Cybersecurity has never been more important than it is now. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and cybercrime are daily news. Organisations and people are on tenterhooks. If you’ve ever asked yourself what’s involved in protecting digital infrastructure or thought about a career in it, taking up a Cybersecurity course is the ideal starting point.
But just what do you learn from a Cybersecurity class? In this blog, we outline the ten most critical skills you’ll acquire—skills that not only enable you to safeguard systems, but also make you extremely attractive to potential employers globally.
Table of Contents
- Cybersecurity Skills in Demand: Why They Matter
- Mastering Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
- Understanding Network Security Fundamentals
- Learning the Cybersecurity Course Syllabus
- Creating Information Security Awareness Training
- Threat Detection and Incident Response Skills
- Cloud Security Essentials
- Risk Assessment and Management
- Cryptography and Data Protection Techniques
- Legal and Compliance Knowledge for Cybersecurity
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Cybersecurity Skills in Demand: Why They Matter
Cyber attacks have changed significantly in the last decade. From advanced phishing attacks to state-sponsored cyber-spying, the scenario is more intricate than ever. Organisations are in a hurry to onboard professionals with Cybersecurity skills in demand, but a wide skill gap still exists.
A Cybersecurity program equips you with the skills and knowledge that today’s employers can’t get enough of. These abilities transcend textbook learning—they prepare you to address actual cyber threats.
In-demand Cybersecurity Skills You’ll Acquire:
- Techniques in vulnerability assessment
- Incident response tactics
- Monitoring security operations
- Cloud security principles
- Penetration testing and ethical hacking
- Risk management techniques
- Understanding compliance and regulations
- Security architecture design
- Threat intelligence analysis
- Fundamentals of cryptography
According to Cybersecurity Ventures– there will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs globally by 2025… a clear signal of how valuable these skills are.
Mastering Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
One of the most exciting aspects of a Cybersecurity course is learning the art of ethical hacking. You’ll gain insider knowledge on how hackers think, behave, and exploit vulnerabilities—but for good.
Penetration testing and ethical hacking are about emulating cyberattacks on networks, applications, or systems to expose vulnerabilities before bad guys do. This is one of the most technical yet rewarding skills.
Primary Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Skills:
- Reconnaissance and information gathering
- Ethically exploiting vulnerabilities
- Employing tools such as – Metasploit, Burp Suite & Wireshark
- Web application penetration testing
- Wireless network testing
- Reporting and communicating findings effectively
A TechRepublic article points out that ethical hackers rank among the most in-demand occupations in the current cybersecurity environment.
Understanding Network Security Basics
At the center of every aspect of cybersecurity is one indispensable field—network security. Through your Cybersecurity course, you’ll gain a bedrock comprehension of network security basics.
Securing networks is similar to constructing a fortress around virtual infrastructure. Lacking the proper defenses, sensitive information, financial assets, and business operations are ever-exposed to attack.
Critical Network Security Concepts:
- TCP/IP and network protocols
- Firewall and intrusion prevention system (IPS) configurations
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and remote access
- Network segmentation and zoning
- Secure Wi-Fi settings
- Common network attack detection and mitigation (DDoS, MITM)
Here’s a quick summary table for better understanding:
| Concept | Description |
| Firewall | Controls incoming/outgoing traffic based on rules |
| VPN | Encrypts network connections for secure access |
| IPS | Detects and prevents malicious network activities |
| Network Segmentation | Divides networks to limit attack spread |
| Secure Wi-Fi | Configures wireless networks to prevent intrusion |
Familiarization with the Cybersecurity Course Syllabus
Prior to joining any learning program, it’s important to go through the Cybersecurity course syllabus. A good syllabus guarantees you both theoretical and practical skills.
A detailed Cybersecurity course syllabus equips you to solve real-world situations confidently. It gives you a direct path of learning and indicates the areas in which you’ll excel.
Common Cybersecurity Course Syllabus Topics:
- Introduction to Cybersecurity and Threat Landscape
- Fundamentals of Networks and Security Protocols
- Ethical Hacking and Vulnerability Assessment
- Web and Application Security Principles
- Cloud Security Essentials
- Information Security Governance and Risk Management
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Legal, Compliance, and Privacy Considerations
- Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Planning
- Hands-on Labs and Capstone Project
Building Information Security Training Awareness
Information is probably the most important asset for individuals and companies these days. That’s why a Cybersecurity course spends considerable time on information security training.
Information security training goes beyond technology—it fosters a security-first mindset across organisations. You’ll learn to protect sensitive information from theft, manipulation, or destruction.
Benefits of Information Security Training:
- Reduces human error—the leading cause of breaches
- Increases organisational resilience to cyberattacks
- Ensures compliance with data protection laws
- Encourages proactive identification of risks
- Boosts individual confidence in security practices
Many global security breaches stem from a lack of information security awareness, as noted by IBM’s Data Breach Report.
Threat Detection and Incident Response Skills
Cyberattacks occur inevitably yet the outcome relies on how swiftly and effectively you react to these incidents. A Cybersecurity course trains you to detect threats proactively and respond effectively. The course teaches you how to recognize attack indicators before they reach critical stages and how to study attack routes and implement planned responses to minimize damage.
Threat Detection and Incident Response Techniques:
- Log analysis and security events
- Identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs)
- Deploying security information and event management (SIEM) tools
- Coordinating response teams and communication
- Conducting post-incident reviews
- Documenting lessons learned
Cloud Security Essentials
With businesses rapidly migrating to cloud platforms, cloud security is now a must-have skill. The Cybersecurity course provides students essential knowledge for protecting both data and operations which operate within cloud infrastructure. Cloud environments require organizations to address specific security difficulties which emerge from shared responsibility frameworks and data protection issues. The ability to handle these challenges correctly remains essential for success.
Core Cloud Security Concepts:
- Cloud architecture and deployment models
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Data encryption and secure storage
- Cloud provider security best practices
- Cloud compliance standards (e.g., ISO 27017, CSA STAR)
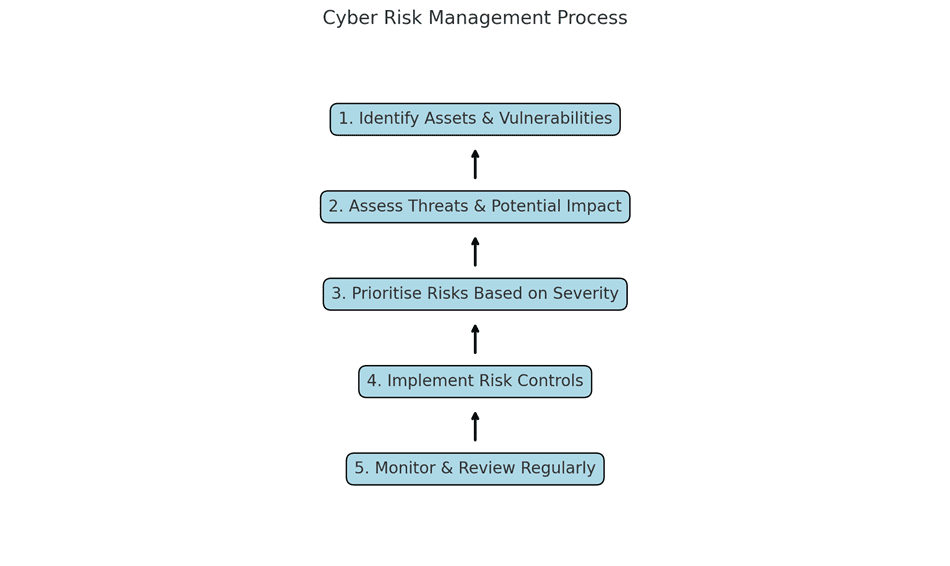
Risk Assessment and Management
Every organisation faces security risks but their future survival depends on how they control these risks. Cybersecurity courses require risk assessment and management as fundamental elements. You will develop abilities through case studies and practical activities to identify and assess risks while implementing methods to minimize threats to systems and data and operational processes.
Elements of Risk Management:
- Identifying assets and weaknesses
- Determining threat likelihood and impact
- Applying controls to reduce risks
- Designing risk management frameworks
- Communicating risks to stakeholders
Cryptography and Data Protection Techniques
In the digital age, protecting information means you must have strong cryptography skills. Your Cybersecurity course takes a deep dive into data protection techniques.
Cryptography isn’t just for coders.. it’s essential for anyone tasked with safeguarding digital information – from passwords to classified documents.
Cryptography Techniques You’ll Learn:
- Symmetric and asymmetric encryption
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA)
- Digital signatures and certificates
- Secure key management
- Data masking and tokenisation
Legal and Compliance Knowledge for Cybersecurity
The understanding of legal and regulatory cybersecurity factors stands vital for people working in this field. Your Cybersecurity course will cover essential laws, standards, and frameworks. Global data privacy regulations are intensifying so businesses need to meet compliance standards. Knowing these requirements helps stop legal problems while building trust with customers.
Legal and Compliance Subjects Discussed:
- Data Protection Legislation (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
- Industry-specific compliance standards (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA)
- ISO 27001 information security management
- Regulatory reporting requirements
- Cybercrime and intellectual property law
Key Takeaways:
- A Cybersecurity course provides you with vital technical and strategic expertise.
- You’ll gain expertise in -ethical hacking, threat detection, cloud security, and risk management.
- Knowledge of legal & compliance frameworks is vital in today’s regulated environment.
- Demand for professionals with Cybersecurity skills in demand is rapidly growing.
- Information security awareness is critical for both individuals and organisations.
FAQs
1. What is a Cybersecurity course?
A Cybersecurity course offers organized education on the ways and means of defending networks, systems, and information against cyber attacks, giving students both technical and strategic skills.
2. Is ethical hacking taught in every Cybersecurity course?
The majority of fully featured Cybersecurity course programs incorporate ethical hacking and penetration testing to enable students to learn system weaknesses from the point of view of a hacker.
3. How many months or years does it take to finish a Cybersecurity course?
The length of time depends on the course, but the majority of entry to expert Cybersecurity courses range from 3 to 12 months.
4. Is there a job prospect after taking a Cybersecurity course?
There exists a high market need for Cybersecurity professionals who can fill positions such as Security Analyst along with Ethical Hacker and Cloud Security Specialist roles.
5. What is the difference between information security training and cybersecurity?
Information security training focuses on protecting information assets while cybersecurity focuses on protecting networks and systems and digital infrastructure.
6. Do I get to learn about legal regulations in a Cybersecurity course?
Sure, most Cybersecurity course curricula include GDPR, CCPA and industry guidelines as an essential part of their curriculum.
7. Are there practical labs involved in Cybersecurity courses?
The practical labs together with real-world cases and simulations form an essential part of quality Cybersecurity course programs.
8. Do I require coding skills for a Cybersecurity course?
Coding skills at a basic level (Python, Bash) prove beneficial for ethical hacking and penetration testing roles although they remain optional for Cybersecurity courses.
9. How up-to-date is cloud security in contemporary Cybersecurity courses?
Cloud security is nowadays an essential element since cloud services have been widely implemented across sectors.
10. Can a Cybersecurity course enable me to switch from another profession?
Absolutely. Most programs are for new students or career switchers, offering the basis to get into the field of cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Studying cybersecurity unlocks entry into one of the most sought-after and highly influential professional fields today. Modern businesses require immediate protection of digital assets through skilled professionals who defend against escalating complex cyberattacks.
If you’re willing to develop future-ready Cybersecurity skills in demand, check out the MBA in FinTech course by Imarticus Learning. It provides a great blend of technology, finance, and security expertise that matches industry requirements.
Get set to be part of a community of security professionals and do your bit to secure the digital world.
Ready to secure the digital frontier? Begin today!