Correlation and covariance are fundamental to understanding relationships between variables in finance. Correlation is any statistical relationship between two random variables or bivariate data, whether causal or not.
For financial analysts, mastering these concepts—and understanding financial data analysis techniques—is not just a matter of passing exams or ticking boxes on a financial analysis course syllabus; it’s about unlocking insights that can shape investment strategies and drive business decisions.
In this post, we’ll understand the details of correlation and covariance, illustrating their importance in statistical analysis for financial analysts.
Understanding correlation and covariance for risk management
Both correlation and covariance measure how two variables move together. Covariance gives us a glimpse into the direction of the relationship—whether they tend to increase together or move in opposite directions. However, it lacks a standardised scale, making it challenging to interpret.
This is where correlation steps in, providing a value between -1 and +1 that indicates the strength and direction of the relationship. This makes it far easier for financial analysts to interpret and communicate findings.
Covariance Equation
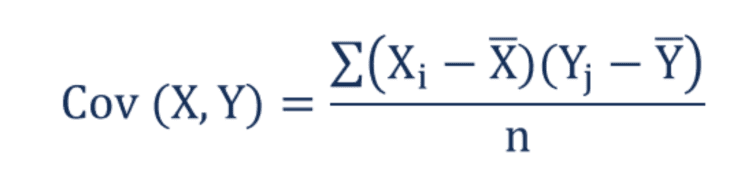
This formula, Σ(X) and Σ(Y) represent expected variable values. Furthermore, xi is the data value of x, yi is the data value of y, x̄ is the mean of x, ȳ is the mean of y. N is the number of values.
Correlation Equation
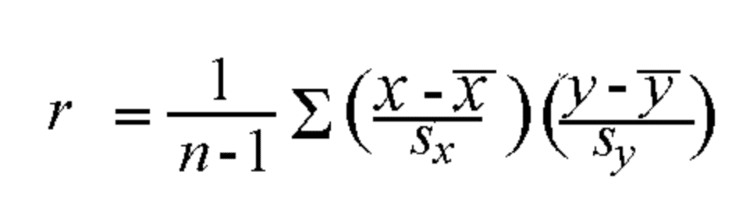
The equation for correlation is as follows:
‘n’ refers to the number of data points in the dataset represented by (x,y) pairs. Sqrt(Var(X)) represents the standard deviation of X. In contrast, Sqrt(var(Y)) represents the standard deviation of Y. Cov(X, Y) represents the covariance between X and Y. This equation demonstrates the strong relationship between covariance and correlation.
The Role of Financial Analysts
Financial analysts are essential for guiding businesses through the complex financial model. They assess a company’s financial health by analysing balance sheets, income, and cash flow statements. This detailed evaluation helps identify trends, potential risks, and areas for improvement.
Moreover, financial analysts forecast future performance using statistical analysis. This predictive capability allows organisations to adapt quickly to market changes, ensuring agility in planning.
Collaboration is vital in their role. Analysts work closely with various departments, including accounting and marketing, to foster data-driven decision-making. Communicating complex financial concepts builds stakeholder trust and enhances the company’s credibility.
Many analysts specialise in investment banking or risk management, deepening their expertise and value. Whether advising on mergers or managing investments, their insights drive growth.
What is the difference between correlation and covariance?
Covariance assesses how two variables depend on each other, indicating whether a change in one variable might lead to a change in another. On the other hand, correlation reveals the strength and direction of the relationship between them, showing how one variable may influence the other. Although these concepts sound alike, they play distinct roles in statistical analysis and offer unique insights.
Correlation vs. Covariance in Finance
- Definition: Covariance measures how two variables move together, while correlation standardises this measure, providing a clearer understanding of their relationship.
- Interpretation: A positive covariance indicates that both variables move in the same direction. In contrast, correlation quantifies the strength and direction of their linear relationship, ranging from -1 to +1.
- Applications: In finance, covariance helps portfolio diversification by assessing how different assets move together. Conversely, correlation identifies relationships between assets, aiding in risk management and investment strategies.
Practical Applications in Finance
So, how do these concepts play out in real-world financial data analysis techniques? Let’s delve into a few examples:
-
Portfolio Management
Analysts use correlation to assess how different assets behave toward each other. A well-diversified portfolio will contain assets with low or negative correlations to reduce risk. For instance, if you’re holding stocks and bonds, understanding their correlation can help you make better decisions about asset allocation.
-
Risk Assessment
Covariance is vital for assessing an investment’s risk relative to the market. A high positive covariance with a market index indicates that the investment moves in tandem with the market, which might be desirable for some investors but not for others seeking lower risk.
-
Market Predictions
Financial analysts leverage these statistical concepts to predict future market trends. By analysing historical data, they can determine which variables are strongly correlated and use this information to forecast future movements.
-
Enhancing Your Skills
If you’re keen on sharpening your analytical skills, enrolling in a financial analysis course focusing on statistical analysis for financial analysts is a great start. Look for classes that cover both theoretical aspects and practical applications, ensuring you have a firm grasp of how to apply correlation and covariance in your analyses.
Transform Your Career with Imarticus Learning’s Postgraduate Financial Analysis Programme
Understanding Correlation vs Covariance in finance is not merely academic; it’s a key component of practical financial analysis. These tools empower analysts to make data-driven decisions that can significantly impact investment strategies and financial planning.
Imarticus Learning has successfully facilitated over 45,000 career transitions, creating an illustrious 200+ hour Postgraduate Financial Analysis Programme. This programme is specifically designed for graduates with less than three years of experience in the finance domain, empowering them to transform their professional careers.
Participants will also be well-prepared for CFA Level 1 roles available in the industry. This financial analysis course offers a job assurance guarantee, providing seven guaranteed interviews at leading finance organisations.
Experience a hands-on approach with a financial planning and analysis course, utilising cutting-edge learning engagement solutions such as simulation tools replicating real workplace scenarios. Boost your professional presence with a personal branding project and LinkedIn challenge, giving you a competitive edge in today’s job market.
Enrol in Imarticus Learning’s Postgraduate Financial Analysis Course today and unlock your potential!

