When I meet people who are curious about building a CMA Career, I often sense a similar pattern. They know the credential is respected. They hear about global mobility, sharper analytical skills, and strong roles in finance. Yet they rarely see the full landscape that shapes how a CMA grows over time. I want to discuss that landscape in a way that speaks to students, mid-career professionals, career switchers, and even senior leaders who want to sharpen their strategic finance lens.
The world of management accounting shifts fast. Businesses expect finance talent to solve problems with numbers, operations, technology and foresight. A CMA stands right in the middle of that expectation.
The learning from the US CMA course pushes you to see a business as a living system. You start connecting cost flows, decisions, risks, and long-term plans. That is why a CMA Career remains relevant even as tools, markets and industries change.
As you read further, I will break down how CMA career options unfold in real workplaces, the skills that grow with each stage, the roles that open up across industries, and how the qualification shapes long-term financial leadership potential.
You will also see the salary patterns, job pathways, and practical examples that show how the CMA translates into daily decision-making. By the end, you will have a clear view of what this journey looks like from start to senior roles, and what it can mean for your future in finance.
Understanding CMA as the Foundation of Your Finance Journey
A strong CMA Career starts with a simple understanding ofwhat is CMA and how it changes the way you interpret financial information. The certification offered by IMA blends analytics, planning, cost insights, and strategic thinking into one learning track. It is designed for people who want to work beyond traditional accounting roles and contribute to business decisions at a deeper level.
CMA at a Glance
This table offers a simple snapshot of what the CMA course stands for, what it covers, and why it supports a strong CMA Career pathway for learners and working professionals.
| Aspect | Details |
| Full Form | Certified Management Accountant (US CMA) |
| Governing Body | Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), USA |
| Primary Focus Areas | Financial Planning, Performance Management, Cost Management, Internal Controls, Strategic Decision Making |
| Exam Structure | 2 Papers: Part 1 (Financial Planning, Performance, Analytics) and Part 2 (Strategic Financial Management) |
| Eligibility | Bachelor’s degree (can enrol as a student and submit the degree later), plus a work experience requirement for certification |
| Exam Duration | Each exam is 4 hours with MCQs and essay scenarios |
| Course Duration | Typically, 6 to 9 months of preparation, depending on the schedule |
| Career Relevance | Builds skills for roles in FP&A, corporate finance, cost analysis, management accounting, and strategic decision making |
| Global Recognition | Accepted in 170+ countries and valued across multinational corporations |
To understand this better, I’ll break the journey into three layers. These layers form the foundation for every role and decision you take as a CMA. They also shape the CMA career opportunities that open over time.
1. The Market Forces That Shape a CMA Career
Every profession evolves with its environment. For CMAs, the environment is a blend of digital transformation, global finance standards, increasing regulation, and data-driven decision-making practice. This pattern reveals a simple truth. Companies reward the blend of analytical and managerial ability. They treat CMAs as drivers of clarity.
Many candidates still wonder, is CMA a good career for the next decade? I believe it is, for one reason. The role keeps expanding. A CMA today works closely with decision makers. They advise on pricing, supply chain, costing, capital allocation, profitability models, and scenario plans. These tasks demand financial discipline and strategic understanding. That blend plays a major role in shaping the scope of CMA USA roles.
A CMA Career also thrives because companies want professionals who understand risk. Businesses face unpredictable shifts. Currency fluctuations, rising input costs, new competitors, talent shortages, regulatory changes and sudden technology jumps. Each shift hits margins. A CMA steps in to build cost structures that survive these shocks. The ability to solve using numbers and logic is a central driver of CMA career prospects.
2. Skill Foundations Behind Strong CMA Career Prospects
People often think the US CMA course is only about costing and financial analysis. That is a narrow view. The learning builds a system of thinking. This system shapes the CMA jobs in a powerful way. Let me break the core skill foundations into simple, relatable ideas.
a. Decision Framing
A CMA learns how to frame a decision. I do not only look at numbers. I check the structure of a problem. I map the drivers behind it. Most business issues are not only financial. They are operational and behavioural too. This wider lens allows a CMA to support leadership teams with clarity.
b. Quantitative Logic
The numbers in management accounting are not random. They reveal patterns. A CMA develops the ability to spot these patterns quickly. For example, when sales rise, but cash flow stays tight, a CMA looks at receivables cycles, production delays, or discounting patterns. This ability makes your career after CMA both versatile and stable.
c. Forecasting
Businesses move on forecasts. CMAs get trained to build them with precision. I like to think of forecasting as storytelling with numbers. You take past trends, insert new assumptions and convert them into realistic expectations. This is one skill that keeps your CMA career future-ready.
d. Ethical Reasoning
IMA’s ethics framework is a major part of the training. Ethics protects the quality of decisions. It helps companies build trust. A finance leader without ethics cannot grow long-term. This is one of the most underrated CMA Benefits.
e. Technology Adoption
Automation is changing finance. A CMA learns to use analytics tools, dashboards, ERP systems, and data modelling platforms. These tools allow faster analysis and easier reporting. This is why global firms continue to invest in CMAs for new-age finance roles.
3. Industries That Create Strong CMA Career Opportunities
A CMA Career does not restrict you to one industry. The skill set travels well across sectors. Each industry has its own flavour of costing, risk and financial planning. This variety opens wide career options.
Manufacturing
The roots of management accounting sit deep in manufacturing. If you enjoy understanding how products are made, this sector builds a strong foundation. Costing, variance analysis, overhead allocation and capacity planning remain major tasks. The CMA career prospects in manufacturing stay steady because companies always aim to improve unit economics.
Technology
Tech firms operate with rapid change cycles. A CMA helps them evaluate new features, pricing strategies and expansion plans. The focus is often on managing the cost of scaling. Forecasting and decision modelling become daily tasks.
Banking and Financial Services
This sector values risk analysis and portfolio-level thinking. A CMA contributes to budgeting, planning, regulatory reporting and risk scenarios. The roles link financial analysis with decision support.
Consulting
If you enjoy solving diverse business problems, consulting creates interesting CMA career opportunities. Clients expect you to diagnose issues quickly. The variety strengthens your judgment.
Retail and e-commerce
These businesses run on thin margins. A CMA monitors pricing, supply chain costs, returns management and promotion effectiveness. The insights help companies stay profitable in competitive markets.
Healthcare
Hospitals face complex regulations, insurance cycles, and cost structures. CMAs bring control and transparency. They set up dashboards for doctors, departments, and supply teams.
Shared Services and GCCs
India has become a hub for global capability centres. These centres need stable financial planning talent. The scope of CMA USA has grown here due to the global nature of reporting and analytics.
People often assume that only commerce graduates move into a CMA Career, but the entry pathways are far wider. The qualification is designed to help diverse backgrounds build a shared foundation in cost management, planning, and performance analysis, which is why the CMA ecosystem attracts such a wide mix of professionals, as illustrated below:
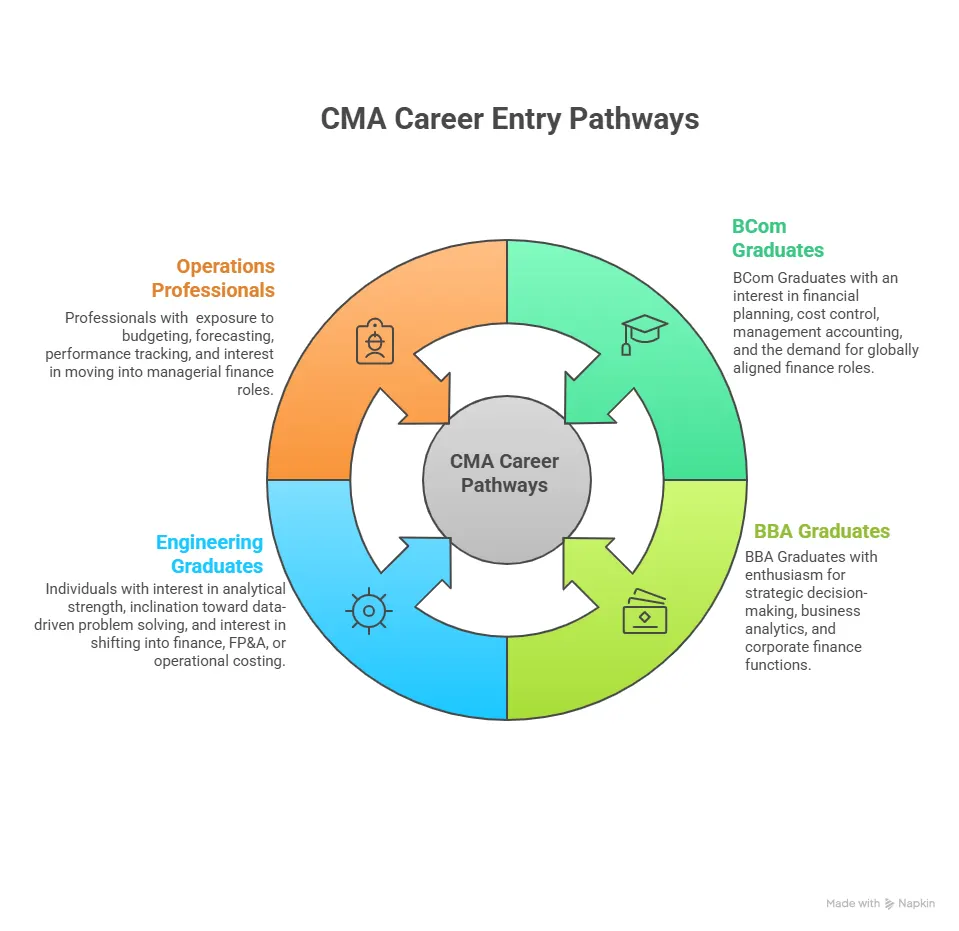
A Simple Way to Visualise CMA Career Options
Below is a table that I often use when explaining the spread of roles. It helps candidates see how their skills convert into real positions. This table also shows how the CMA adds value to your career as your experience grows.
The table maps career stages to common roles and the type of responsibilities that define growth.
| Career Stage | Typical Roles | Type of Responsibilities |
| Early Stage | Cost Analyst, Budget Analyst, Junior Financial Analyst | Building reports, costing, variance study, and basic forecasting |
| Mid Stage | Management Accountant, Financial Planning Analyst, Business Finance Partner | Decision support, planning cycles, performance analysis, risk evaluation |
| Growth Stage | Finance Manager, FP&A Lead, Plant Controller | Strategy modelling, cross-functional leadership, long-term planning |
| Leadership Stage | Corporate Controller, Director of Finance, CFO Track Roles | Enterprise strategy support, capital planning, stakeholder communication |
This progression is not fixed. Many CMAs pick unique journeys. Some join startups. Some join Big 4 consulting teams. Some build domain expertise and move into leadership faster. This flexibility is what makes a CMA Career resilient.
Did You Know?
CMAs report 21% higher median total compensation than their non-certified peers. (Source: IMA Global Salary Survey)
The Multi-Level Role Structure in Modern CMA Careers
A CMA Career does not have a single fixed ladder. It looks more like a set of clusters. Below is a breakdown of how the career after CMA evolves through typical internal steps.
Role Cluster 1. Analytical Foundations
These roles work closely with data and processes.
- Financial Analyst
- Cost Analyst
- Budget Analyst
- Pricing Analyst
Professionals in this stage sharpen the art of clear measurement. They create models, reconcile data, and build scenario views. These are the years when many people develop strong habits that stay with them.
Role Cluster 2. Planning and Operations
These roles are where strategic insight begins to grow.
- FP and A Specialist
- Operations Accountant
- Plant Controller
- Business Analyst
Planning teams need someone who can hold the story behind numbers. A CMA uses concepts from the US CMA course to produce meaning, not just figures. This is where CMA jobs in India begin to widen.
Role Cluster 3. Leadership and Control
These roles lead teams and shape big decisions.
- Finance Manager
- Cost Controller
- Divisional Controller
- Risk and Governance Lead
People in these positions gain a seat at the leadership table. Their skill lies in turning what looks complex into a simple direction. This stage offers a strong CMA career scope for professionals ready to lead teams.
Role Cluster 4. Strategic and Executive Roles
These roles include decision makers at the top.
- Head of Finance
- Strategy Lead
- CFO Track Roles
- Global Controller
The CMA career path can move into senior leadership because financial clarity is a key requirement for long-term business stability. CMA salary also depends on the experience level and can be compared with the lens of verified vs non-certified peers.
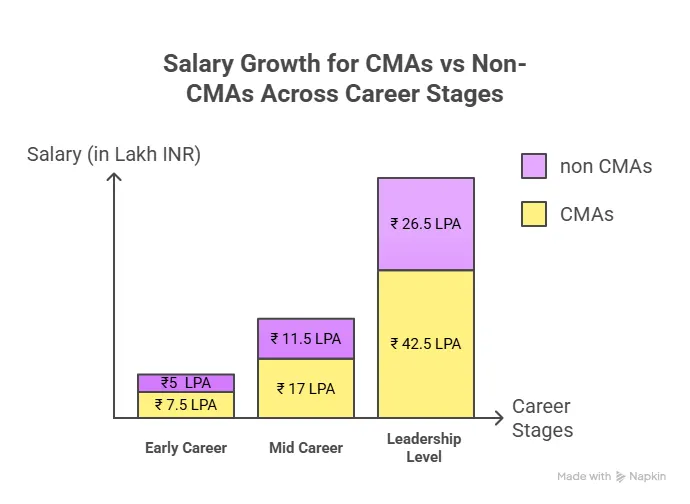
Understanding Career Progression Through a Practical Table
This table shows how skills grow at each stage and how responsibilities expand over time. The description below prepares the reader for what to expect.
How CMA Skills Translate Into Career Stages
| Stage | Skill Focus | Typical Output | Career Impact |
| Early Analyst | Measurement and cleanup | Reports, reconciliations, spreadsheets | Builds reliability |
| Mid Planner | Forecasting and modelling | Plans, budgets, dashboards | Influences decisions |
| Control Lead | Governance and discipline | Policies, metrics, control systems | Strengthens operations |
| Strategic Leader | Direction and clarity | Long-term plans, board inputs | Shapes business goals |
Professionals often move across stages at different speeds. What remains common is the understanding that clean financial thinking is valuable across every team. To give you a better perspective on the depths of roles, this video explains the value of CMA as a global certification:
How the Scope of CMA USA Expands Career Reach
Many professionals search for roles across borders. A CMA does not guarantee a job abroad. It makes the profile relevant across global teams and enhances readiness for multinational settings.
The value comes from three practical strengths.
- Strength 1 | Standardised Skills: Companies across countries know the CMA curriculum. They know what a candidate can deliver. This helps with mobility and also makes remote roles possible.
- Strength 2 | Cross-Functional Fit: A CMA works closely with operations, supply chain, technology, or marketing teams. That gives global managers confidence that the hire can adapt to different cultures.
- Strength 3 | Financial Storytelling: Global firms need professionals who can explain numbers without jargon. This is one of the largest CMA career opportunities today because companies run teams across several locations.
1. Case Style Examples for Clarity
These small illustrations help readers picture the skills in action.
Example: Manufacturing Planning
A new FP&A analyst joins a plant finance team. The plant manager faces rising input costs. The analyst builds a simple model that shows how a small change in batch size reduces cost. The manager adjusts operations. Margins improve. This is a typical win for someone building a CMA Career in manufacturing.
Example: Technology Product Finance
A tech firm wants to introduce a new subscription plan. A CMA maps the revenue and cost cycles. The team uses the insights to adjust pricing. The launch meets targets. This is common in US CMA career paths linked to digital firms.
Example: Retail Inventory Review
A retail chain struggles with stockouts. A CMA studies SKU-level patterns. They discover that one category drives most misses. The buying team adjusts orders. Sales improve. This is how CMA career options appear in commercial teams.
Compensation reflects how organisations value strategic finance talent. The ranges discussed in the video show how salaries evolve from analytical positions into decision-support and leadership tracks.
The Middle Career Pivot in a CMA Career
A CMA can move from a pure finance role into planning or strategic work. This pivot often happens between years three and seven. It allows professionals to break out of low-growth roles. Many mid-career professionals use the US CMA course for this pivot. It offers confidence and structure.
Some people shift from accounting into analytics. Some enter the supply chain. Others move into global reporting. The common thread is the ability to read information with discipline and precision.
Below is a short list of pivot-friendly skill sets.
Skills That Support Mid-Career Transitions
Mid-career professionals often reach a point where technical experience alone no longer drives growth, and this is where CMA-aligned skills create the bridge to strategic and higher-impact roles.
- Ability to map cost flows
- Comfort with large data sets
- Understanding of process gaps
- Clarity in business storytelling
- Steady forecasting habits
These skills open doors in many companies. They also support remote and hybrid roles.
Did you know?
Many Fortune 500 firms list CMA as a preferred credential for planning and analysis roles. These companies operate in complex, fast-moving environments, so they prioritise professionals who can link financial data to business decisions with clarity.
Role Transition Table for 5 to 10 Year Window
This table helps you visualise the evolution of responsibilities.
| Years of Experience | Typical Roles | Key Contribution | Type of Growth |
| 0 to 3 | Analyst roles | Clean data, fast models | Skill building |
| 3 to 6 | Planning roles | Forecasts, budgets, insights | Influence building |
| 6 to 10 | Control or managerial roles | Governance, leadership, systems | Team building |
| 10 plus | Strategic roles | Vision, long-term plans | Enterprise impact |
The Role of Ethics and Decision Support in CMA Careers
Ethics is often underestimated. A CMA cannot function without a strong ethical grounding. Businesses trust professionals who protect shareholder value. They need people who question assumptions and use sound judgment.
CMA skills teach you to apply ethical standards in daily work. They know how to avoid conflicts of interest. They know how to structure reviews. They know how to protect sensitive information. These habits help them earn seats in important rooms.
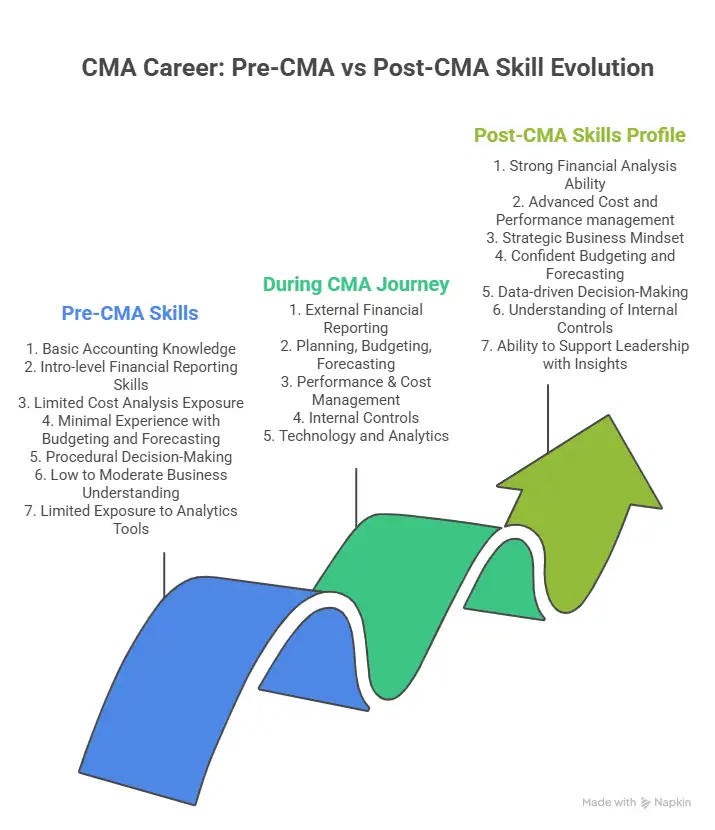
Before completing the CMA course duration, most skills sit in separate pockets. As you go through the CMA modules, those pockets start connecting. After earning the credential, this way of thinking becomes natural, helping you link data to decisions and contribute with confidence to long-term planning.
CMA Career Options Across Remote Work Models
Remote work has created new forms of CMA career opportunities. Many global teams run analytics, reporting, and planning work from India. A CMA brings discipline and reliability to these roles. A few patterns have emerged.
- Remote FP&A Pods: Companies hire analysts to support monthly closings and forecasts from remote locations.
- Controller Support Pods: Firms set up small teams for reconciliations, audits, and controls.
- Project-Based Models: Short-term assignments for pricing, modelling, or business case reviews.
These pathways show that the CMA career path can support flexible and family-friendly work models.
Understanding Value Creation in a CMA Career
A CMA creates value by improving clarity. They show teams where money comes from and where it goes. They help leaders understand cost structures. They support growth decisions. This is true across small and large companies.
The simple loop of measure, interpret, guide, and follow through defines the CMA mindset. It is one of the core CMA Benefits that stays relevant throughout the career.
Where Imarticus Learning Fits in the Journey
Learners who want to build a strong US CMA career need structured preparation. Imarticus Learning provides live classes, doubt clearing, simulation tests, and job readiness support. These elements help professionals become industry-ready.
- Industry-Led US CMA Program: The US CMA program at Imarticus is industry-led and co-created with KPMG in India, offering real-world case studies and a joint certification that gives your resume a competitive edge.
- Gold Learning Partner of IMA, USA: Imarticus Learning is a Gold Learning Partner of the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), USA, which ensures alignment with global industry standards and high-quality program delivery.
- Expert Faculty and Structured Teaching: The course includes monthly webinars, live sessions with industry practitioners, and structured teaching designed to build strategic financial skills, performance management capabilities, and analytical judgment.
- Money-Back Guarantee: Imarticus offers a money-back guarantee, refunding 50% of the course fee if you do not pass the US CMA exams; a strong confidence signal in the quality of training and support.
- Internship Opportunity with KPMG in India: High-performing learners become eligible for a hands-on internship with KPMG in India, a rare opportunity that brings professional exposure and global working experience.
- Pre-Placement Bootcamp & Career Assistance: Students gain access to a pre-placement bootcamp, resume support, interview training, and assured interview opportunities with leading firms, making the transition into a CMA Career smoother.
Explore the CMA course now!
FAQs About CMA Career
This section addresses the most frequently asked questions learners and professionals ask when exploring a CMA Career. It brings clarity to job roles, salary expectations, exam difficulty, and long-term growth possibilities so you can understand how the CMA pathway supports strong, future-focused career decisions.
What jobs can I get after CMA?
A CMA Career opens doors across finance, accounting, strategy, and operations. After completing the US CMA course, you can work in roles that shape planning, reporting, forecasting, performance measurement, process controls, and cost optimisation. These responsibilities sit at the heart of high-impact positions such as Financial Analyst, Management Accountant, Cost Strategist, Business Planner, Budget Specialist, Plant Controller, and FP&A Analyst. For structured guidance for these roles, Imarticus Learning provides clarity and training aligned to industry expectations.
Is CMA a good career choice?
For anyone who wants a finance profession built on analysis, structured thinking, and company-wide visibility, a CMA Career is a strong choice. It suits people who enjoy reading business scenarios, interpreting numbers, and joining the dots between commercial actions and financial consequences. The role of a CMA blends financial control with decision impact, which means your work reaches managers, business heads, and even board-level teams. There is also strong global mobility because the CMA credential is recognised across 170+ countries.
Can CMA earn 1 lakh per month?
Reaching earnings of 1 lakh per month is a realistic milestone within a mature CMA Career, especially for those who build experience in FP&A, costing, controlling, and business partnering roles. Salaries vary by industry, city, and job complexity, yet the earning graph tends to rise steadily because CMAs manage decisions that influence budgets and profitability. As experience grows, performance responsibilities expand, and salary growth follows.
What does a CMA do?
A CMA Career revolves around turning business numbers into direction, clarity, and action. CMAs analyse cost structures, build forecasts, evaluate risks, assess investments, and prepare management reports that shape decisions. In many organisations, CMAs act like the bridge between finance teams and operational managers because they translate financial language into practical recommendations. The mix of skills built through the US CMA course helps professionals move into jobs that sit close to strategy and business development.
How hard is the CMA exam?
The CMA exam challenges candidates on applied thinking, which means the questions test reasoning and interpretation. Many students describe the difficulty as balanced and fair once they build a method of studying concepts along with numerical practice. The test expects you to connect theories with practical situations, similar to workplace finance decisions. The best way to reduce the challenge is to follow structured learning support at Imarticus Learning, where the content is broken into digestible topics with guided problem-solving.
How many months to pass the CMA?
A focused learner can complete the entire journey in about 12-18 months, depending on work schedules, study patterns, and exam windows. Many candidates choose to prepare for each section over four to six months. This duration balances concept learning with revision cycles and mock tests, which help align with real exam patterns. Imarticus Learning supports students with planned study calendars so the timeline stays predictable.
Do Big 4 hire CMA India?
Yes, the Big Four firms recruit CMA candidates and working professionals for finance transformation, risk advisory, costing, performance consulting, and shared service operations. These teams rely heavily on structured financial evaluation and reporting, which fits the CMA skillset. A CMA Career inside the Big Four often begins with analytical roles and later progresses into specialist or leadership tracks in advisory or controllership support.
Can I pass the CMA on the first attempt?
Many candidates pass the exam on their first attempt when they use a structured study plan that blends concepts, numerical practice, and mock testing. The CMA exam rewards understanding rather than memorisation, so understanding linkages between topics is important. Imarticus Learning helps candidates move through topics logically and revise efficiently. Success in the first attempt becomes realistic when consistency is maintained across weeks of study.
Is CMA a qualified accountant?
Yes, a CMA is a qualified accounting professional with a specialised focus on management accounting, planning, analysis, and decision support. A CMA career covers cost analysis, planning systems, performance measurement, budgeting, reporting, and internal controls. The qualification sits at the intersection of accounting and strategy, which gives employers confidence in a CMA’s ability to support and improve organisational decisions.
The Future You Can Build with a CMA Career
A CMA career allows individuals across professional life stages to find a steady and upward-moving path in finance. Students discover a structured entry into analysis and planning. Working professionals use it to shift into roles that offer visibility and responsibility. Entrepreneurs rely on it to read their own financial signals with sharper judgment. Companies value it because CMAs understand how business choices influence money and performance. Across roles such as costing, forecasting, planning, risk evaluation, investment analysis, and reporting, the CMA identity supports long-term relevance.
As industries adopt analytics, automation, and global workflows, the ability to interpret data and shape financial direction grows more important. This is where the CMA benefits become visible for someone building a sustainable, future-ready profession. Whether the goal is a local leadership role, a global finance position, or a diversified career after CMA, the qualification strengthens clarity, confidence, and decision-making.
Anyone who wants structured guidance for this journey can explore CMA course prep with Imarticus Learning, where the curriculum, support, and methodology are aligned with industry expectations. A CMA is more than a credential. It is a way of understanding the financial heartbeat of a business and shaping decisions that determine its future.