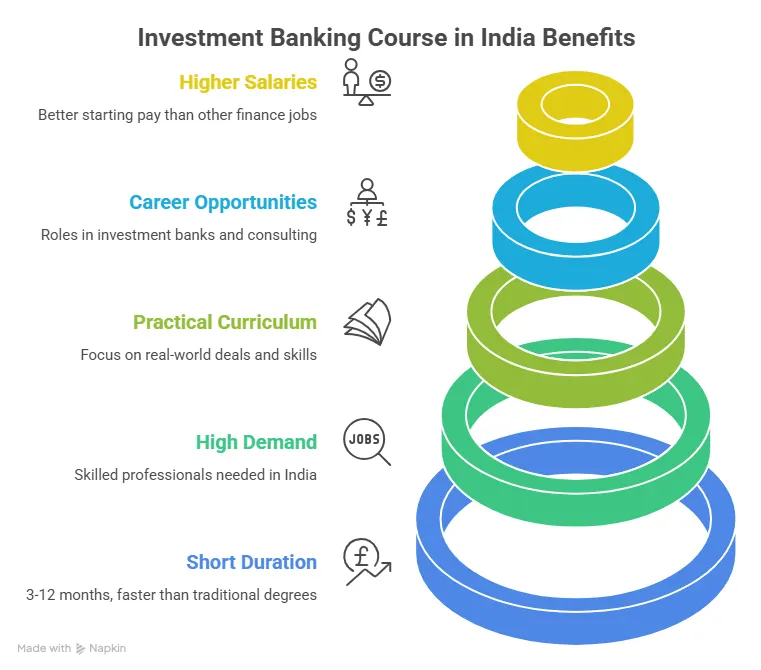
If you’ve ever been curious about how big deals happen, how companies get listed on the stock market, or how mergers and acquisitions shape entire industries, then the thought of pursuing an investment banking course in India has probably crossed your mind. It’s the part of finance where decisions move fast, numbers carry weight, and the impact is real.
In India, investment banking courses are no longer limited to a small group of finance insiders. They’ve become one of the smartest ways for students and working professionals to step into high-growth finance roles without committing to long, traditional degrees. These courses are designed for the real world, not just classrooms.
An investment banking course in India isn’t about memorising definitions or studying theory for exams. It’s about understanding how actual transactions work, how businesses are valued, how funds are raised, and how financial strategies drive success. This is where finance becomes practical, dynamic, and career-defining.
In this blog, I’ll break down everything you need to know about the Investment Banking Certification – from eligibility, fees, career scope and job opportunities, so you can decide if it’s the right next step for your investment banking career.
Why the Investment Banking Course in India Is Booming
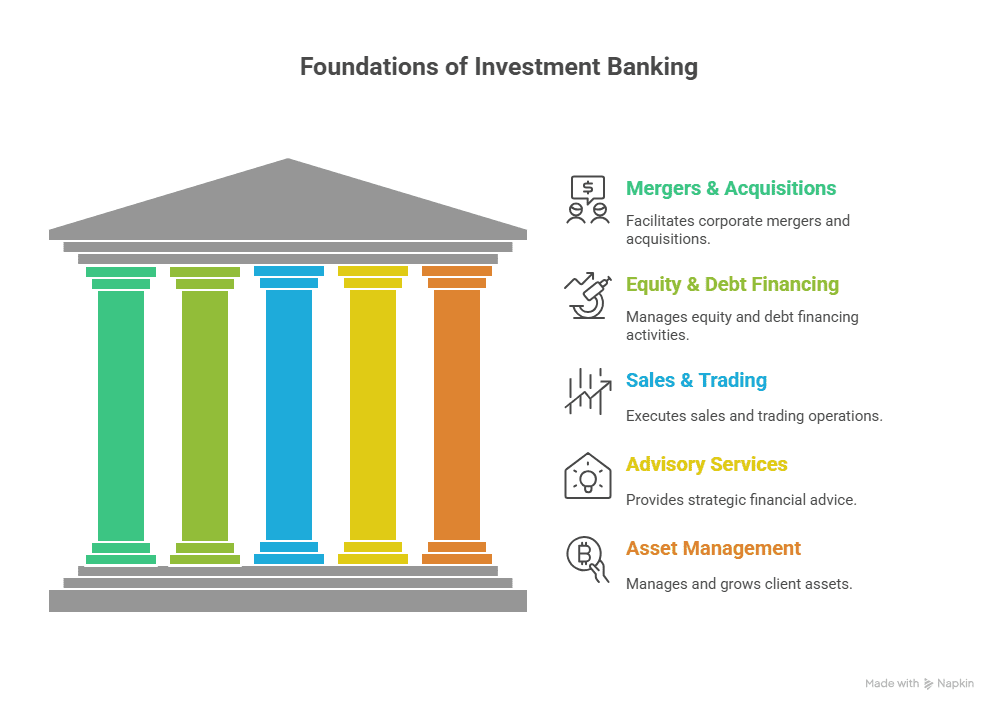
Before exploring the best investment banking courses in India, I’ll answer the question that I get asked the most: What is investment banking, and what exactly does it do? At its core, investment banking is simply the business of helping companies raise money, grow through mergers or acquisitions, and make smart financial decisions that shape their future.
India’s financial ecosystem is growing rapidly. Startups are raising funds, companies are going public, and global banks are expanding their back offices and deal teams here. This growth has created a demand for professionals who understand:
- Financial modeling
- Valuation
- M&A processes
- Capital markets
- Corporate finance
Traditional degrees often don’t teach these skills in a job-ready way. An investment banking course in India fills that gap by focusing on practical, industry-relevant training.
Also Read: How to become an Investment Banker?
What Is an Investment Banking Course in India?
An investment banking course in India is a practical, short-term program that gets you ready for real finance roles, not just investment banking exams. It’s built to make you job-ready by teaching the exact skills used in the industry.
More than anything, it trains you to think like a decision-maker. You start learning how to answer the kind of questions companies actually care about – where to invest, how much a business is worth, when to raise funds, or whether a merger makes sense. These are the questions that shape big financial moves and influence the future of businesses.
It teaches you:
How to analyse companies?
How to build financial models?
How are deals structured?
How are financial presentations created?
How do investment banks actually work?
Think of it as a bridge between academic finance and real investment banking jobs.
Whether you’re looking for the best investment banking courses in Bangalore, the best investment banking courses in Chennai, professional investment banking coaching in Hyderabad, or quality investment banking courses in Jaipur and investment banking courses in Kolkata, you’ll find a variety of investment banking course in India across cities that are designed to deliver practical training, industry exposure, and strong career outcomes.
To give you a clear picture of life in investment banking beyond just numbers and models, here’s a video that explains exactly what investment bankers do on a day-to-day basis, breaks down the roles, responsibilities, and real work involved in investment banking in a simple, practical way.
Investment Banking Course Syllabus in India
When you look at a good investment banking course in India, you’ll notice one thing immediately – it’s built to feel like real work, not classroom study. It mirrors what actually happens inside banks, advisory firms, and corporate finance teams. Instead of reading theory, you’re learning the tools bankers use every day and learning the skills required in investment banking.
You usually begin with Financial Accounting and Analysis. This is where you stop seeing financial statements as boring tables and start seeing them as stories about a business. You learn how to read balance sheets, income statements, and cash flows the way a banker does – to understand where a company is strong, where it’s weak, and where the risks and opportunities lie.
Then comes Corporate Finance, where the bigger picture comes in. You learn how companies decide when to raise money, how much debt is too much, and how they plan their growth. This is where numbers meet real business strategy.
Excel and Advanced Financial Modelling is where everything becomes hands-on. You start with building financial models from scratch, learn connecting financial statements, forecasting their performance, and figuring out the what-if scenarios. It feels less like studying for an exam and more like doing the actual job.
Valuation is another core part of the journey. With methods like DCF, Comparables, and Precedent Transactions, you learn how to answer the most common question in finance: What is this company really worth? and you quickly realise how small changes in assumptions can completely change that answer.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) shows you how the deals really happen. You understand why companies merge, buy, or sell businesses, and how a deal moves from an idea to a signed agreement. It gives you insight into one of the most exciting parts of investment banking.
The IPO and Capital Markets module takes you into the world of stock markets. You learn how companies go public, how share prices are decided, and how investor demand shapes the outcome. It’s like getting a behind-the-scenes view of the biggest market events.
Pitch Books and Deal Documentation are where communication comes in. You learn how to present ideas clearly, structure data visually, and tell a financial story that clients can understand and trust. This is a huge part of a banker’s daily life.
In the advanced Investment Banking Course in India, you also get exposure to LBO Modelling, which is especially valuable if you’re interested in private equity. It teaches you how large acquisitions are funded using debt and how investors calculate their returns.
And it’s not just about technical skills. Strong Investment Banking Degree Courses in India also focus on soft skills and interview preparation. You learn how to communicate professionally, think clearly under pressure, and present yourself with confidence in interviews and at work.
The best part? None of this feels like memorising for an exam. It feels like training for a real role. You’re not just learning finance, you’re learning how to think, work, and solve problems like investment bankers.
Did you know?
An investment banking course in India isn’t just another certification – it’s a practical training programme built to bridge the gap between academic finance and real industry work. You don’t just learn concepts; you learn how to apply them in real-world scenarios, just like analysts and associates do every day.
Best Investment Banking Course in India by City
When it comes to building an investment banking career, where you learn can be just as important as what you learn. Different cities in India offer unique advantages – from strong industry networks and corporate hubs to emerging finance ecosystems and specialised job opportunities.
Investment Banking Courses in Mumbai
Mumbai is India’s financial capital. Courses here benefit from proximity to Investment banks, Private Equity, Venture Capital firms, Stock exchanges, and Corporate finance teams. Investment Banking Courses in Mumbai are ideal for those seeking direct exposure to deal environments. You will get the best institute for investment banking course in India in the financial capital.
Investment Banking Courses in Bangalore
Bangalore blends finance with fintech and startup funding. Bangalore is perfect if you’re interested in valuations for startups, venture capital, and tech-focused finance roles in top investment banking companies in Bangalore. Opting for an Investment banking institute in Bangalore is a great choice for those who want to work in venture capital, fintech, or advisory roles focused on new-age businesses.
Investment Banking Courses in Chennai
Chennai has a solid base of corporate offices, manufacturing companies, and analytics-driven finance teams. An investment banker course in Chennai is ideal for building strong fundamentals in corporate finance, financial analysis, and modelling. It suits students who want a stable, structured entry into investment banking and related finance roles.
Investment Banking Courses in Pune
Pune offers quality education with a relatively lower cost of living and a growing corporate and IT presence. The investment banking course in pune here attract students who want strong training without the intensity and expense of metro cities like Mumbai. Investment banking classes in Pune are a smart option for focused learning and long-term career preparation.
Investment Banking Courses in Hyderabad
Hyderabad is quickly becoming a major hub for global banks and financial services firms. With many banks expanding their operations and analytics teams here, courses for investment banking in Hyderabad are well-suited for aspiring IB analysts, financial modellers, and middle-office roles that demand strong technical skills.
Investment Banking Courses in Delhi
Delhi NCR provides a unique mix of investment banking, consulting, corporate finance, and advisory exposure. With proximity to large corporations, consulting firms, and policy-driven financial institutions, courses here are ideal for those who want a broader business and finance perspective alongside investment banking.
Investment Banking Courses in Kolkata
Kolkata is emerging as a growing centre for finance education and investment banking back-office operations. Investment banking course in Kolkata is well-suited for students interested in operations, research, and analytical roles that support global banking teams, while still gaining strong technical foundations.
Investment Banking Courses in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad is gaining attention for its strong academic environment and expanding corporate finance opportunities. With the rise of GIFT City as an international financial hub, the region is attracting global banks, financial services firms, and fintech companies. With a growing number of companies and financial institutions, investment banking courses in Ahmedabad are ideal for students who want a solid finance education with increasing access to real-world corporate exposure.
Beyond the major metros, students are also exploring investment banking courses in Coimbatore, investment banking courses in Kerala, and investment banking courses in Thane, as these locations offer quality training, lower living costs, and growing access to finance and corporate opportunities without the pressure of bigger financial hubs.
Before you dive into courses or interviews, this video helps you understand the core skills and mindset investment banks look for. It breaks them down in a simple, clear way and gives you a realistic idea of what employers expect and how you can start building the right capabilities.
Investment Banking Course Fees in India
Usually, an investment banking course in India costs somewhere between ₹1.5 lakhs and 5 lakhs. That range exists merely because every course offers a different level of depth and support. Think of it like choosing a gym membership. Some give you basic access, others give you a personal trainer, structured plans, flexibility to freeze the membership, switch between branches, and real guidance. The price changes with the value.
So when you see a higher fee, it usually means you’re paying for more than classes. You’re paying for structure, exposure, mentorship, and a clearer path into the job market. And in a field like investment banking, that support can be just as important as the technical skills you learn.
| Program Format / Mode | Duration | Fees |
| Full-time / Standard Certification | ~3 months | ~₹1,60,000 |
| Online mode (shorter/different schedule) | ~2 months | ~₹1,50,000 |
Investment Banking Course Duration in India
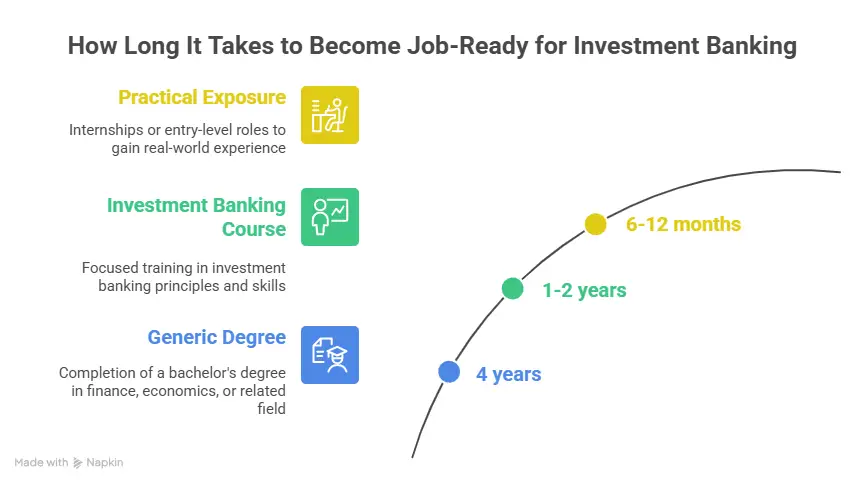
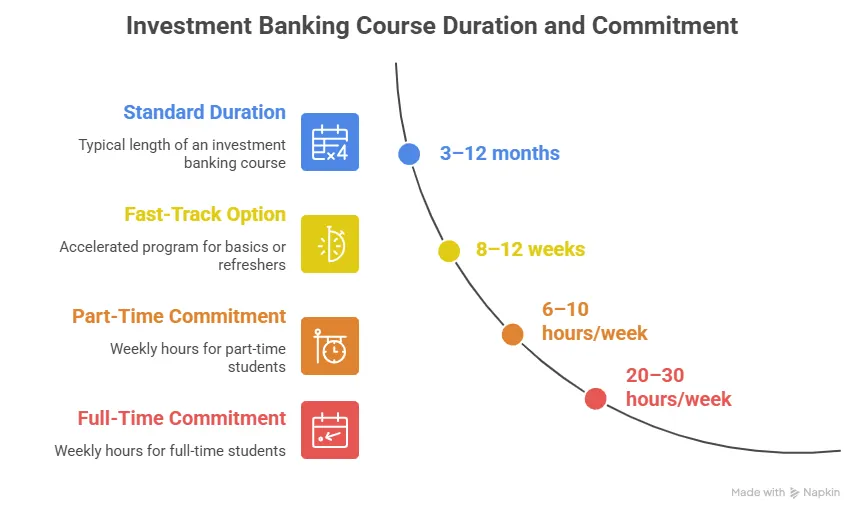
The investment banking course in India is designed to be short and focused, usually lasting anywhere between 3 and 12 months. They’re built to fit around your life, whether you’re a student or a working professional, so you can upskill without putting your career on hold for years.
Investment banking courses are meant for anyone who enjoys working with numbers and wants to build a serious career in finance. The investment banking eligibility is broad enough to make it accessible for most aspiring finance professionals. Students join to prepare early, and professionals enrol to shift into more analytical, high-impact roles. You don’t need a deep finance background to begin, just a basic understanding and the right mindset.
Interesting Fact:
When pursuing an investment banking course in India, you’re not just paying for a course. You’re investing in faster career movement, stronger skills, and a clearer entry into the finance industry.
Investment Banking Jobs in India
Once you complete an investment banking course in India, a whole range of exciting finance roles open up for you. You’re no longer just learning about finance; you’re ready to work in it.
Investment banking jobs in India are no longer something you only hear about in movies or global finance stories. They’re very real, and they’re growing fast. With startups raising funds, companies going public, and international banks expanding their teams here, the need for skilled finance professionals has never been higher.
What’s exciting is that these job roles aren’t limited to just a handful of top firms anymore. Today, you’ll find investment banking opportunities in deal teams, valuation firms, consulting companies, private equity, venture capital, and even corporate finance departments. If you have strong skills and the right training, India offers a genuine chance to build a powerful and rewarding career in investment banking.
An investment banking course in India doesn’t just give you a certificate. It gives you access to real, high-impact roles where your work directly influences business investment decisions and financial outcomes.
| Job Role | What You Do | Where You Work |
| Investment Banking Analyst | Support live deals, build financial models, and work on mergers, acquisitions, and fundraising activities | Investment Banks |
| Financial Analyst | Analyse company performance, forecast growth, and support business decision-making | Investment Banks, Consulting Firms, Corporate Finance Departments |
| Valuation Analyst | Value companies, startups, and investment opportunities using financial models | Investment Banks, Private Equity Firms, Venture Capital Firms |
| Equity Research Analyst | Research companies and industries, analyse stocks, and prepare investment reports | Investment Banks, Research Firms, Asset Management Companies |
| M&A Analyst | Assist in mergers and acquisitions, deal structuring, and strategic transactions | Investment Banks, Consulting Firms, Corporate Strategy Teams |
| Corporate Finance Executive | Manage capital, budgets, financial planning, and company growth strategies | Corporate Finance Departments, Large Corporations |
If you want a feel for what investment banking actually looks like on the job, this video gives you a look at day-to-day work, team dynamics, and what makes the role both challenging and exciting:
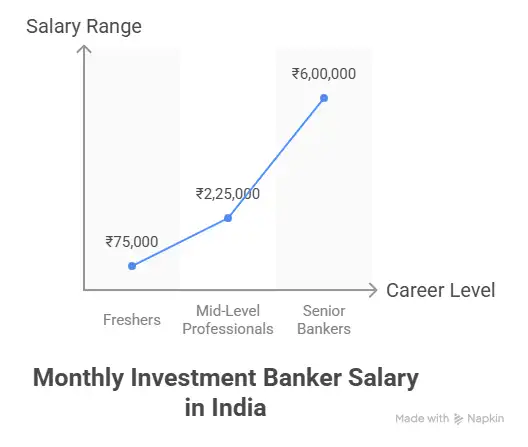
Investment Banking Salary City-wise
When it comes to investment banking salary in India, location matters – just like it does in most finance roles. Bigger financial hubs tend to offer higher pay, but the cost of living and opportunities also play a role. Here’s a breakdown of what you can typically expect across major Indian cities:
| City | Investment Banking Salary Range |
| Mumbai | ₹ 20 – 24 LPA |
| Delhi NCR | ₹ 18 – 22 LPA |
| Bangalore | ₹ 15 – 22 LPA |
| Hyderabad | ₹ 12 – 20 LPA |
| Chennai | ₹ 10 – 18 LPA |
| Pune | ₹ 8 – 16 LPA |
| Kolkata | ₹ 7 – 15 LPA |
| Ahmedabad | ₹ 7 – 14 LPA |
| Indore | ₹ 6 – 12 LPA |
| Bhopal | ₹ 5 – 10 LPA |
| Bhubaneshwar | ₹ 5 – 10 LPA |
| Lucknow | ₹ 6 – 12 LPA |
Note: Salary depends on your role, skills, institute reputation, and experience. Metro cities usually offer higher pay, while emerging cities provide strong learning opportunities with lower living costs.
Did you know?
Choosing an investment banking institute in Hyderabad gives you access to strong technical finance roles, as the city is becoming a major centre for global banking operations and financial analytics in India.
Top Investment Banking Companies Hiring in India
When you start looking seriously at investment banking, these are the names you keep hearing again and again. They’re the firms behind the biggest mergers, IPOs, fundraising rounds, and strategic deals. Working with any of them means you’re not just learning finance, you’re living it, right at the centre of where decisions are made and money moves. It’s also why professionals working with these firms usually feature at the top end of the investment banking salary range.
Here’s a list of some of the top Investment banking companies that hire in India:
- Global Investment Banks – Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, Morgan Stanley, Citi, and Barclays.
- Global/ Regional Investment Banks – Nomura, Credit Suisse, and Kotak Investment Banking.
- Big 4 Accounting Firms – EY, KPMG, PwC, and Deloitte.
- Indian Boutique Investment Banks – Avendus Capital, JM Financial, and others.
Getting into any of these companies is more than just a job. It’s a career milestone that gives you credibility, exposure, and a strong foundation for long-term growth in the world of finance.
If you are pursuing an investment banking course in India, this video will help you prepare even better for your investment banking interview.
Investment Banking Course Vs MBA
Picture booking a dream trip. General agent handles flights + hotels, which is reliable but slow and costs more. Now, picture a specialist for business class only? This one saves atleast 30%, cheaper, faster, knows every airline rule and upgrade hack.
That’s MBA, taking 2 years and costing roughly ₹25 Lakhs vs an investment banking course in India, taking 1 year and costing around ₹1.5 Lakhs.
| Factor | Investment Banking | MBA |
| Salary Potential & ROI on Education | ✅ | ❌ |
| Global Demand & Industry Prestige | ✅ | ❌ |
| Career Acceleration | ✅ | ❌ |
| Entry into Finance | ✅ | ❌ |
| Work Impact & Market Relevance | ✅ | ❌ |
| Job Security | ✅ | ❌ |
| Work-Life Balance | ❌ | ✅ |
| Career Flexibility | ❌ | ✅ |
| Leadership Role Diversity | ❌ | ✅ |
While an MBA offers flexibility, an Investment Banking course in India offers clarity, prestige, higher income, faster career growth, and stronger global positioning. For anyone serious about finance, capital markets, and elite corporate exposure, Investment Banking delivers a sharper, more powerful career trajectory than a general MBA.
Why Choose the Imarticus Learning Investment Banking Course in India
If you’re serious about getting into an investment banking course in India, this course is a very practical place to start. It doesn’t overcomplicate things or stay stuck in theory. Instead, it focuses on what actually happens inside banks and financial institutions, so you’re prepared for real work, not just exams.
- Built Around Real Banking Work – The course covers the full trade lifecycle, risk and compliance, KYC/AML, securities, and settlement processes. These are the everyday responsibilities in investment banking operations, so what you learn is directly useful on the job.
- Beginner Friendly – Whether you’re a fresh graduate or at the early stage of your career, this programme gives you a clear entry point into finance without needing an MBA or years of experience.
- Strong Career Support – The support is not limited to learning. You’re not left alone after the teaching is done. The course support also includes CV building, interview preparation, and hiring support to help you move confidently into banking roles.
- Practical, Not Just Academic – With real-world projects, case studies, and simulations, you gain experience that feels close to what you’ll do in a professional environment, which makes the transition into a job much smoother.
- Quick Route into Finance – Instead of spending years on a degree, this course helps you enter the industry faster and start building experience early.
- Recognised Certification – The certification adds credibility to your profile and shows employers that you’re trained in investment banking operations, not just general finance.
- A Clear Finance Identity – Instead of being a general business graduate, you build a strong identity as an investment banking professional, which is exactly what employers look for.
In simple terms, the Investment Banking Course in India is for those who want a direct, practical, and efficient route into the finance industry, without unnecessary detours.
FAQs About Investment Banking Course in India
Choosing an investment banking course in India naturally brings up a lot of questions. With these frequently asked questions, I’ll try to make things clearer and help you understand what lies ahead so you can decide with confidence if an investment banking course suits your career ambitions.
Which investment banking course in India is best suited for a career in investment banking?
There’s no single best course for getting into investment banking in India. It depends on your goal. Choose an investment banking course for quick, practical entry into the field, CFA for deep financial expertise, and an MBA in Finance for broader business and leadership exposure.
What is the best investment banking course in India to become an investment banker?
There are many practical investment banker courses in India with strong training in financial modelling, valuation, and deal processes, which is the best starting point. It prepares you directly for real banking roles and is much quicker and more affordable than a traditional MBA.
What is the qualification required for investment banking in India?
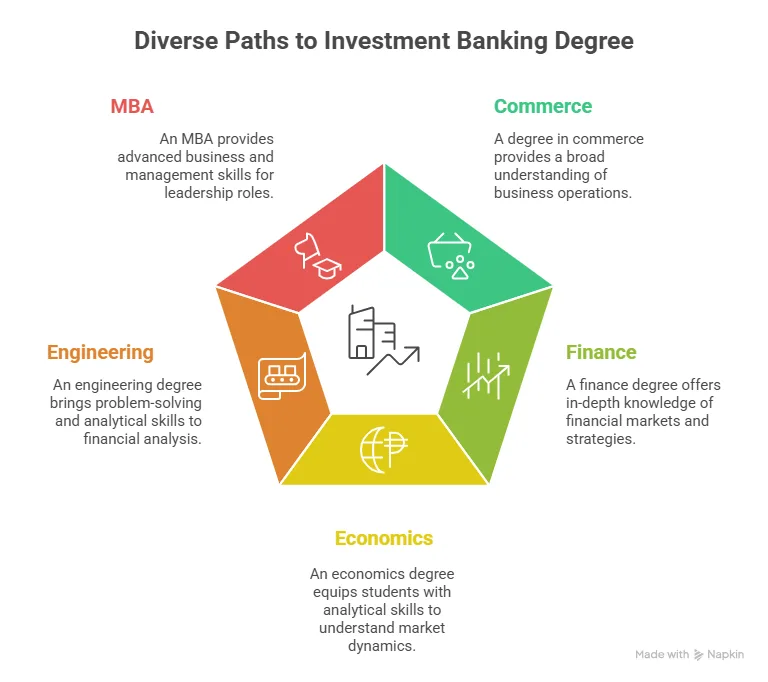
A graduation degree in any stream is usually enough, or having a background in commerce, finance, economics, engineering, or maths helps, but it’s not compulsory. You can pursue investment courses in India. What matters more is strong analytical skills and the right professional training.
What are the top investment banking courses in India?
The top investment banking course in India is the one that teaches you how the job actually works, not just the theory behind it. You want a course that helps you build real skills like financial modelling, valuation, understanding deals, and working with live market data. That’s what truly prepares you for an investment banking role. Specialised certification programmes from institutes like Imarticus Learning are a great choice to help you move confidently into the industry.
What are investment banking certification courses in India?
Investment banking certification courses in India are designed for people who want to learn industry-relevant skills beyond the theory. They’re short, practical programmes where you pick up skills like financial modelling, valuation, M&A, and how capital markets work in real life. If you’re looking for a quicker and more focused way to enter investment banking or move into core finance roles, investment banking online courses in India make a lot of sense. They help you get job-ready without spending years in a traditional degree programme.
How do I start my career in investment banking?
To start your career in investment banking, you can begin by getting your basics in finance and accounting right. Later, you can choose a practical investment banking course that teaches you real skills like financial modelling, valuation, and how deals actually work. Getting some hands-on experience through internships or projects, and preparing well for interviews, will help you be in a much stronger position. With the right training, breaking into investment banking becomes far more achievable.
How long is the investment banking course in India?
Most investment banking courses last between 3 and 12 months, depending on the depth of the programme and whether it’s full-time, part-time, or online.
Start Your Career With an Investment Banking Course in India
An investment banking course in India isn’t just about big numbers and big deals. It’s about being part of decisions that shape companies, industries, and markets. And today, you don’t need years of traditional education to get there. With the right investment banking course, you can build real skills, real confidence, and real career momentum in a much shorter time.
Investment banking courses give you clarity, focus, and practical exposure. You stop learning finance as a subject and start using it as a tool. That shift is what truly sets your career in motion.
If you’re serious about working in high-impact finance roles, don’t wait for the perfect time. The industry is growing, opportunities are expanding, and skilled professionals are in demand. Compared to longer and more expensive degrees, the investment banking course in India offers quicker employability and a more focused career direction.
Start now by investing in your skills and building your career with an investment banking certification.