A café near my home was always full. Still, the owner struggled with cash. Sales were strong. Profits were weak. Costs were leaking through waste, discounts, and poor supplier terms. Once someone actually read the numbers properly, small changes fixed the problem. Menu prices shifted slightly. Inventory was tracked better. Profit quietly doubled in months. That is the kind of real-world impact and the benefits of the ACCA qualification.
So what are we really talking about when we say ACCA benefits? We are talking about the ability to look at a business and see the story behind the numbers. Not just revenue. Not just expenses. The full picture of where money is earned, lost, saved, or invested.
Why do some companies grow fast while others with the same product struggle? Why do some startups run out of cash even when customers love them? Why do big firms collapse after years of success? These are not luck-based events. They are financial patterns. The benefits of studying ACCA certification train you to spot those patterns early.
I often see people focus only on salary when they think about qualifications. Salary matters. Still, strong careers are built on skills that stay useful for decades. The benefits of doing ACCA include decision-making, risk awareness, and financial planning. These skills apply in corporations, startups, consulting firms, and even personal ventures.
In the sections ahead, I break down ACCA benefits in a way that connects directly to real careers. You will see how the qualification builds practical skills, how it supports different finance roles, how it creates global opportunities, and why employers value it across industries. The goal is simple. To help you understand not just what ACCA is, but what it actually does for your long-term career path.
Did You Know?
ACCA has members and students in over 170 countries. This global network adds to the ACCA qualified benefits because your credential is recognised across borders. Source from the official ACCA global site can support this data.
How ACCA Builds Real-World Skills
Before we go deeper into ACCA benefits, it helps to clearly understand what is ACCA and why it carries so much weight in global finance.
ACCA stands for the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants. It is an international professional accounting body that trains finance professionals in financial accounting, audit & taxation, management, and ethics. The qualification is designed to match real business needs rather than only academic progression.
In simple words, ACCA teaches you how money moves inside a business, how to track it, how to report it, and how to guide decisions based on it. That is why the benefits of the ACCA qualification extend far beyond bookkeeping.
Here is a clear snapshot of the ACCA course details:
| Component | What It Covers | Why It Matters for ACCA Benefits |
| Applied Knowledge | Basics of accounting and business | Builds strong financial foundations |
| Applied Skills | Tax, audit, and financial reporting | Develops practical job-ready abilities |
| Strategic Professional | Strategy, risk, leadership | Prepares for senior decision-making roles |
| Ethics Module | Professional ethics and judgment | Builds trust and credibility |
This layered structure is what drives long-term ACCA course benefits. You do not just learn how to prepare numbers. You learn how to interpret them and support the business strategy.
Another key part of ACCA benefits comes from its global relevance. The syllabus aligns with international financial reporting and auditing standards. That means the knowledge works across borders, industries, and company sizes.
Also Read: ACCA Course Subjects: Difficulty Levels & Preparation Guide
How ACCA Learning Translates to Real Jobs
What you study in ACCA is closely tied to what finance professionals actually do at work. Concepts from reporting, audit, tax, and financial management show up in everyday tasks like preparing statements, analysing costs, supporting compliance, and helping managers make better money decisions. This direct link between the ACCA exam and workplace responsibilities is what makes ACCA learning feel practical rather than purely theoretical.
- Financial reporting knowledge helps prepare investor-ready statements.
- Audit skills support compliance and risk checks.
- Tax knowledge helps businesses plan legally and efficiently.
- Performance management helps control costs and improve profits.
- Financial management supports funding and expansion decisions.
These are not abstract subjects. These are daily business functions. That practical design explains the strong ACCA program benefits seen in the job market. Before we look at specific roles, it helps to understand what the ACCA program benefits really mean in day-to-day work life. Below is a quick view of how skills from the course map relate to business problems.
| ACCA Skill Area | Real Life Business Use | Why It Matters |
| Financial Reporting | Prepares clear financial statements | Helps owners and investors trust the numbers |
| Performance Management | Tracks costs and profit per product | Stops money leaks in operations |
| Taxation | Plans legal tax savings | Improves cash flow |
| Audit | Checks if records are accurate | Reduces fraud risk |
| Financial Management | Plan funding, and investments | Supports growth |
The ACCA certificate benefits come from this mix of theory and application. Employers like professionals who can both read data and advise on decisions.
Finance qualifications keep evolving to match global business needs. Updated exam structures, industry-relevant skill focus, and stronger alignment with international reporting standards are shaping how future professionals prepare for global roles. For students planning their path, understanding what ACCA covers helps set realistic expectations around learning, career scope, and long-term professional growth.
ACCA Benefits for Career Flexibility
One strong aspect of ACCA benefits is career mobility. I am not locked into one narrow job path. The benefits of doing ACCA include roles in audit, consulting, banking, corporate finance, and even startups. Here are examples of roles many ACCA students move into:
- Financial Analyst
- Internal Auditor
- Risk Analyst
- Tax Consultant
- Management Accountant
- Finance Business Partner
Each of these roles uses a different slice of the benefits of the ACCA qualification. Some focus on numbers. Some focus on strategy. Some work closely with top management.
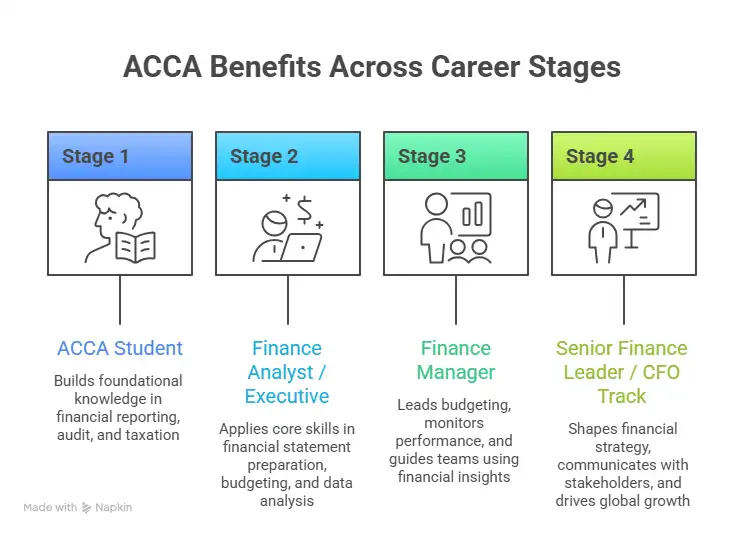
ACCA Benefits to Employers
Companies care about return on salary. They want professionals who reduce risk and improve profit. That is where the benefits of ACCA to employers become very clear.
When a firm hires someone with ACCA training, they get a person who understands internal controls, compliance, and financial planning. This lowers the chance of costly errors. It also improves reporting quality. Investors and banks trust firms that follow strong financial practices.
Let me explain this with a daily life example. Think about a family that tracks its monthly expenses. If no one monitors spending, money disappears fast. If one person tracks bills, plans savings, and avoids waste, the family grows wealth. That person plays the same role an ACCA professional plays inside a company.
Also Read: How I Passed All My ACCA Exams on the First Try
Benefits of Being an ACCA Member
The benefits of ACCA membership go beyond exams. Members get access to professional updates, industry reports, and global networking events. Continuous learning is part of the system. Finance rules change often. Staying updated protects career growth.
There is also an ethical framework. Professional Ethics is not just a theory. It affects trust. Banks, investors, and regulators value professionals trained to follow strong ethical standards. That trust adds to long-term ACCA program benefits.
ACCA Course Benefits for Long-Term Growth
I see the benefits of the ACCA course as a long game. Early roles may be technical. Over time, the same knowledge supports leadership positions. Many finance heads and CFOs have strong backgrounds in accounting and financial management. ACCA builds that base.
Here are some long-term advantages in simple terms:
- Better understanding of how businesses earn and spend money
- Ability to speak with auditors, bankers, and investors confidently
- Skills that help in both large firms and small startups
- Strong base for roles in strategy and planning
These are not short-term perks. These are career foundations.
Interesting Insight→ Global demand for finance professionals with international standards knowledge has been rising as companies expand across borders. This trend supports the growing ACCA certificate benefits for professionals who want global exposure. International hiring reports from large job portals often reflect this shift.
ACCA Benefits in India and Career Demand
When I looked closely at ACCA benefits in the Indian market, I noticed how strongly global finance is blending with local business. Indian companies now deal with overseas clients, foreign investors, and cross-border transactions. This shift increases the benefits of ACCA in India because the qualification is built on international standards.
A company in Pune exporting software to Europe must understand global tax rules and reporting norms. A retail chain in Delhi raising funds from foreign investors needs clean financial statements. These situations create real space for ACCA-qualified benefits in daily business operations.
Below is a simple overview of where demand is visible.
| Sector | How ACCA Skills Are Used | Career Impact |
| IT and Tech | Global revenue reporting and compliance | Faster entry into finance analyst roles |
| Consulting Firms | Audit support and risk reviews | Exposure to multiple industries |
| Manufacturing | Cost control and budgeting | Roles in plant finance and planning |
| Banking and NBFCs | Regulatory reporting and analysis | Strong base for risk and treasury roles |
| Startups | Cash flow planning and investor reporting | Early responsibility and growth |
The ACCA benefits in India are not limited to metro cities. Growing companies in Tier 2 cities also need structured finance functions.
BCom With ACCA Benefits
Many students now pursue BCom with ACCA benefits in mind. A graduation degree covers broad commerce topics. ACCA adds global technical depth. Together, ACCA after graduation makes a strong profile.
Think of BCom as learning the map of a city. ACCA is like learning how to drive on every road confidently. The combination improves employability in both Indian firms and multinational companies.
Key advantages of this combination include
- Early start in professional exams
- Better understanding of accounting subjects during college
- Stronger CV during campus placements
- Ability to apply for global finance roles later
This pathway increases the benefits of studying ACCA while still in college.
Choosing between CA and ACCA often depends on where someone wants their career to grow. Understanding how each qualification shapes skills, career options, and work environments can make the decision clearer for students exploring long-term opportunities in finance and accounting.
Benefits of ACCA to Employer in India
Indian employers face strict compliance requirements. Tax rules change. Reporting standards evolve. Digital systems bring more data. Companies value professionals who can manage this complexity.
The benefits of ACCA to employer include
- Improved financial controls
- Accurate regulatory reporting
- Better budgeting and forecasting
- Lower risk of penalties
For example, if a company files tax reports with errors, penalties can be heavy. An ACCA-trained professional reduces this risk. This practical value explains why ACCA-qualified benefits are noticed by recruiters.
Also Read: How Globally Recognised Is the ACCA Qualification?
Salary Influence and Growth Path
The growth of ACCA salary in India is one of the visible ACCA course benefits. Entry roles may start at the analyst level. Over time, professionals move into senior analyst, manager, and finance lead roles.
Annual Salary Range for ACCA Roles in India
| Career Stage | Typical Job Titles | Approx. Salary Range (₹ per annum) |
| Entry Level (0-2 yrs) | Junior Accountant / Accounts Executive / Financial Analyst | ₹3 – 7 LPA |
| Associate Level (2-5 yrs) | Senior Accountant / Tax Consultant / Internal Auditor | ₹6 – 12 LPA |
| Mid Level (5-8 yrs) | Finance Manager / Financial Controller / Senior Analyst | ₹12 – 20 LPA |
| Senior Leadership (8+ yrs) | Finance Director / Head of Finance / CFO Track | ₹20 – 50 LPA+ |
A useful way to see the benefits of the qualification is to connect ACCA skills depth with pay growth. As responsibility increases, so does compensation. Employers pay more for professionals who can interpret numbers and guide decisions.
Did you know?
India’s finance hiring has seen consistent demand for roles in financial planning, audit, and compliance, according to industry hiring trend reports published by major job platforms. This supports the long-term ACCA program benefits.
Specialised Knowledge Areas in ACCA
One part of ACCA benefits that often goes unnoticed is exposure to advanced topics like audit committees and integrated reporting.
- Benefits of audit committee for ACCA knowledge
Professionals learn how governance works inside large firms. They understand how audit committees review financial statements and internal controls. This knowledge is useful in listed companies and large private firms. - Benefits of integrated reporting in ACCA learning
Integrated reporting links financial results with environmental and social impact. Many global firms now follow such reporting models. Understanding this improves career relevance in sustainability and ESG reporting roles.
These niche areas expand the benefits of being an ACCA beyond traditional accounting.

Diploma in IFRS ACCA Benefits
IFRS knowledge is a strong global requirement. The diploma in IFRS ACCA benefits professionals who work with multinational firms or foreign subsidiaries. Financial statements prepared under international standards are easier for global investors to understand.
Imagine two companies. One uses local rules only. The other uses global standards that foreign investors recognise. The second company attracts more international interest. That difference explains the practical diploma in IFRS ACCA benefits.
ACCA Certificate Benefits for Career Switching
Some professionals enter ACCA after starting in other fields. They may begin in operations or general commerce roles. The ACCA certificate benefits help them shift into core finance. Skills gained during the course help in
- Reading financial statements confidently
- Participating in budgeting meetings
- Supporting audits and compliance work
This makes internal career movement easier.
Also Read: Why ACCA UK Certification Is a Must-Have for Aspiring Accountants
Long-Term Scope of ACCA and Global Mobility
When I think about ACCA benefits over a full career span, I see a qualification that grows with experience. Early years focus on technical skills. Mid-career roles move into supervision and planning. Later stages involve strategy and leadership.
The benefits of the ACCA qualification are linked to global standards. This matters when companies expand across borders. A professional trained in international accounting and finance principles can move between regions with less friction. A simple example makes this clear.
Suppose a firm in India acquires a small company in Singapore. Financial reports must follow global norms so investors can compare performance. An ACCA professional can handle this transition smoothly. That practical ability reflects strong ACCA qualification benefits.
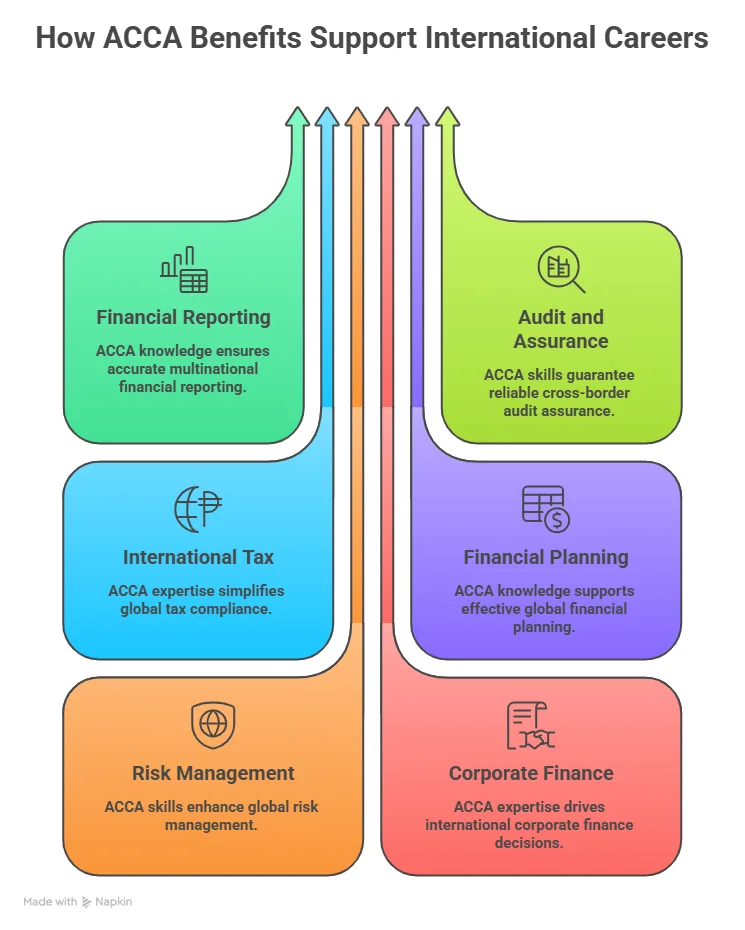
Benefits of ACCA Membership and Professional Network
The benefits of ACCA membership continue even after exams are cleared. Members must follow continuing professional development. This keeps knowledge fresh. Finance rules change often. Tax laws update. Reporting formats evolve. Staying updated protects career value.
Membership also connects professionals to a global network. This network includes finance leaders, auditors, consultants, and academics. Discussions, webinars, and industry updates support ongoing growth. These connections strengthen long-term ACCA benefits in ways that go beyond textbooks.
Benefits of Being an ACCA in Emerging Fields
Finance is expanding into new areas like sustainability reporting, data analytics, and risk management. The benefits of being an ACCA include exposure to ethics, governance, and strategic thinking. These areas support work in emerging fields.
For example, many firms now publish sustainability reports. These reports combine financial and non-financial data. Professionals who understand reporting frameworks and controls can support this work. Knowledge connected to the benefits of integrated reporting makes ACCA useful here.
Also Read: Simplifying the ACCA Qualification: A Guide to Aspiring Accountants
Career Stability and Future Relevance of ACCA
Automation is changing many jobs. Routine data entry tasks are declining. Analytical and advisory roles are growing. The benefits of studying ACCA include learning how to interpret data, not just record it. This supports future-ready career paths.
Roles that involve judgment, risk analysis, and planning remain important. ACCA training builds these abilities. This makes the ACCA program benefits relevant even as technology changes finance functions.
Benefits of the ACCA Qualification for Entrepreneurs
Some professionals use their knowledge to start their own firms. The benefits of the ACCA qualification help in setting up accounting practices, consulting services, or advisory roles. Understanding tax, compliance, and financial planning is useful for business owners, too.
Imagine a small manufacturing unit. The owner knows production well but struggles with finances. An ACCA-trained consultant can guide pricing, cost control, and funding. This improves survival and growth chances for the business.
Social Trust and Professional Credibility
Finance roles involve trust. Stakeholders rely on accurate information. Errors or fraud damage reputation. The ethical framework within ACCA training supports responsible behaviour. This builds long-term credibility.
The benefits of ACCA membership include a commitment to ethical conduct. Employers and clients value this reliability. Trust often leads to bigger responsibilities and leadership roles.
Preparing to clear ACCA exams on the first attempt usually comes down to planning, consistency, and understanding how the exams test application rather than memorisation. A clear study strategy, regular practice with exam-style questions, and familiarity with the format can make a noticeable difference.
Why Choose Imarticus Learning for Your ACCA Journey
When you aim for strong ACCA benefits that translate into career impact, the right preparation partner makes all the difference. The ACCA Course prep offered by Imarticus Learning stands out because it blends global expertise, structured support, industry exposure, and career outcomes. The following points highlight the true USPs that help learners unlock meaningful ACCA benefits.
Here are the key reasons many students choose Imarticus for ACCA preparation:
- Gold Status ACCA Learning Partner: Imarticus is recognised as a gold status learning partner by ACCA UK, ensuring high-quality training aligned with global standards and current exam requirements.
- Collaboration with KPMG in India: The program features real-world case studies and curated resources developed with KPMG practitioners. Top performers get access to internships and hands-on exposure to global finance practices.
- Dual Certification Opportunities: Alongside the core ACCA credential, learners may earn a joint certification that strengthens their resume and enhances global appeal.
- Money-Back Assurance: A unique guarantee helps reduce risk for learners: a refund option if professional-level ACCA exams are not cleared under specific conditions.
- Comprehensive Placement Support: The program offers 100 % placement or internship guarantee after completing key levels, helping learners transition into roles in audit, finance, consulting, and shared services.
- Kaplan Powered Study Materials: Course content is built in partnership with Kaplan, a leading ACCA-approved content provider. Students get access to books, question banks, practice papers, flashcards, and expert-led sessions.
- Pre-Placement Bootcamps & Soft Skills Support: Learners receive targeted interview preparation, resume workshop sessions, and soft skills bootcamps to help build confidence for real job opportunities.
These USPs are designed to directly boost the tangible benefits of doing ACCA, equipping learners not just to pass exams but to thrive in careers that value strategic finance talent.
FAQs on ACCA benefits
Questions often come up when students try to understand the real career value behind ACCA benefits. Clear answers help connect the qualification with salary growth, job roles, global mobility, and employer demand, making it easier to see how this path fits into long-term finance goals.
What are the benefits of ACCA?
ACCA benefits include global recognition, strong technical knowledge, and career flexibility across industries. Professionals gain skills in financial reporting, audit, tax, and performance management. These abilities help in roles that involve analysis and decision support. The qualification also supports international mobility, which adds long-term career value.
Is ACCA a high-paying job?
ACCA benefits often translate into strong salary growth over time. Entry-level roles build experience in reporting and analysis. As professionals move into senior roles, pay increases with responsibility. Skills in budgeting, risk management, and financial strategy are valued by employers. These competencies support higher-paying positions in consulting, corporate finance, and multinational firms.
Is doing the ACCA over a CA a better option?
ACCA benefits are linked to global accounting standards and international mobility. Some professionals prefer ACCA when they aim for roles in multinational companies or overseas markets. The course structure focuses on financial management, strategy, and global reporting frameworks. Imarticus Learning often guide students on how ACCA aligns with global career paths. Individual goals and preferred work locations influence this decision.
What is the scope of doing ACCA in India?
ACCA benefits in India are growing as companies deal with cross-border trade and foreign investment. Firms need professionals who understand international reporting and compliance. This creates opportunities in consulting firms, global capability centres, and large corporations. Knowledge of IFRS and global finance practices adds relevance in the Indian job market.
What are the advantages of doing an ACCA over a CMA and a CA in India?
ACCA benefits focus on international standards, global mobility, and a wide finance skill set. Professionals learn reporting, audit, tax, and strategic finance. This range supports roles beyond traditional accounting. Many students explore programs with institutes such as Imarticus Learning to align ACCA with global finance careers. Career goals and industry preferences shape the right choice for each student.
Does ACCA have a high salary?
ACCA benefits can support strong earning potential, especially as professionals gain experience. Skills in financial analysis, planning, and compliance are valued across industries. As responsibility increases, salary often rises with it. Roles in multinational firms and consulting environments can offer competitive pay linked to global finance expertise.
Is ACCA good for the future?
ACCA benefits remain relevant as finance roles shift toward analysis and strategy. Automation handles routine tasks, while professionals focus on interpretation and planning. Training in ethics, governance, and financial management supports future-ready careers. Global recognition also keeps options open across different markets.
Does Big 4 hire ACCA in India?
ACCA is valued by large consulting and audit firms that work with international clients. Knowledge of global reporting standards and audit practices is useful in such environments. Professionals with ACCA backgrounds often find opportunities in audit support, advisory, and compliance roles. Training with Imarticus Learning helps candidates prepare for such career paths.
Make the Most of ACCA Benefits for Your Future
ACCA benefits build slowly and stay strong for years. They shape how you read numbers, how you think about risk, and how you guide business choices. From early analyst roles to senior finance leadership, the same foundation keeps supporting growth. The benefits of the ACCA qualification reach across industries, cities, and even countries, giving professionals room to move as their goals evolve.
I see the benefits of studying ACCA as a steady upgrade to career confidence. You understand reports with ease. You speak the language of finance clearly. You become someone teams rely on when money decisions matter. These ACCA course benefits do not fade after one job change. They stay useful as markets shift and businesses grow more complex.
For students planning their path, structured guidance can make the journey smoother. Learning environments that blend concept clarity with practical exposure help unlock the full ACCA benefits in a shorter time. Many learners explore the structured ACCA Program with Imarticus Learning to stay consistent, exam-ready, and industry-aligned.
The road ahead in finance belongs to professionals who combine technical skill with a global perspective. ACCA supports exactly that mix, helping careers grow with confidence and direction.