Risk does not sleep. And neither does the demand for people who understand it. Every time a bank approves a thousand crore loan, someone has already stress-tested what happens if 30% of it goes bad. Every time a trading desk takes a position on interest rates, someone has already modelled the downside. Every time a fintech disburses a micro-loan to a first-time borrower in Tier 3 India, an algorithm built by a risk professional is doing the underwriting in the background. That person, in every scenario, holds one of the most quietly powerful jobs in finance. FRM jobs might not be glamorous in the way investment banking is.
That person, in every scenario, holds one of the most quietly powerful jobs in finance. FRM jobs might not be glamorous in the way investment banking is. There are no flashy deal announcements or league table rankings. But here is what risk management does have: it is indispensable. Companies do not cut risk teams when markets get volatile. They expand them. That is what makes FRM certification one of the most durable bets in the banking and financial services industry today.
Think about what happened globally between 2020 and 2024:
→ A pandemic
→ A war in Europe
→ Three central bank rate cycles moving simultaneously
→ And a wave of fintech collapses.
In each of those episodes, the institutions that survived best were the ones with the strongest risk infrastructure. The ones that did not had one thing in common: they underinvested in risk talent.
So, what you will find in this guide is a full picture of where the opportunities actually are, what the work looks like at each stage of your career, what cities and countries are hiring, what the salary progression looks like from year one to year fifteen, and how to position yourself to land the best of these roles.
Did You Know?
According to GARP, over 57,000 professionals worldwide currently hold the FRM designation across 190+ countries. In India, the number of active FRM candidates has grown by over 25% in the last three years alone.
What Is FRM and Why Are Employers Paying a Premium for It?
The FRM, or Financial Risk Manager, is a globally recognised certification issued by the Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP). It is the only credential in the world built exclusively around risk management, not accounting, not investment analysis, not general finance. Just risk.
To understand what is FRM in practical terms, think of it this way. Every large financial institution manages enormous amounts of money that do not belong to it. Banks hold depositors’ savings. Asset management companies hold investors’ capital. Insurance companies hold policyholder premiums. The job of a risk professional is to make sure none of that money disappears due to bad loans, volatile markets, rogue processes, or regulatory failures.
The FRM certification trains you to do exactly that, at the highest technical standard.
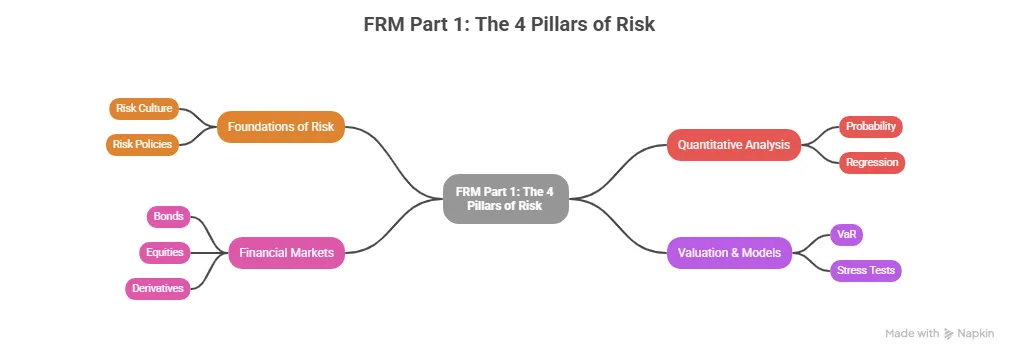
The FRM Exam: A Quick Breakdown
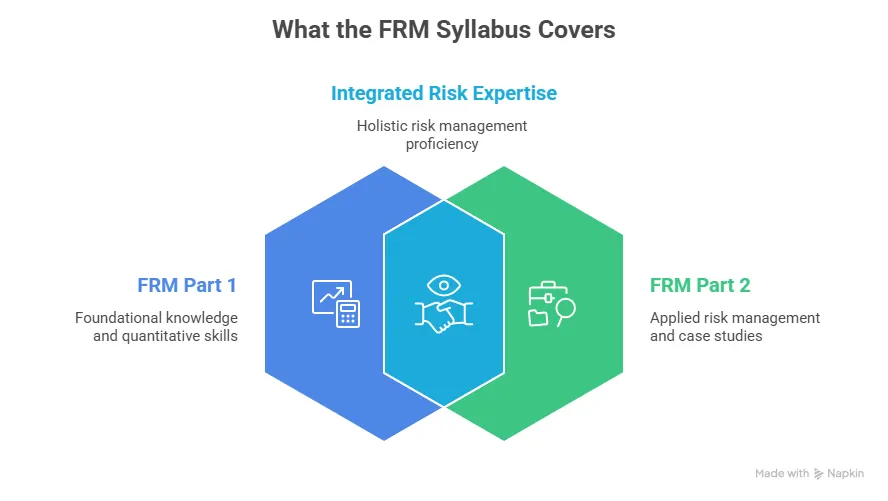
The certification is split into two parts. Both are rigorous, quantitative, and globally standardised.
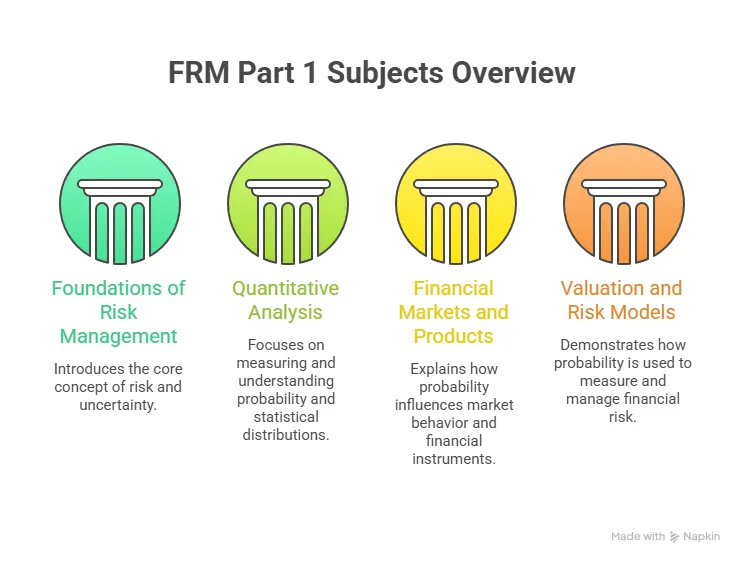
| Aspects | FRM Part 1 | FRM Part 2 |
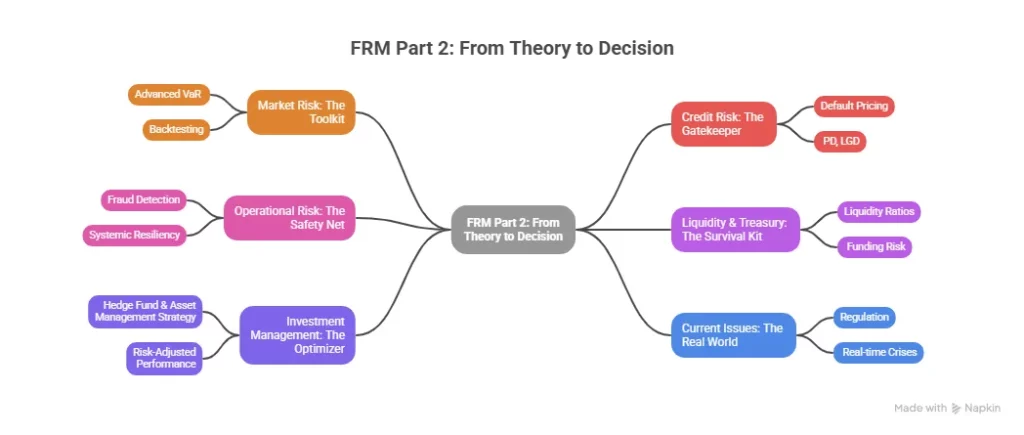
| Focus | Foundations of risk: quantitative analysis, financial markets, valuation, risk models | Applied risk management: market risk, credit risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, risk in investment management |
| Format | 100 multiple-choice questions | 80 multiple-choice questions |
| Duration | 4 hours | 4 hours |
| When to Appear | May or November | May or November (after clearing Part 1) |
| Pass Rate (Global) | ~40 to 45% | ~55 to 60% |
Source: GARP FRM Exam Overview
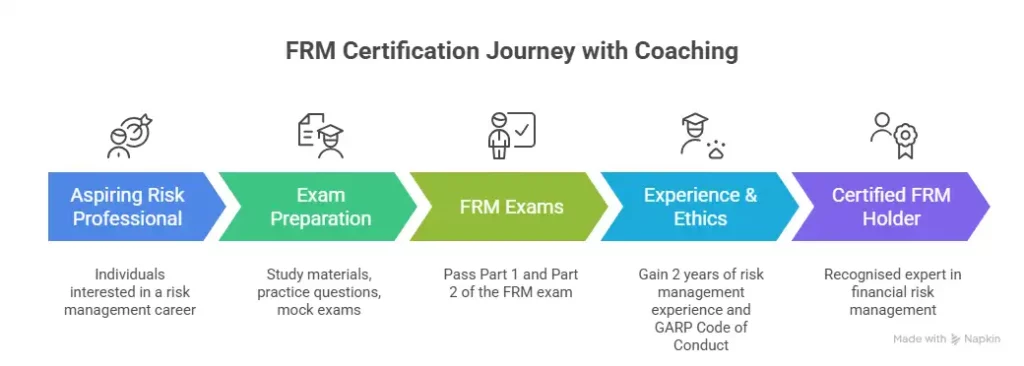
To earn the full FRM designation, you need to clear both FRM Part 1 and Part 2. You should then complete two years of relevant work experience in financial risk management, completing the full FRM course duration.
What the FRM Actually Tests
The FRM syllabus is built around four core risk domains that mirror what risk professionals actually do on the job:
- Quantitative Analysis: Probability, statistics, regression, and time series analysis; the mathematical backbone of every risk model.
- Market Risk: How to measure and manage the risk of losses from movements in interest rates, currencies, equities, and commodities.
- Credit Risk: How to assess the probability that a borrower, counterparty, or issuer will default and what the financial impact will be.
- Operational Risk: How to identify and mitigate risks from internal processes, systems, people, and external events.
Why Employers Pay a Premium for It
The FRM course structure is not a theoretical qualification. GARP designed it in direct consultation with risk professionals and financial institutions, which means every concept in the curriculum maps to something that happens in a real risk team. That alignment between exam content and job requirements is why FRM jobs consistently command salaries 20 to 30% higher than equivalent roles held by non-certified finance professionals.
The FRM is one of the most respected credentials in global finance. Understanding the course structure, exam breakdown, and study requirements upfront makes the entire journey significantly more manageable.
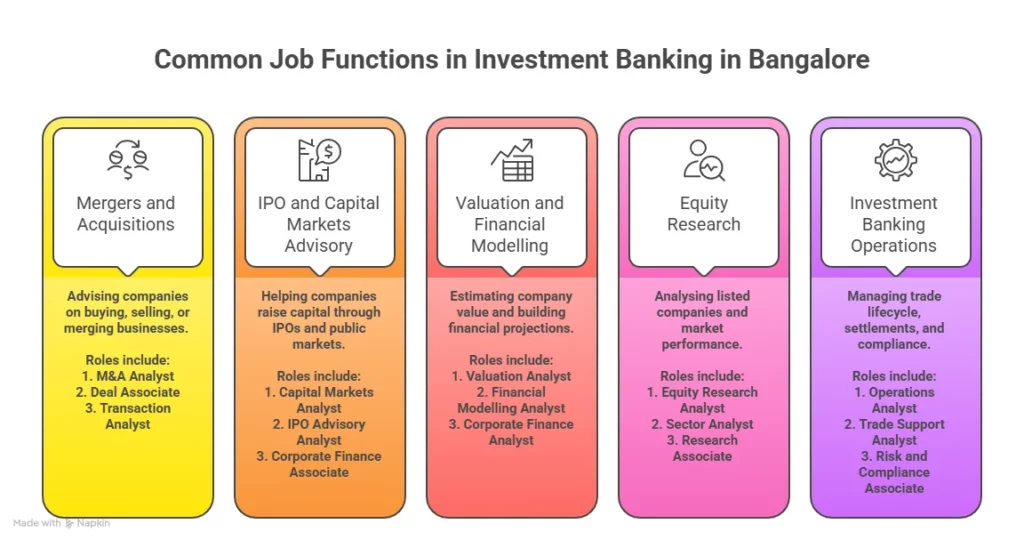
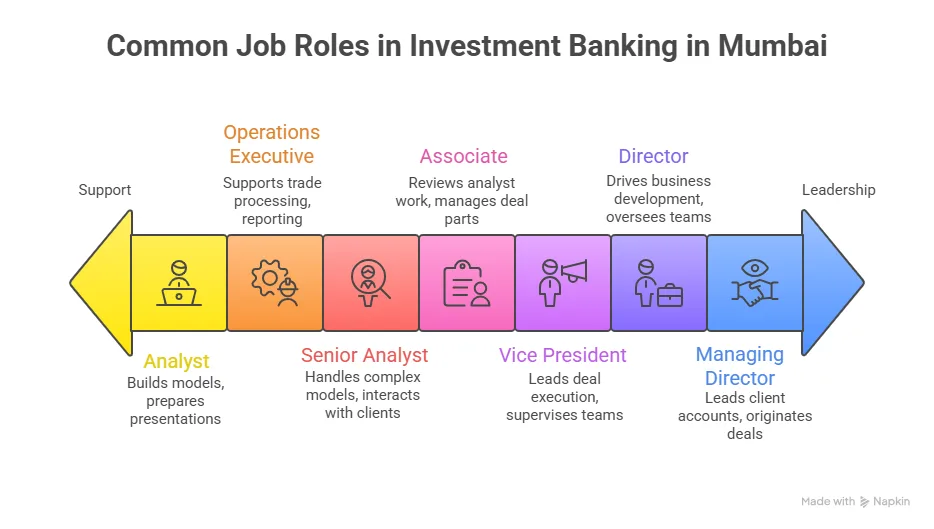
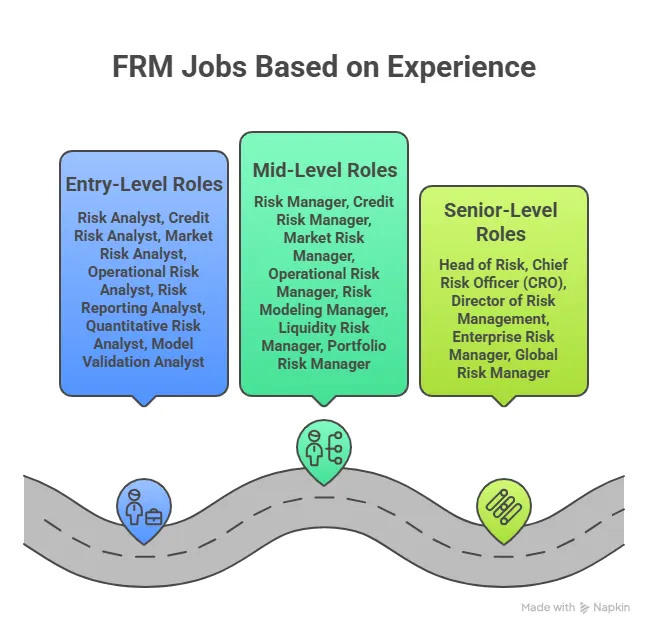
FRM Job Roles and Profiles
A common misconception is that FRM professionals sit in the back office running numbers all day. The reality is more dynamic than that. Risk managers today sit in boardrooms, present to C-suites, and directly influence strategic decisions worth crores.
Here is a clear breakdown of the core job roles you will encounter after you’ve met the FRM course eligibility criteria and completed the certification:
| FRM Job Profile | What You Actually Do | Who Hires You |
| Risk Analyst | Identify, measure, and report risk exposures across portfolios | Banks, NBFCs, Consulting firms |
| Credit Risk Analyst | Assess borrower creditworthiness, build scoring models | HDFC, ICICI, Deutsche Bank |
| Market Risk Analyst | Monitor interest rate, FX, and equity risk on trading desks | Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, JP Morgan |
| Operational Risk Manager | Find system failures, process gaps, and internal fraud vectors | Big 4, Global banks, Insurance firms |
| Quantitative Risk Analyst | Build statistical models for risk forecasting and stress testing | Hedge funds, Investment banks |
| Regulatory Risk and Compliance Officer | Ensure Basel III, RBI, and SEBI compliance frameworks are met | Domestic banks, MNCs, Consulting |
| Chief Risk Officer (CRO) | Lead the entire risk strategy of the firm, report to the board | Large banks, NBFC groups, Fintechs |
Once you know how to become a successful risk manager, each of these FRM job profiles has its own trajectory. A Credit Risk Analyst at a mid-sized bank today can become a Head of Credit in eight to ten years. A Quantitative Risk Analyst who learns Python and machine learning can transition into AI risk, one of the fastest-growing sub-fields in finance today.
Also Read: How Much Should You Budget for the FRM Certification in India?
FRM Jobs for Freshers
Starting a career in risk management often begins with analytical and support roles that build a strong foundation in financial risk. This section explains the types of entry-level opportunities available to fresh graduates and what their early responsibilities typically involve.
After Clearing FRM Part 1:
Many large banks and consulting firms actively consider candidates who have cleared FRM Part 1 for entry-level risk roles. You do not need a full certification to start. Jobs after FRM Part 1 typically include Risk Analyst Associate, Junior Credit Risk Analyst, and Risk Operations roles. These positions offer real exposure to live risk frameworks while you continue preparing for Part 2.
After Full Certification:
Completing both parts and fulfilling GARP’s two-year work experience requirement unlocks the full FRM designation. At this stage, FRM entry-level jobs shift in quality and compensation. You are no longer a candidate with a half-credential. You are a certified specialist.
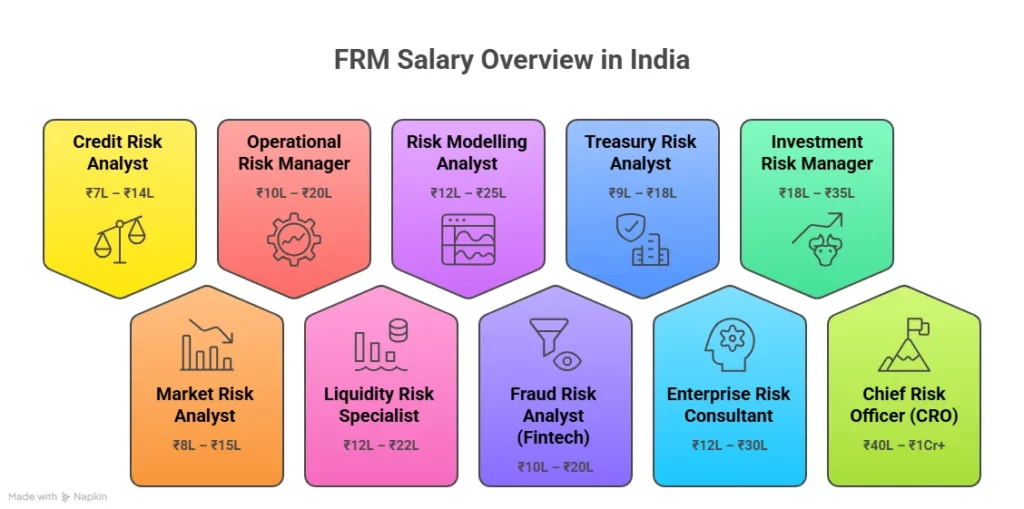
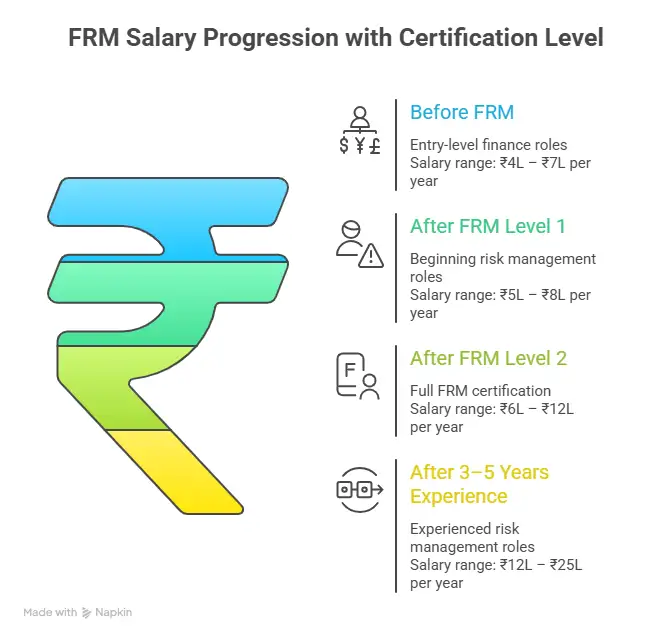
Here is a realistic salary snapshot for FRM fresher jobs in India:
| Stage | Typical Roles | Salary Range |
| After FRM Part 1 | Risk Analyst Associate, Junior Credit Analyst | ₹4 to ₹7 LPA |
| After Full FRM Certification | Credit Risk Analyst, Market Risk Analyst | ₹6 to ₹10 LPA |
| 2 to 4 Years Post-Certification | Senior Risk Analyst, Risk Manager | ₹12 to ₹20 LPA |
| 5 to 8 Years | Head of Risk, VP Risk | ₹20 to ₹35 LPA |
| 10+ Years | Chief Risk Officer (CRO) | ₹40 LPA to ₹1 Cr+ |
Sources: AmbitionBox, Glassdoor India, Quintedge FRM Salary Research
How to Land Your First FRM Job:
The GARP Career Centre is genuinely underused by Indian candidates. It lists active job openings from firms that specifically want GARP-certified professionals. Pair that with Naukri, LinkedIn, and the following practical steps:
- Build a risk-specific resume. Generic finance resumes will not work here. Lead with your FRM status, then your quantitative skills.
- Learn at least one data tool. Python, SQL, and Advanced Excel are the three most cited technical requirements in FRM job openings on LinkedIn India right now.
- Target your city’s dominant risk sector. Mumbai is a banking and treasury hub. Bangalore is fintech and quantitative risk. Gurgaon is consulting and credit. Chennai and Pune lean toward process and operational risk. Match your application strategy to where the jobs actually are.
Also Read: What Risk Management Skills Do You Learn in the FRM Program?
FRM Jobs in India
India does not have one job market for risk professionals. It has several, each shaped by the kinds of financial institutions dominant in that city. Here is how the landscape breaks down:
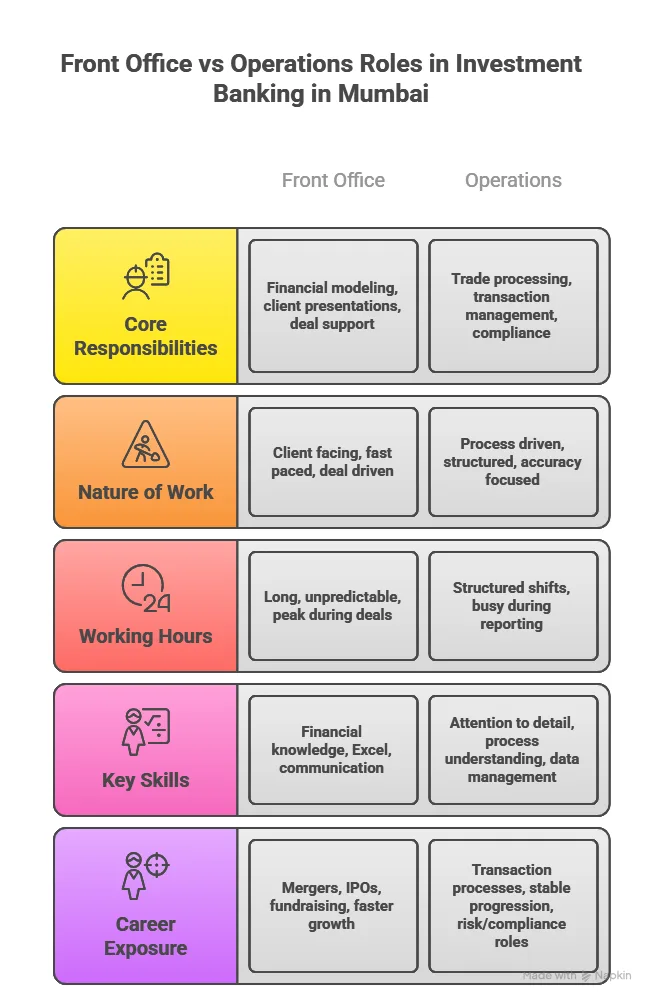
FRM Jobs in Mumbai
Mumbai is the headquarters of Indian finance. If you want the highest volume of FRM job openings and the widest range of risk roles, this is the city.
- FRM jobs in Mumbai cover the full spectrum: credit risk, market risk, treasury risk, and regulatory compliance.
- Entry-level FRM professionals can earn up to ₹10 LPA, especially at top banks and consulting firms.
- FRM fresher jobs in Mumbai are most commonly available at JP Morgan, Goldman Sachs, HSBC, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, Kotak Mahindra, and the Big 4 consulting firms.
FRM Jobs in Bangalore
Bangalore is the go-to city if your interest lies in quantitative risk, model validation, or fintech risk. The tech-first character of the city is shaping an entirely new category of risk roles.
- FRM jobs in Bangalore are concentrated in cybersecurity risk, digital risk, and quantitative risk analytics.
- Senior FRM roles in fintech here are projected to reach ₹25 to ₹40 LPA as the sector scales.
- Active hirers include Razorpay, CRED, Zerodha, and Societe Generale’s GBS unit for risk analytics and model validation.
FRM Jobs in Delhi and Gurgaon
Delhi and Gurgaon together anchor the consulting and corporate risk ecosystem of North India. If advisory work and enterprise risk interest you, this is your market.
- FRM jobs in Delhi are led by regulatory compliance, enterprise risk advisory, and investment management roles.
- FRM jobs in Gurgaon are dominated by the Big 4 and McKinsey, all of which run large risk advisory practices from here.
- Mid-level FRM professionals with three to five years of experience can earn upwards of ₹20 LPA.
FRM Jobs in Pune
Pune is a steadily growing market for risk professionals, particularly for those targeting global banks and NBFC operations.
- FRM jobs in Pune are strongest in operational risk, process risk, and credit risk.
- Key hirers include BNP Paribas and Deutsche Bank, both of which run significant back-office and risk operations.
- Starting salaries are slightly lower than in Mumbai, but scale competitively at the mid-level.
FRM Jobs in Chennai
Chennai’s financial sector is shaped by insurance, public sector banking, and a growing GCC presence. It is a strong market for regulatory and modelling roles.
- FRM jobs in Chennai are led by insurance companies, public sector banks, and IT-driven financial services firms.
- Key hirers include LIC, Indian Overseas Bank, and Standard Chartered’s GCC operations.
- Roles are concentrated in risk modelling, regulatory compliance, and credit portfolio management.
FRM Jobs in Kolkata
Kolkata is a focused market, best suited for professionals targeting public sector banking and NBFC credit risk roles.
- FRM jobs in Kolkata are concentrated in credit risk and regulatory compliance within public sector banks and NBFCs.
- Key hirers include UCO Bank, Indian Bank (formerly Allahabad Bank), and several NBFC regional offices.
- Roles here centre on credit portfolio oversight and regulatory risk reporting.
Did You Know?
On LinkedIn India alone, Goldman Sachs currently lists 298+ active risk management jobs in India, including roles in Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Mumbai!
FRM Jobs Abroad: Where the Global Market Stands in 2026
The FRM designation is recognised in over 190 countries. That is not marketing language. It reflects the fact that GARP built the curriculum around the risk frameworks used by global regulators, the Basel Committee, and international financial institutions. This means an FRM-certified professional from Mumbai or Hyderabad carries a credential that is directly legible to employers in London, Dubai, New York, and Sydney.
Here is how the international FRM job market breaks down by geography:
| Location | Top Employers | Key Risk Roles | Salary Range |
| Dubai | Commercial Bank of Dubai, HSBC, Visa, MasterCard, Deloitte, Al-Futtaim | Credit Risk, Treasury Risk, Regulatory Compliance | AED 180,000 to AED 300,000 per year (approx. ₹40 to ₹67 LPA) |
| UK | Barclays, HSBC, Standard Chartered, Big 4, fintech lenders | Market Risk, Credit Risk, Risk Advisory, Insurance Risk | £80,000 avg. per year + £10,000 avg. bonus; CRO roles avg. £145,000 |
| USA | Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, BlackRock, Citibank, and Federal Reserve-supervised banks | Quantitative Risk, Credit Risk, Regulatory Risk, Hedge Fund Risk | $55,000 to $211,000 per year, depending on seniority |
| Australia | Commonwealth Bank, ANZ, NAB, Westpac | Regulatory Risk, Credit Risk, Operational Risk | AUD 90,000 to AUD 180,000+ per year (senior roles approx. ₹90 LPA) |
BCom graduates today have more high-value certification pathways than any previous generation. Here is a closer look at how the four most sought-after credentials in finance compare when it comes to real-world earning potential.
CFA and FRM Jobs: What Happens When You Hold Both
CFA FRM jobs sit at a distinct salary tier. This is not about collecting credentials. It is about what the combination signals to a hiring manager: you understand how to price risk (FRM) and how to value investments (CFA). Those two lenses together are exactly what portfolio risk managers, chief investment officers, and senior treasury professionals need.
FRM CFA jobs, where both are required or preferred, carry a premium. The practical benefit of dual certification shows up most at the seven to ten-year mark of a career..
| Credential | Primary Use Case | Key Industries |
| FRM Only | Pure risk management, credit, market, and operational risk | Banking, Consulting, Fintech |
| CFA Only | Investment analysis, portfolio management, equity research | Asset Management, IB |
| CFA + FRM | Portfolio risk, investment risk, enterprise risk leadership | Hedge Funds, Asset Management, MNCs |
Also Read: Where Should You Study FRM in India to Build a Successful Risk Career?
Emerging Roles in FRM Jobs
The scope of risk management careers has expanded significantly in recent years as financial markets, regulations, and technology continue to evolve. This shift has created several new roles focused on advanced analytics, emerging risks, and data-driven risk management within modern financial institutions.
| Emerging Role | Who Is Hiring | Salary Potential |
| ESG Risk Analyst | Moody’s, EY India, State Bank of India (Sustainability Desk), Tata Capital | ₹12 to ₹25 LPA at mid-level; growing sharply |
| AI Risk Manager | HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Razorpay, JP Morgan India | ₹30 to ₹50 LPA at the senior level |
| Cyber Risk Analyst | Razorpay, PayU, CRED, Axis Bank, Standard Chartered | One of the fastest-hiring FRM sub-categories on LinkedIn and Naukri right now |
| Climate Risk Officer | RBI-regulated banks, large NBFCs, and multilateral finance institutions | Niche but exceptional pay; very thin competition for certified talent |
Salary premiums, global mobility, emerging risk roles, regulatory tailwinds, here is a clear-eyed look at every factor that determines whether the FRM is worth your time and money right now.
Top Companies Actively Hiring FRM-Certified Professionals in India
The firm you join at the beginning of your career shapes your professional language, your network, and your trajectory. Here is a categorised view of who is actively hiring FRM professionals in India right now:
Global Investment Banks and Financial Institutions
These firms hire FRM professionals for high-complexity roles in market risk, counterparty credit risk, and regulatory reporting. Salaries are at the top of the market.
- Goldman Sachs (Bengaluru, Mumbai, Hyderabad)
- JP Morgan (Mumbai, Bengaluru)
- Deutsche Bank (Mumbai, Pune)
- Barclays (Pune)
- HSBC (Mumbai)
- Standard Chartered (Chennai, Mumbai)
Indian Private and Public Sector Banks
The domestic banking sector is a significant hirer of FRM-certified talent, especially for credit risk and Basel compliance roles.
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Kotak Mahindra Bank
- Axis Bank
- State Bank of India
Big 4 and Consulting Firms
Consulting is the pathway if you want breadth over depth. You will work across clients and industries, building a risk advisory skill set that is transferable across sectors.
- KPMG India
- Deloitte India
- EY
- PwC
Fintech Companies
FRM certification jobs in fintech are newer but increasingly specialised. These firms move faster, pay competitively, and offer high autonomy.
- Razorpay
- Paytm
- Zerodha
- CRED
- Pine Labs

Also Read: Why FRM Certification is the Best Career Option for Finance Experts?
How Imarticus Learning Prepares You for FRM Jobs
Getting the FRM certification is one thing. Being job-ready for the roles it unlocks is another. The gap between the two is where preparation infrastructure matters most.
Imarticus Learning’s FRM Program training is built in collaboration with KPMG in India, one of the Big 4 firms that actively recruits FRM-certified professionals for risk advisory roles. Key features that make the Imarticus approach distinct for anyone targeting FRM jobs in India:
- GARP-Authorised Content: The programme uses official GARP curriculum materials, so there is no gap between what you study and what the exam and the job market test.
- Placement Support: Access to Imarticus’ hiring network across banking, consulting, and fintech firms, with direct referrals for FRM entry-level jobs.
- Career Mentorship: One-on-one guidance for resume building, interview preparation, and role selection. Particularly useful for FRM jobs for freshers who are mapping their first role.
- Industry-Live Projects: Risk modelling exercises built on real financial data, giving you portfolio work that you can show hiring managers.
For anyone targeting FRM jobs in India and salary packages that scale quickly, starting with the right preparation infrastructure cuts the learning curve significantly.
FAQs About FRM Jobs
As interest in risk management careers grows, many professionals search for clarity on roles, opportunities, and long-term growth. Here are accurate answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about FRM jobs.
What Jobs Can You Get with FRM?
FRM jobs span credit risk, market risk, operational risk, treasury, compliance, and quantitative analysis. Entry roles include Risk Analyst and Credit Risk Associate. Senior tracks lead to Head of Risk and Chief Risk Officer. Global banks, Big 4 firms, NBFCs, insurance companies, and fintechs all actively hire FRM-certified professionals.
Does Big 4 Hire FRM?
Yes. KPMG, Deloitte, EY, and PwC all maintain dedicated risk advisory practices in India, recruiting FRM professionals for credit risk, compliance, and model validation roles. Salaries range from ₹10 LPA to ₹35 LPA+. Imarticus Learning’s collaboration with KPMG in India gives students direct exposure to Big 4 risk hiring.
Is FRM Worth It in India?
Absolutely. FRM-certified professionals earn 20 to 40% more than non-certified peers. RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI regulations are creating structural demand for risk talent across India. The designation is globally recognised, opening doors in Dubai, the UK, and the USA. For a risk management career, the FRM delivers returns that compound over time.
What Is the Salary After FRM?
FRM salaries in India range from ₹6 LPA for freshers to ₹1 crore+ for Chief Risk Officers. Mid-level professionals earn ₹12 to ₹25 LPA. Globally, US roles offer $55,000 to $211,000, and UK roles average £80,000 annually. Experience, city, and sector determine where you land on that spectrum.
What Are Some Opportunities for an FRM Fresher in India?
FRM fresher jobs are concentrated in private banks, MNC banks, Big 4 consulting, NBFCs, and fintech. Entry roles include Risk Analyst, Credit Risk Associate, and Market Risk Analyst. Mumbai, Bangalore, and Gurgaon have the highest demand. Imarticus Learning’s placement support connects freshers directly with risk hiring managers across these sectors.
What Is the Average Salary Hike After Finishing FRM Part 1 and FRM Part 2?
FRM Part 1 typically delivers a 15 to 20% salary improvement. Full certification pushes mid-level salaries to ₹10 to ₹18 LPA. Freshers with the complete designation start 20 to 30% higher than non-certified peers. Over five years, the compound salary advantage of holding the FRM is substantial.
What Are the Job Opportunities at Goldman Sachs After Doing FRM?
Goldman Sachs actively recruits FRM-certified professionals across its Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Hyderabad offices. Roles include Market Risk Analyst, Credit Risk Analyst, and Portfolio Risk Analyst. Their India risk division handles global risk monitoring directly, making the work substantive. Goldman also runs structured analyst programmes that specifically recruit from GARP-certified candidate pools.
What Are the Job Opportunities If I Do an MBA and an FRM?
An MBA builds leadership credibility. The FRM adds deep technical risk expertise. Together, they unlock senior roles like Chief Risk Officer, VP Risk Management, and Head of Risk at top banks and consulting firms. Imarticus Learning offers a structured program to complement an MBA and accelerate entry into these positions.
Your Next Step With FRM Jobs
The FRM job market in India in 2025 is not just healthy. It is structurally expanding, driven by regulatory pressure, digital risk, ESG mandates, and the continued internationalisation of Indian financial institutions. The roles are more varied than ever. The salaries are more competitive than they have ever been. And the global mobility the certification provides is a genuine advantage for professionals who want to work in Dubai, the UK, the USA, or Australia at some point in their careers.
The certification alone, however, is only part of the equation. The preparation infrastructure you choose, the city you target, the skills you build alongside the FRM, and the network you develop in the first three years of your career all compound into your long-term earning potential.If you are serious about pursuing FRM jobs in India or internationally, Imarticus Learning’s FRM Course prep, built in collaboration with KPMG in India and powered by Kaplan Schweser content, gives you the preparation depth, placement support, and mentorship to make the most of one of finance’s most durable certifications.