With the current hyper-competitive digital age, selecting a Chief Technology Officer Program is no longer part of the choice of technology leadership professionals but something that needs to be undertaken to professional develop. With companies transforming at historic highs and embracing newer technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing, there has never been a higher demand for innovative leaders to lead businesses through this transition. A CTO is not longer the head of IT but the innovation architect, the creator of digital transformation, and a strategic-level executive partner. This blog discusses in wonderfully great detail what needs to be covered under a Chief Technology Officer Program, the most significant CTO program benefits, the criteria for eligibility, and how a program like that can revolutionize your career. Whether you’re an experienced technology manager, executive of the future, or a business owner in need of becoming a better technologist leader, this article will provide you with everything you’ll need to decide intelligently.
Why Consider a Chief Technology Officer Program?
The modern CTO function is much more than IT ops management. Chief Technology Officer Program provides authorization to leaders to lead in cutting-edge technology, create sense of sophisticated environments, and align technology spend with strategic long-term business objectives. Leaders who finish such programs are equipped with templates and tools they are required to use to drive innovation, improve operating excellence, and enhance competitive edge to the firm. For those wanting to become digital transformation leaders, a CTO course is the key to unleashing higher-level strategic and leadership skills. It also provides access to the networking, mentoring, and exposure to new industry developments which are all essential ingredients of any technology leader wanting to future-proof their own career.
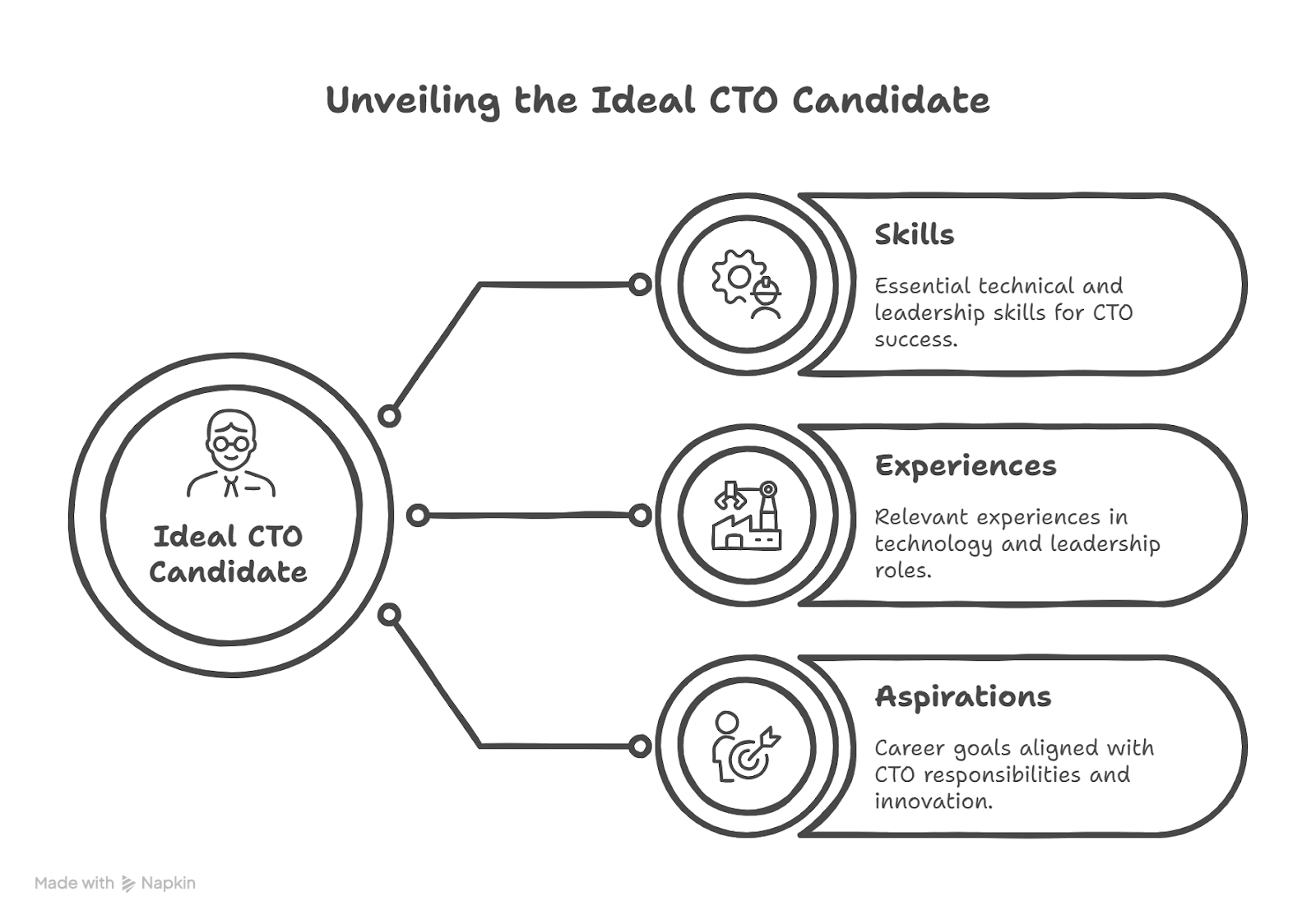
Who Can Join a CTO Course?
1. Senior Technology Managers
They are already mature team management, project budgeting, and technical strategy delivery experts. But too many of them are running into a glass ceiling as they try to break into the C-suite. A next-generation tech leader CTO program gives such managers a chance to apply their organizational dynamics, financial management, and long-range strategic planning acumen. It also makes them fit to work for a high-executing executive group, such as the CFO and the CEO, and makes them well-equipped enough to manage the multi-faceted requirements of a CTO role.
2. Aspiring CTOs
Not a CTO yet, but want to be? The majority of CTO certification candidates fall into this category, according to chief software architects, principal engineers, or IT directors who want to transition careers. A Chief Technology Officer Program equips such professionals with leadership, innovation, and business strategy skills to transition to executive positions. It equips them with the language, frameworks, and confidence to play in the boardroom.
3. Entrepreneurs and Startup Founders
It is not a choice for startup founders, and especially tech startup founders, to master how to balance technology strategy. While they might end up with a full-time CTO, founders can learn much by being quite familiar with the CTO role. Most of the potential candidates to be part of the CTO program as founders are startup founders who have highly dependent products or services with a disruptive attitude. The programs teach IT governance, security, scalability, and digital strategy basics that the founders should be capable of deciding accordingly.
4. Product Managers with Tech Focus
Today’s product managers need to be well-equipped with a solid foundation of next-gen technology, user interface, and system architecture. For those interested in advancing, a CTO development program is in order. With greater insight into digital transformation, innovation management, and technical strategy, product managers are able to excel at the mediator’s role between business stakeholders and development teams and adopt early the future leadership of tech careers.
CTO Program Eligibility: What Are the Requirements?
Different institutions might have varying CTO program eligibility, but generally, the requirements are:
- Bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering, or a related field to their operating space
- 5-10 years of experience as IT or technical management professionals
- History of delivering success in leading team or cross-functional projects
- Willingness to apply technological solutions that scale to business needs
These certifications are not only for technology coders but for technology-savvy leaders who appreciate the application of technology as a business accelerator. CTO certificate aspirants also must be visionary, innovation enthusiasts, and flexible.
CTO Training Requirements: What Will You Learn?
Enrolling in a Chief Technology Officer Program like IIM Nagpur’s Global Senior Executive Leadership Programme means a challenging but enriching syllabus:
- Digital Transformation Masterclass: Find out how to drive and oversee digital projects throughout the whole of the business, from operations right through to customer facing.
- Emerging Technologies: Get familiar with trends like AI, machine learning, blockchain, quantum computing, and IoT, the technology itself and also its business applicability.
- IT Governance and Cybersecurity: Discover how to craft secure systems which protect confidential information, adhere to regulation, and reduce risk within an increasingly connected world.
- Strategic Leadership: Discover how to align technology projects with strategic business goals so that all technology investments create measurable value.
- Innovation Culture: Create an experiment and innovation culture to enable teams to develop breakthrough solutions.
CTO Program Benefits: Why Enroll?
Benefits of CTO course are numerous and can transform your career graph:
- Career Progression: Open up new opportunities for top-level positions such as CTO, Chief Innovation Officer, or Head of Digital Transformation.
- Global Accreditation: International school certification by well-known institutions such as IIM Nagpur commands a huge premium in the international job market and enhances your professional passport.
- Unparalleled Networking: Be part of an international network of peers, mentors, and business leaders in the technology industry, collaborating to shape new ideas and co-op projects.
- Hands-On Learning: Practice-based access to live case studies, simulation, and masterclasses that integrate theory and practice.
- Mentoring: Experience chamber consulting and one-on-one mentoring by veteran CTOs and technology leaders.
Best Candidates for CTO Program: Are You One?
Are you among the most promising prospects for CTO program? You may be if
- You are constantly on the lookout for new tech and looking for a way to experiment with them against business challenges.
- You are working in spaces where innovation, velocity, and agility are top priorities.
- You desire to get out of the technical specificity of your role and deal more with business strategy.
- You are attracted to building cross-functional leadership capabilities and interdepartmental teamwork.
- You envision leaving a lasting legacy with your organization through creating significant, enduring change.
CTO Course for Tech Leaders: Stand Out from the Crowd
With this job market, it’s flooded, and a CTO program can provide that competitive advantage that you require as a technology leader. You’re not only getting the technological knowledge of technology management, but also organizational leadership, negotiation, and communication skills are enhanced. Prospective employers are looking for individuals with the technical and business savvy, and this program instills in them that you have it.
Who Can Join CTO Course from IIM Nagpur?
IIM Nagpur Chief Technology Officer Programme is for:
- Senior IT and technology managers aspiring to move to the next level
- Lead software architects aspiring to become strategic leaders
- Head of innovation or digital transformation position
- Founder and start-up entrepreneurs aspirants to become tech leaders
- High tech domain specialist product managers aspirants to develop their executive skill set
With hands-on, case-study based CTO training and masterclass access, the program offers an in-depth, real-world learning experience.
CTO Program Financial Commitment
While a fee for Chief Technology Officer Program is expensive, the ROI down the road is worth it. Program alumni can negotiate the best executive positions with high salary packages, have improved job security, and generate new business prospects all over the world. It’s not an educational option but a development investment in one’s future.
FAQs
1. Who is eligible for a Chief Technology Officer Program?
Any graduate of a bachelor’s degree with 5-10 years of experience as a technical or leadership professional can apply, i.e., senior managers, engineers, architects, and entrepreneurs.
2. What are the biggest benefits of a CTO program for tech leaders?
You will gain leadership, learn new technologies, sharpen your strategic mind, and expand your professional network, setting yourself up for an executive career.
3. How long is IIM Nagpur CTO Program?
The certification alone takes six months to finish in an integration of web-based sessions, masterclasses, and heavy interludes at the campus.
4. Why should consideration be given for the CTO certification?
CTO certification strengthens your professional positioning in the business, gives you access to better opportunities, and gives you access to a world-wide peer network.
5. Can product managers enroll in a CTO program?
Yes, product managers with a technology bias are perfect for CTO courses because CTO courses train strategic and leadership capabilities to be an executive role.
6. What do I learn from CTO training?
Digital transformation, innovation management, IT governance, cybersecurity, business alignment, and strategic leadership.
7. Why do I study IIM Nagpur’s CTO program?
The program provides highly-desirable certification, real-time business case studies, masterclasses with seasoned CTOs, and one-on-one coaching access by chamber consulting-based.
Conclusion
Lastly, taking the effort to acquire a Chief Technology Officer Program is probably the wisest thing you can do to secure your future in the industry in this technology-always-changing era. Whether or not you aspire to be a future CTO, seasoned manager, product manager, or an entrepreneur, the programme prepares you with the competencies at a senior level, strategic thinking, and international networking to lead on the top-tier leadership. Under a programme like the Global Senior Executive Leadership Programme at IIM Nagpur, you put yourself on the route to being among the next generation of technology leaders shaping the future digital.
Don’t wait for the door to open — take charge of your career, expand your definition of leadership, and drive your company forward with confidence. Your journey to visionary Chief Technology Officer begins with one, bold step: enrolling in the right program. Ready to unleash your leadership potential? The future is yours to seize.