Last updated on November 6th, 2025 at 06:13 pm
Are you aiming to be a future financial leader? If you’re gearing up for the CMA US exam, chances are you’ve come across the term ‘COSO framework.’ One concept you absolutely need to master is the COSO Framework. It might sound a bit technical, but here’s the truth – it’s crucial!
Think of COSO as your secret weapon, helping you understand how successful organisations stay on track, manage risks effectively, and make confident decisions every day.
Knowing the COSO framework well can give you a solid edge not just in the exam, but also in your future career as a management accountant. Once you grasp the core of COSO, you’ll not only boost your exam preparation but also build skills that top finance leaders boast. Are you ready to boost your CMA US exam preparation?
We’re here to break down the COSO Framework, explain why it’s a big deal for your CMA US exam, and show you how mastering it can help boost your career.
So, let’s break it down in a simple way.
What is the COSO Framework?
Before diving deep into COSO, it helps to get a clear picture of what is CMA and what the CMA course really involves, so you can see how internal controls and strategic decision-making fit into your role.
If you’re running a large company – thousands of employees, endless data, and money moving every second. Now the big question is:
How do you keep things in control without stress taking over?
How do you balance risks, daily work, and long-term growth all at the same time?
This is exactly where COSO comes in.
COSO stands for the Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission; it’s a quite long name – but don’t worry, no one actually says the full form in real life. What really matters is what the COSO Framework helps companies do.
COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission) – a private sector initiative, has representatives from five organisations:
- Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
- Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA)
- American Accounting Association (AAA)
- Financial Executives International (FEI)
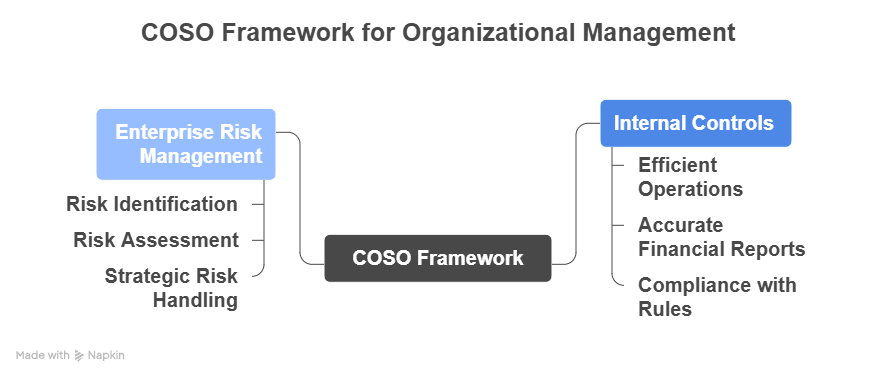
The COSO Framework gives organisations a structured, reliable way to manage two major things:
Internal Controls and Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
“Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” – Warren Buffett
Think of COSO as the key for:
- Avoiding chaos.
- Making smart decisions.
- Keeping everything running smoothly.
- Protecting the business from uncertainties.
And here’s the part that matters for you:
If you’re preparing for the CMA USA certification, COSO is something you’ll see repeatedly. Not just in the exam – but in the real corporate world too.
Because good finance professionals don’t just deal with numbers – they understand how to control risk, structure processes, and guide strategic decisions. That’s the mindset COSO helps you build.
Objectives of COSO Framework
The COSO Framework was designed to help organisations achieve three core objectives. Understanding these is essential for your CMA exam preparation:
Operations
COSO ensures optimum, effective and efficient utilisation of a company’s resources. Think of it like this: you don’t want your employees doing mundane tasks or wasting time on avoidable mistakes. Proper internal controls reduce operational risks and thus result in improved productivity.
Reporting
Accurate and reliable financial reporting is critical. Whether it’s monthly financial statements or investor reports, COSO helps to ensure the data you rely on is transparent, accurate and trustworthy. This is crucial for CMAs, who often interpret financial results for decision-making.
Compliance
From tax laws to corporate policies, organisations need to comply with regulations and follow rules. COSO establishes a system that prevents violations and reduces the risk of penalties. In short, it keeps the company out of legal trouble by maintaining ethical standards.
Understanding these objectives makes it easier to see why COSO matters beyond the exam – it’s about creating real value in a business.
Before we go further, it’s useful to know how COSO connects to other topics in the CMA program. You can review the CMA course subjects list to understand how internal controls support broader exam concepts.
“Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning.” – Benjamin Franklin
Key Pillars of COSO Framework
Think of COSO like a strong, well-built house, and it stands firmly on five key pillars:
- Control Environment
This is the “tone from the top.” It’s about the company’s ethics and culture. When leadership sets the right example, it naturally guides everyone else.
Example – If the CEO and finance leaders emphasise honesty and ethics, employees are more likely to follow suit, reducing the risk of fraud.
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.” – Warren Buffett - Risk Assessment
This is where the organisation asks: “What could go wrong?”
Whether it’s financial mistakes, operational delays, or compliance issues, risks are identified before they become real problems.
Example – Before launching a new product, the company identifies supply chain risks and plans how to mitigate them.
“It’s not the risk that scares you; it’s how you manage the risk.” – Robert Kiyosaki
- Control Activities
These are the checks and safeguards put in place – approvals, audits, reviews, segregation of duties – all designed to prevent errors and stop fraud before it starts.
Example – A finance team requires two approvals for transactions above a certain limit to avoid mismanagement of funds.
“An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” – Benjamin Franklin
- Information & Communication
This ensures that the right information reaches the right people at the right time. Clear communication keeps everyone aligned and avoids confusion.
Example – Regular financial dashboards shared with management help leaders make informed decisions quickly.
“The art of communication is the language of leadership.” – James Humes - Monitoring
This is the ongoing review – making sure everything is still working as intended. Internal audits, evaluations, and continuous improvements happen here.
Example – A quarterly audit identifies that expense approvals are not being followed, and corrective action is taken immediately.
“What gets measured gets managed.” – Peter Drucker
Why The COSO Framework Matters for CMA US Exam Success
The CMA exam tests your ability beyond accounting and costing. It trains you to think strategically and ethically, not just to crunch numbers.
- The COSO Framework appears heavily in the Strategic Financial Management and Performance Management sections.
- As a CMA professional, you’ll use COSO principles daily: from managing risks to ensuring reliable financial data and ethical governance.
- Understanding COSO boosts your value in any organisation by helping you guide decision-making and safeguard assets.
“Leadership is not about being in charge. It is about taking care of those in your charge.” – Simon Sinek
Why COSO Keeps Appearing in CMA Exam Questions
The CMA exam is not just about crunching numbers – it’s about thinking like a strategic, ethical finance leader. Here’s why COSO is a heavyweight in the CMA syllabus:
- Risk Management is at the heart of your role as a CMA. COSO’s ERM framework gives you a clear structure to identify and respond to risks.
- Internal Controls ensure the data companies use to decide is reliable. COSO’s framework shows you how those controls work.
- Ethical Governance is a pillar of COSO, reflecting the high standards CMAs are expected to uphold.
- Real-World Relevance: COSO is used globally. Understanding it not only helps you pass but also thrives in your career.
Choosing the right preparation approach matters. While COSO is a core topic, how well you learn it depends on the study program you pick – and if you’re still exploring your study options, make sure you choose the best CMA review course that gives you strong conceptual clarity, not just memorisation.
Tips to Master The COSO Framework for the CMA US Exam
If you’re wondering whether you’re even eligible for CMA, you’re not alone – many aspirants ask this first before diving into COSO and exam preparation – and if you’re still figuring out whether you qualify, reviewing the complete CMA eligibility criteria will help you plan your timeline better.
Start applying COSO principles today: review your organisation’s controls, think about risks, and strengthen communication. By the time you sit for your CMA exam, you won’t just know COSO – you’ll live it.
Here are a few smart tips to master the COSO Framework:
- Understand how the five pillars connect and interact.
- Apply COSO concepts to real-world scenarios.
- Use CRAIM as your mnemonic anchor.
- Practice CMA questions focused on internal controls, risk, and governance.
- Discuss and teach the framework to peers – it cements your knowledge.
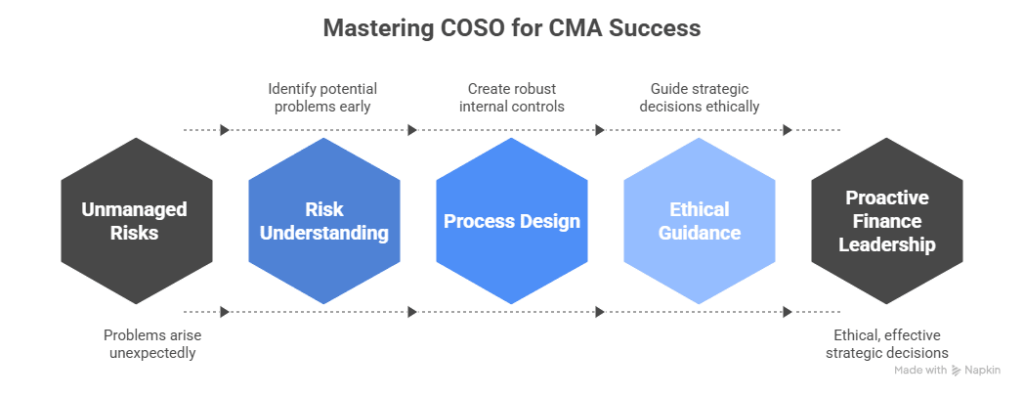
And here’s the kicker – COSO knowledge doesn’t just help you ace the CMA exam. It prepares you to step into finance roles where you’re not just part of the numbers team – you’re a trusted advisor who drives real business results.
Mastering COSO doesn’t just help you clear the exam – it also strengthens the competencies that influence your earning potential. To understand how CMA professionals are compensated in different roles and locations, you can explore the CMA salary overview as well.
Master COSO and Lead with Confidence.
Mastering COSO prepares you to:
- Proactively manage risks in your career and organisation
- Deliver reliable financial insights
- Uphold ethical business standards
- Strengthen your leadership and strategic thinking skills
The COSO Framework is your roadmap to becoming a risk-aware, ethical, and strategic finance professional. Start applying its principles now:
- Review internal controls
- Think about risks
- Strengthen communication
By exam day, you won’t just know COSO – you’ll live it. And beyond exams? You’ll be prepared for real-world roles as a trusted advisor who drives business decisions.
It’s always smart to understand the investment before you begin the journey. Since you’re planning to include CMA preparation in your schedule, make sure you’re also aware of the CMA course fees and how different training plans structure their costs.
Why is the COSO Framework important for CMA Aspirants?
The CMA exam isn’t just about numbers; it tests your ability to think strategically and ethically. COSO forms a backbone for key sections like:
- Strategic Financial Management
- Performance Management
Understanding these applications helps you answer scenario-based CMA questions effectively. As a CMA professional, understanding COSO helps you:
- Make informed decisions
- Ensure reliable financial reporting
- Guide risk management
- Uphold ethical governance
In short, mastering COSO gives you a competitive edge both in the exam and the real world. Your long-term career goals connect here. Understanding COSO adds real-world value because it links directly to the roles and earnings CMAs can achieve. In fact, strong command over frameworks like COSO is one of the reasons the CMA salary in India continues to grow each year – organisations are willing to pay for strategic problem-solvers.
How COSO Framework Apply in the Real World?
COSO isn’t just a theory. Here’s how it comes to life in organisations:
- Banks: To manage credit risk, fraud risk, and regulatory compliance.
- Manufacturing: For monitoring production quality, operational risks, and supply chain issues.
- IT Companies: To ensure project controls, data security, and ethical reporting.
Understanding frameworks like COSO sets you up for strategic roles – but before you commit time and resources, you’ll want clarity on outcomes. You might find it helpful to read our guide on is the CMA certification is worth it.
Watch this video to understand the real value of the CMA USA qualification – including career scope, salary potential, and a surprising final insight.
COSO Framework vs Other Frameworks
While many frameworks guide specific areas of business, the COSO Framework stands out by providing a complete blueprint for risk management, internal controls, and ethical decision-making across the organisation. Here’s a brief comparison of COSO, SOX and ISO Framework.
| COSO | Other Framework / Law | Key Difference / Analogy | |
| COSO vs SOX | A framework to design controls and manage risk | SOX: A law that holds executives accountable for financial reporting | COSO is the “how”, SOX is the “must” |
| COSO vs ISO 27001 | Covers overall internal controls and risk management | ISO 27001: Focuses on information security management | COSO is the whole building, and ISO 27001 is the security system protecting it |
Master the COSO Framework with Imarticus – Elevate Your CMA Journey
Don’t aim to just clear the exam. Aim to stand out as a finance professional who understands risk, ethics, and strategic decision-making.
At Imarticus Learning, our CMA US course, in collaboration with KPMG in India, goes beyond textbook theory. We help you apply the COSO Framework in real business scenarios, so you’re prepared not only to pass the exam, but to lead with confidence in your career.
Here’s how we support your growth:
- Expert Faculty – Learn from finance professionals who have worked in top global organisations.
- Real-World Case Studies – Understand how COSO and internal control principles are used in actual business decisions.
- Flexible Online Classes – Designed for working professionals and students balancing multiple commitments.
- Dedicated 24×7 Support – We’re with you through every concept, calculation, and practice session.
This isn’t just exam preparation. It’s preparation for becoming a financially responsible, ethical, and strategic leader – someone companies trust to guide decisions and manage risk.
Your CMA journey is more than a qualification. It’s the start of your leadership story, and COSO is one of the tools that will shape it.
FAQs About COSO Framework
To help you grasp COSO even better, here are a few frequently asked questions about the COSO framework.
What are the pillars of COSO?
The five pillars or components of the COSO framework are: Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control Activities, Information & Communication, and Monitoring Activities. These support internal control systems just like strong pillars support a building.
What is COSO’s full form?
COSO stands for Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission. It’s a private group that created the most widely used framework for internal control and enterprise risk management.
What is principle 4 of COSO?
Principle 4 falls under Risk Assessment and focuses on identifying and analysing risks that could prevent the organisation from achieving its objectives. In simple terms, spotting what could go wrong and planning how to handle it.
How many COSO frameworks are there?
There are two main COSO frameworks:
- The Internal Control – Integrated Framework, which helps manage internal controls.
- The Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework focuses on broader risk management tied to strategy and performance.
What is the COSO framework in CMA?
In CMA USA, the COSO framework is a key concept used to explain how organisations design internal controls, manage risks, and ensure accurate financial reporting. It forms a foundation for decision-making, audit planning, and governance topics in the exam. At Imarticus Learning, our expert-led CMA USA program helps you master COSO and all related concepts with real-world case studies and flexible support.
Is the COSO framework mandatory?
No, COSO is not legally mandatory. But it is highly recommended because it helps organisations:
- Strengthen control systems
- Improve transparency
- Build trust in reporting
- Avoid compliance issues
Many large companies use COSO voluntarily because it’s considered the gold standard.
How is COSO different from SOX?
While COSO covers the entire spectrum of internal controls and risk management across an organisation, ISO 27001 focuses specifically on information security and data protection. COSO looks at everything – operations, reporting, governance, and compliance – while ISO 27001 specialises in cybersecurity, IT risks, and protecting sensitive information.
Supercharge Your CMA Journey with COSO Framework
The COSO Framework is more than just a part of your CMA course syllabus- it’s a roadmap for risk-aware, ethical, and strategic finance leadership. For CMA candidates, understanding COSO is crucial for both passing the exam and succeeding in real-world roles.
If you’re ready to move from student to strategic finance professional, now’s the time to dive deep into COSO and other key CMA concepts – through practical case studies, expert guidance, and flexible learning designed to fit your schedule.
Your CMA journey isn’t just about passing exams. It’s about becoming the kind of leader organisations rely on. And it starts here. Start your CMA journey with the COSO Framework and other core skills, backed by the best training and support from Imarticus Learning.