On any given day in Bangalore, a commerce student is attending an accounting lecture, a consulting firm is closing quarterly books for a global client, and a multinational company is preparing financial reports for its international headquarters. These aren’t isolated moments. They reflect how deeply global finance and accounting are woven into the city’s professional landscape. Pursuing ACCA in Bangalore fits directly into this environment.
It helps to look at it simply. If you want a career in accounting or finance that goes beyond borders, you need a qualification that travels with you. ACCA does exactly that. It builds your understanding of accounting standards, taxation, auditing, and financial strategy while preparing you to work with companies across different countries.
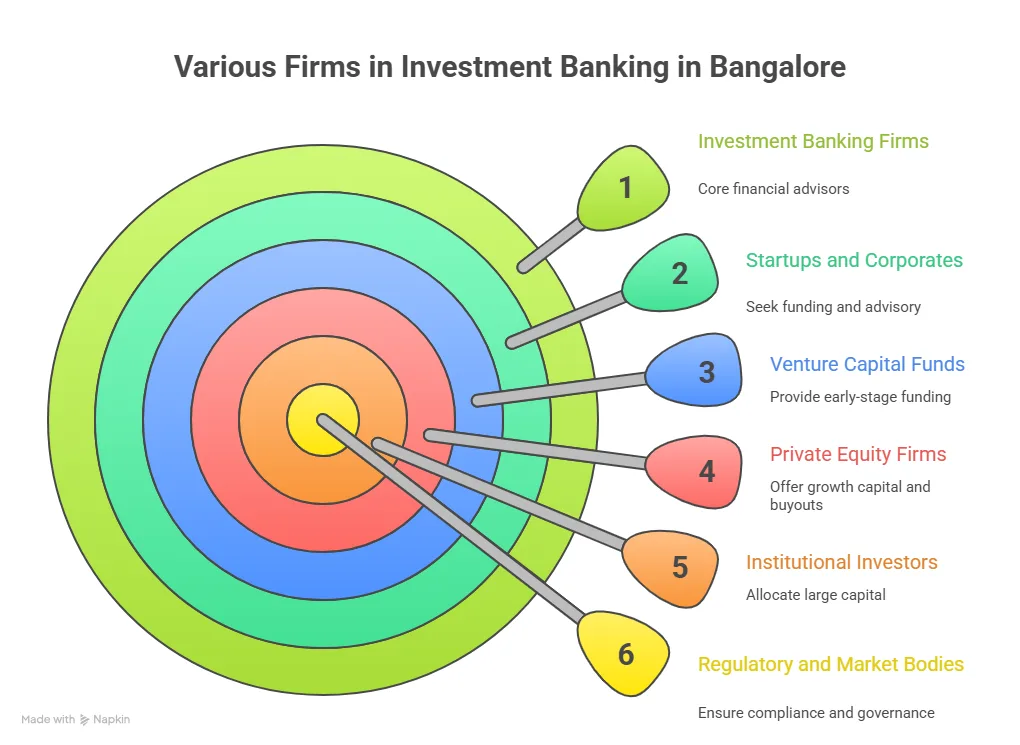
Bangalore adds a clear advantage and another layer to this journey. The city hosts global capability centres, Big 4 firms, consulting companies, and multinational finance teams.
→Many organisations hire professionals with international accounting qualifications.
→ Some offer roles that involve working with global clients and reporting standards.
→ Many firms prefer candidates who understand international financial regulations and compliance standards.
This constant demand creates strong opportunities for students pursuing ACCA in Bangalore.
Let’s go through everything about pursuing ACCA in Bangalore. Which ACCA institutes in Bangalore should you look at? How much will it cost overall? What kind of jobs can you expect after clearing exams? And will the effort truly be worth it in the long run?
Did you know?
Bangalore is one of India’s fastest-growing hubs for global finance and accounting roles, with Big 4 firms, MNCs and global capability centres actively hiring ACCA students and qualified professionals for international accounting and compliance functions.
Why ACCA in Bangalore Is Becoming So Popular
Bangalore is known as India’s tech capital, but over the last decade, it has also become a major finance and consulting hub. Global companies have set up large finance and shared service centres here, creating strong demand for internationally trained accountants. This demand is one of the biggest reasons why students are choosing ACCA in Bangalore.
So if you are still wondering: What is ACCA? Think of it this way. When a multinational company operates across countries, it needs professionals who understand international accounting standards, taxation frameworks and compliance requirements. ACCA professionals are trained exactly for this.
So when you study ACCA in Bangalore, you’re not just studying for an exam. You’re preparing for roles that connect you with global finance teams and international business operations.
Who Should Consider ACCA in Bangalore?
ACCA is not only for toppers or experienced professionals. It suits a wide range of students who want global career options in finance and accounting.
You should consider ACCA in Bangalore if you are:
- A commerce student, after Class 12 planning a finance career
- A BCom or BBA student who wants an international qualification
- Any graduate looking to specialise in accounting or finance.
- A CA aspirant exploring alternative global certifications
- Any working professional who wants strong ACCA career growth in accounting or consulting
As Bangalore offers strong exposure to global companies and finance teams, students often find better internship and job opportunities here compared to smaller cities.
If you’re planning to start ACCA or are already preparing, it’s important to stay updated with upcoming exam changes. This video explains the ACCA pattern changes expected in 2027.
Understanding What the ACCA Course Actually Covers
The ACCA qualification is a UK-based global accounting credential recognised in over 180 countries, which focuses on building expertise in accounting, taxation, auditing, finance and business strategy.
The structure for the ACCA course in Bangalore is designed to build knowledge step by step.
Applied Knowledge level
You begin with the fundamentals of:
- Financial accounting
- Management accounting
- Business technology
Applied Skills level
This moves into deeper finance concepts:
- Corporate and business law
- Financial reporting
- Taxation
- Audit and assurance
- Financial management
Strategic Professional level
This focuses on decision-making and leadership:
- Strategic business leader
- Strategic reporting
- Advanced optional ACCA course subjects
Most students complete ACCA within 2 to 3 years, depending on exemptions and their exam pace. Many also choose ACCA classes or integrated programs like BCom with ACCA in Bangalore, so they can complete graduation and professional qualification together.
Also Read: Why pursuing ACCA after graduation is a smart choice.
Top ACCA Colleges in Bangalore
When students search for the top ACCA colleges in Bangalore, they’re usually looking for institutions that offer structured support and career guidance alongside the qualification.
The good part is that now several colleges offer integrated commerce degrees with ACCA course preparation. These programs help students avoid managing separate coaching and college schedules.
While choosing an ACCA college in Bangalore, focus on:
- Faculty experience
- Pass rates
- Industry exposure
- Placement support
- Internship opportunities
The best college for ACCA in Bangalore is not just about brand value. It’s about how well it prepares you for real finance roles after qualification.
ACCA Institutes and Coaching in Bangalore
I have seen many students who prefer top ACCA institutes in Bangalore or specialised training institutes that offer rather than relying only on self-study. This is why ACCA coaching in Bangalore has grown rapidly.
Good coaching centres offer:
- Structured classes
- Doubt-solving sessions
- Mock exams
- Revision support
- Placement guidance
The best ACCA coaching in Bangalore usually combines conceptual clarity with exam strategy. Since ACCA exams are application-based, having experienced faculty can make a big difference.
Students often compare:
- ACCA coaching centres in Bangalore
- Weekend or online batches or ACCA online courses
- Fees and faculty experience
Choosing the right institute helps maintain consistency across all exam levels.
If you’re preparing for ACCA and wondering how to plan your studies properly, having a clear strategy can make the journey much easier. This video walks you through a practical ACCA exam study plan, from how many hours to study each week to how to balance coaching, revision and mock tests.
ACCA Fees in Bangalore
When it comes to enrolling in a specialised finance course like ACCA, price often becomes the deciding factor. One of the most common questions that students ask me is about ACCA course fees in Bangalore.
Costs usually include:
- ACCA registration and exam fees
- Coaching fees
- Study material
On average:
ACCA global fees come to ₹2 to 3 lakhs overall; the coaching fees vary by institute, and the total investment depends on ACCA exemptions and attempts.
| Fee Component | Estimated Cost (INR) |
| ACCA Registration Fee (one-time) | ₹8,000 – ₹10,000 |
| Annual Subscription Fee | ₹12,000 – ₹14,000 per year |
| Exam Fees (all 13 papers total) | ₹1.8-2.5 lakhs overall |
| Coaching Fees (Bangalore institutes) | ₹1.5-3.5 lakhs total |
| Study Materials & Mock Tests | ₹20,000 – ₹40,000 |
| Total Estimated Cost | ₹3.5-6 lakhs |
While the cost may seem high initially, students often recover this through strong career growth and global opportunities after qualification.
ACCA Exam Centres in Bangalore
ACCA exams in Bangalore are conducted at authorised computer-based exam centres across the city. Students can choose their preferred centre while booking the exam through the official ACCA portal.
Most ACCA exam centres in Bangalore are located in well-connected areas and offer flexible exam slots for Applied Knowledge, Applied Skills, and some Strategic Professional level papers. These centres are equipped with computer-based testing facilities and follow standard ACCA exam guidelines.
Before booking your exam, it’s always a good idea to:
- Check available exam dates and centres on the ACCA website.
- Book your slot early to get a convenient location and timing.
- Visit the centre location in advance if you’re unfamiliar with the area.
Since Bangalore has multiple ACCA exam centres, students usually find it convenient to schedule exams without needing to travel to another city.
Also Read: How ACCA benefits help you make a strong career.
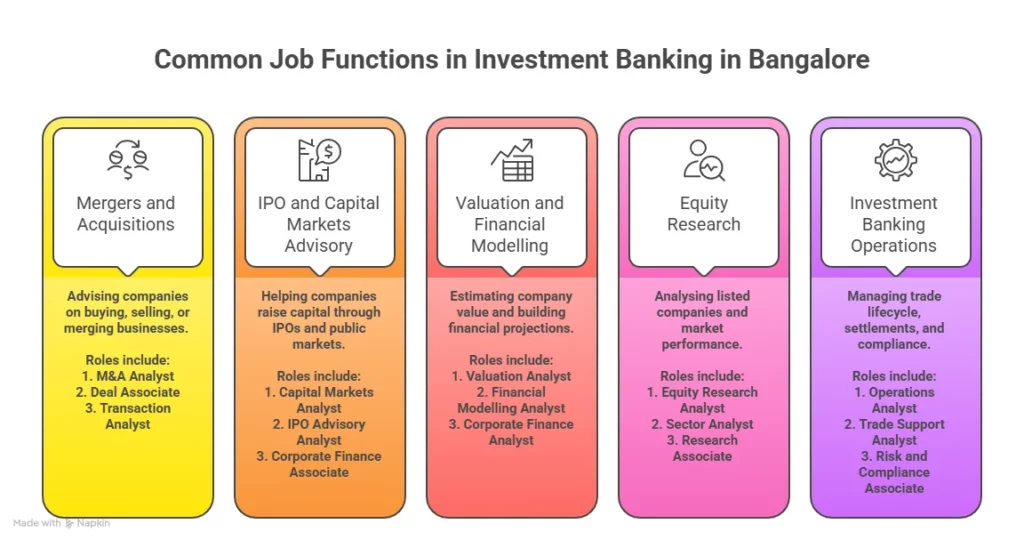
ACCA Jobs in Bangalore
The biggest reason many students choose ACCA in Bangalore is the job opportunities.
| Employer Type | Common ACCA Job Roles | Type of Work Involved |
| Big 4 accounting firms | Audit Associate, Tax Consultant, Financial Analyst | Audit assignments, taxation, compliance, financial reporting and advisory services for global clients |
| Global consulting companies | Business Analyst, Financial Analyst | Financial analysis, consulting projects, performance reporting and strategic finance support |
| MNC finance teams | Accounts Executive, Financial Analyst | Financial reporting, budgeting, compliance, internal controls and global accounting operations |
| Startups and unicorns | Business Analyst, Accounts Executive | Financial planning, fundraising support, cost analysis and growth-focused finance management |
| Shared service centres (GCCs) | Internal Auditor, Financial Analyst, Tax Associate | Global accounting operations, audit support, taxation compliance and financial data management |
There are also many ACCA job openings in Bangalore for part-qualified students who have cleared a few ACCA papers.
ACCA Jobs in Bangalore for Freshers
Freshers often wonder whether they can get jobs after the ACCA results are out. Many students begin with an ACCA internship in Bangalore and later convert to full-time roles.
Many companies hire:
- ACCA interns
- ACCA trainees
- Junior accountants
- Finance analysts
ACCA fresher jobs in Bangalore usually focus on helping you build practical experience first. As you clear more papers, your salary and responsibilities grow. ACCA freshers in Bangalore earn at par with ACCA fresher salary in India.
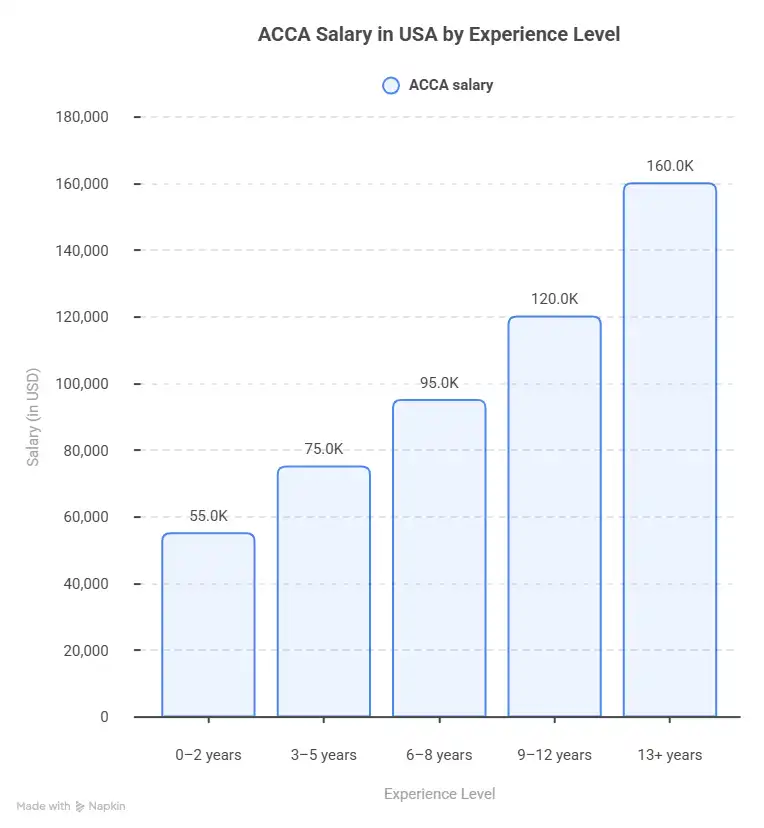
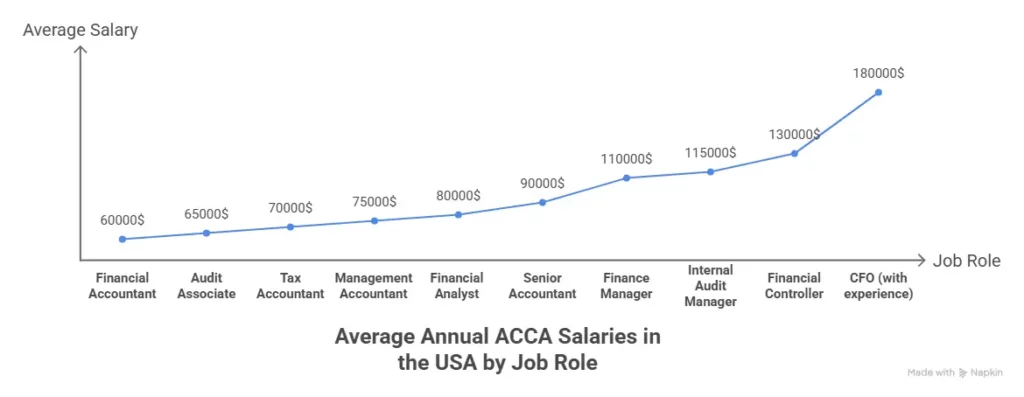
ACCA Salary in Bangalore
ACCA salary in India depends on experience, skills and qualification level. Typical ranges in Bangalore include:
| ACCA Qualification Level | Average Salary Range (India) |
| ACCA Fresher | ₹4-7 LPA |
| ACCA Part-Qualified | ₹6 -10 LPA |
| Fully Qualified ACCA | ₹8 -18 LPA |
| Experienced ACCA Professionals | ₹20 LPA and above |
Because Bangalore has many global companies, salary growth can be faster compared to smaller cities.
Before choosing ACCA, most students want clarity on career scope and salary. To understand the career scope and salary potential in detail, watch this quick overview.
ACCA Training and Career Preparation
Completing exams alone is not enough. Employers look for practical skills. Good ACCA training in Bangalore focuses on:
| Skill Area | What Students Learn | How It Helps in Careers |
| Financial Reporting | Students learn how to prepare and analyse financial statements using international accounting standards like IFRS. | Accurate reporting and compliance are critical in Audit firms, consulting companies and multinational finance teams. |
| Taxation | Covers corporate tax, compliance requirements and regulatory frameworks. | Helps with handling taxation, filings and financial planning in accounting firms and corporate finance teams. |
| Audit Processes | Introduces internal and external audit procedures, compliance checks and risk assessment methods. | Audit firms, assurance roles and compliance-based finance positions. |
| Excel & Financial Analysis | Includes financial modelling basics, data analysis, spreadsheet skills and reporting techniques. | Finance roles, internships and corporate decision-making tasks. |
| Business Communication | Focuses on presentation skills, report writing and professional communication. | Present financial insights clearly and work confidently in corporate and client-facing environments. |
This makes candidates job-ready alongside exam preparation.
Is ACCA in Bangalore Worth It?
For students who want to create a long-term career in accounting and finance, ACCA is definitely a valuable investment. The qualification requires time commitment, consistent effort, and persistence, but it also opens doors to global roles and steady salary growth.
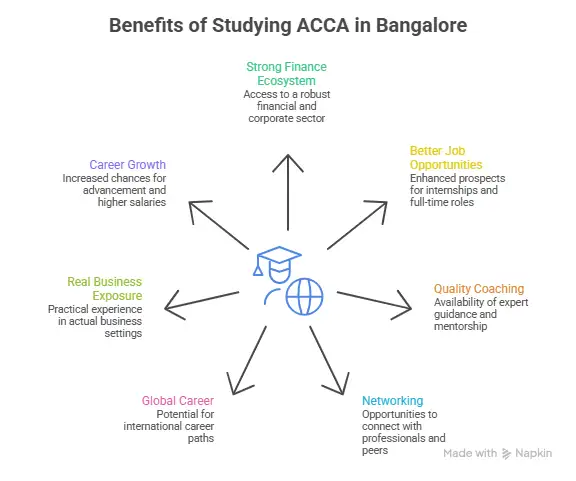
Bangalore makes this journey easier because:
- Global companies actively hire finance professionals.
- Internship opportunities are easier to find
- Salary growth is faster compared to many cities.
- Exposure to international work environments is higher.
If your goal is to build a career that connects with global finance rather than staying limited to one market, ACCA in Bangalore is definitely worth considering.
Also Read: ACCA Books every finance aspirant should read.
Future Scope of ACCA in Bangalore
Bangalore continues to grow as one of India’s leading global finance and consulting hubs. With more multinational companies setting up global capability centres and finance teams in the city, the demand for internationally qualified accountants is expected to rise steadily.
| Career Areas After ACCA in Bangalore | Scope & Demand in Bangalore |
| Financial reporting and analysis | High demand across MNCs and global capability centres for accurate reporting and financial insights |
| Audit and assurance | Strong hiring by Big 4 firms and audit companies for compliance and assurance roles |
| Taxation and compliance | Growing opportunities in corporate tax, regulatory compliance and consulting firms |
| Risk and consulting roles | Increasing demand in consulting and advisory firms supporting global clients |
| Corporate finance and business strategy | Valuable for roles in financial planning, business expansion and strategic decision-making |
Also Read: Choose the right ACCA study material to boost your preparation.
Why Many Students Choose Imarticus Learning for ACCA in Bangalore
Preparing for ACCA on your own can feel overwhelming because the syllabus is vast and exams are application-based. This is why many students explore structured training programs that combine coaching, practical learning, and placement support.
Institutes like Imarticus Learning have built a strong presence for ACCA in Bangalore for finance and accounting training. Their ACCA program focuses not just on clearing exams but also on preparing students for real job roles.
What Imarticus Learning offers:
- Gold status learning partner of ACCA
- Structured classes and revision support
- Experienced faculty and mentors
- Industry-relevant resources
- Practical case studies
- Course material powered by Kaplan
- Internship opportunities with KPMG in India
- Pre-placement bootcamp
- Career guidance alongside exam prep
For those who prefer guided learning instead of managing everything alone, structured programs can make the ACCA journey more organised and career-focused.
FAQs About ACCA in Bangalore
If you are looking to pursue ACCA in Bangalore, here are a few frequently asked questions that can help you get ahead in your career.
Is ACCA worth studying in Bangalore?
Yes. Bangalore has a strong demand for globally qualified accountants due to the presence of multinational companies and consulting firms. These organisations regularly hire professionals with international accounting knowledge.
What are the total ACCA course fees in Bangalore?
The total ACCA course fees in Bangalore are as per the standard norms and typically include registration, exam fees and coaching fees. On average, the overall investment can range between ₹2.5 lakh and 4.5 lakh, depending on exemptions and coaching choices. Some institutes also offer instalment plans to make the course more affordable for students.
What is the salary after ACCA in Bangalore?
Freshers typically earn ₹4-7 LPA, while qualified ACCA professionals can earn ₹8-18 LPA or more, depending on experience. Part-qualified candidates can earn between ₹6 lakh and ₹10 lakh annually, depending on skills and experience. Fully qualified ACCA professionals with a few years of experience can earn significantly higher, especially in consulting and multinational firms.
Can I get a job after ACCA in Bangalore?
Yes. Many companies hire part-qualified and qualified ACCA candidates for roles in audit, accounting, taxation, and financial analysis. Once you clear a few papers, you can apply for entry-level roles like accounts executive, audit assistant or financial analyst. These roles help you gain experience while completing the remaining exams. Over time, your job profile and salary improve as you progress through the ACCA qualification.
Which is the best institute for ACCA in Bangalore?
The best institute depends on faculty, placement support, and training quality. Students should compare institutions based on outcomes rather than brand name alone. Opting for reputed institutions like Imarticus Learning, where you get structured learning, past students’ testimonials, internship and placement opportunities with top employers, is a wise choice.
Are there ACCA internships in Bangalore?
Yes, there are many ACCA internship opportunities in Bangalore. Students often begin internships during their course to gain practical exposure. Internships help you understand real accounting work, improve technical skills and build professional confidence. Many internships also convert into full-time roles once you complete the qualification.
Can non-commerce students pursue ACCA in Bangalore?
Yes. Even students from non-commerce backgrounds can pursue ACCA in Bangalore. However, they may need extra time to build basic accounting and finance knowledge. With consistent preparation and proper coaching, students from any background can complete ACCA successfully.
Is ACCA better than CA for working abroad?
ACCA is widely recognised globally, especially in countries like the UK, UAE, Singapore and Canada. If your goal is to work internationally, ACCA offers strong mobility and global opportunities. However, both CA and ACCA have strong career value depending on your long-term goals and preferred work location.
Is ACCA in Bangalore the Right Move for You?
ACCA is not just another professional course. It’s a qualification that can shape your career for the long term. And when you pursue it in a city like Bangalore, where global finance roles are growing every year, the opportunities become even stronger.
The city offers a unique advantage. Global companies, Big 4 firms, consulting organisations, and multinational finance teams are constantly looking for professionals who understand international accounting and financial standards. This means students don’t just study here, they step into a job market that actively values their qualifications.
Of course, the journey requires commitment. ACCA involves multiple exams, consistent preparation, and practical experience. But the long-term rewards – global career opportunities, steady salary growth, and professional credibility- make the effort worthwhile for students who are serious about finance and accounting.
If your goal is to build a career that goes beyond local roles and connects with global business, ACCA in Bangalore offers a clear and practical path.
Take time to evaluate institutes, understand the costs, and plan your preparation properly. With the right approach, ACCA can become the foundation for a stable, global, and rewarding career in finance.