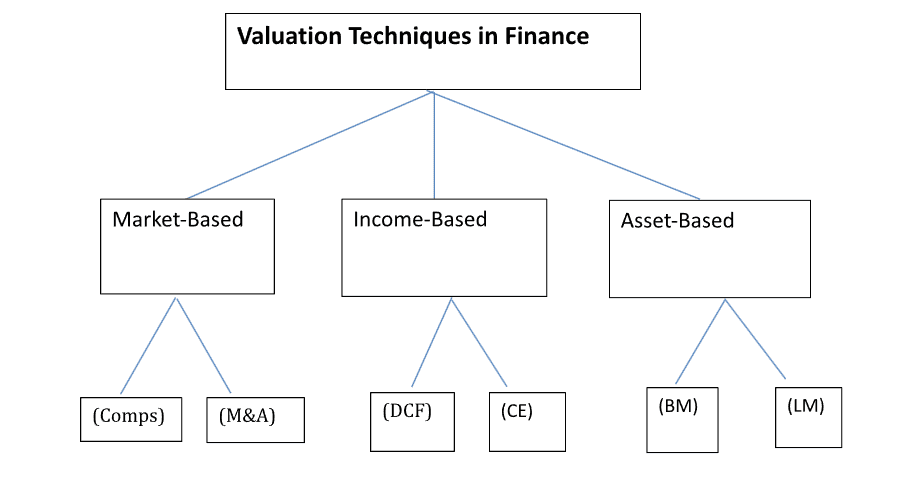
Corporate finance offers certain intriguing and yet complicated attributes that run any business effectively. We shall define the term corporate finance and analyse its functions in the management of financial resources in a company from a practical aspect to a more relativistic one. Corporate finance is important, whether it is for a student, an extreme practitioner, or simply someone out there to understand how the process works.
What is Corporate Finance?
It is the art of management of money in economic units that bears the title of corporate finance. Corporate finance can cover all those financial decisions targeted towards the firm’s operations. This concerns the organisation or the capital layout, mobilising debts or assets for business operations purposes, and taking measures to increase the owners’ value.
The fundamental aim of corporate finance is to provide and protect the stakeholders’ value through developing an optimal financial strategy and making investment choices.
Corporate Finance Basics
Whether it is to get a job in a corporate structure or just from an interest standpoint, understanding the basic tenets of corporate finance is very important.
Corporate finance, in general, is made up of the following broad areas:
- Capital Structure: Capital structure relates to the debt and equity balance employed by the firm to execute its strategies and grow. An ideal structure will, in turn, lower the weighted average cost of capital, thus increasing the profits.
- Working Capital Management: This means committing there cleaning a nits all possible current of broad understanding of current assets and current liabilities for purposes of running a firm and to pay off obligations of a short-term nature as they fall due.
- Financial Analysis: This means an evaluation of how well an organization has done with respect to its financial goals and expectations with the aim of determining the right course of action and strategy to adopt in the business.
- Risk Management: Corporations’ strategies to prevent or minimise potential losses and, therefore, must identify the classification and evaluation of risk. This encompasses, but is not restricted to, risks associated with the market, credit and operations.
These fundamentals of corporate finance serve as a foundation for advanced comprehension of analytical tools employed in such practices.
The Role of Corporate Finance in Business
The scope of corporate finance must be simplified to more than just controlling finances; it is extensive and complicated. Here are some of the points that can be mentioned:
- Decision Making: Corporate finance means to include the supplementary materials of data and analysis which are needed in aid of making strategic decisions. Hence, facts ground investments made, expansion is done and resources moved.
- Financial Health Monitoring: It assists in the evaluation of a company’s financial health. This is achieved through periodic analysis of the corporation’s reports, where some patterns and issues in performance and potential areas for improvement are identified.
- Value Creation: Maximising the shareholders’ value is the primary objective of corporate financing. It is ensuring that profits are the highest possible with the lowest costs and risks involved.
- Strategic Planning: Corporate finance works by providing a financial perspective of how the strategy will work as well as the likely outcome of the strategy after a given time based on changing conditions.
- Resource Allocation: Excellent corporate finance practice guarantees that available resources are well utilised, thereby increasing the efficiency and profitability of the operations in general.
The Corporate Finance Strategies
Strategic management of finance is crucial for the operational success of any company. Below are some of the widely used corporate finance strategies:
- Growth Strategy: In this business expansion strategy, profits are usually appropriated back in the business. This is commonly achieved by companies by merging with or acquiring other companies or venturing into other regions.
- Diversification: Various product lines or industries may be entered into thus good buffer is formed to the corporation from the dangers caused by depending on one uncompounded source of revenue.
- Leverage: This refers to the capability of utilizing borrowed funds in such a way that the equity returns are elevated and optimized. With this comes an additional risk that has to be handled with caution.
- Cost Control: The measures can be overhauling the structure of management to have more efficient operations, cutting the costs charged by suppliers and eliminating irrelevant expenditures.
- Investment in Technology: Incorporation of modern approaches and technologies has the potential to lessen the operational costs and increase the flow of cash. This includes things such as financial management systems, data analysis and even robotics.
A full appreciation of these corporate finance strategies helps a business to effectively deal with adverse financial conditions and also exploit the available opportunities.
Financial Management in Corporations
It cannot be overstated that one of the main segments of corporate finance is financial management. It involves the strategic use of the required resources of an organisation to achieve its financial goals. There are identifiable facets of financial management:
- Budgeting: Creating and implementing Budgets makes sure that there is maximum utilization of resources. This would mitigate the challenge of over-funding as well as help in the strategic fit of the funds available towards the goals of the organization.
- Management of Cash Flows: Any business calls for the realization of the importance of managing and sustaining inflowing and outflowing money from any business. An organisation needs to monitor closely all its customers, suppliers, and other sources of both cash inflow and outflow in the organization.
- Investment choices: Business investment decisions are a major component of corporate finance indeed. This includes the decision against opportunities which could involve investments and its related risks.
- Reporting of Financial Results: There is an increasing expectation for efficient and up-to-date financial reporting in order to enhance accountability. In addition, this approach assists the stakeholders in measuring the success of the business operation.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Financial restraint and risk mitigation measures should be put on place to avoid compromising business operations and shareholders welfare respectively.
The Importance of Education: IIM Lucknow Courses
For people who wish to explore the larger ambit of areas, such as corporate finance, adequately formal education definitely helps in enhancing the understanding and the skill set. This is because there are specialized iim lucknow courses offered by institutions like IIM Lucknow, which provides necessary knowledge and practical skills to the students.
Below are the advantages of taking courses from IIM Lucknow:
- Access to Experienced Faculty: Many of the courses are taught by faculty members who are yet to bring a wealth of experience and insight that is relevant to the subjects taught.
- Opportunities for Networking: Attending a reputed institution such as this, allows one to interact with professionals and alumni in the course, thus providing chances of working in corporate finance.
- Learning by Doing: Most of the courses are practice-oriented and focus on the application of the learned concepts in real-life situations rather than just learning for examination purposes.
- Up-to-Date Programs: The program lasts for a short period and the program content is revised in line with external environmental dynamics affecting the financial services industry.
- Prospects Enhancing: Getting through a course at a well-known school like IIM Lucknow is very likely to improve your chances of getting a job in corporate finance and better still, help you earn more money.
The Future of Corporate Finance
Taking into account the above-mentioned factors, there are a number of factors that will shape corporate finance in the coming years as the financial landscape is becoming much more complex for business entities.
- Digital Transformation: The control of the various portfolios on the finance operations is expected to be a prime focus as well. New technologies such as AI and blockchain are facilitating Efficiency, fairness, and security in transacting so that the whole process of transaction does not just rely on human beings.
- Sustainability: As the concept of sustainable finance grew, so did the audience focus on the ‘S’ in ESG, particularly as more organisations are considering finance with respect to ESG in their decisions. This is due to the consumers’ and regulators’ expectations that these types of companies would actually contribute to society.
- Globalisation: As the economic and geographical boundaries melt, more companies will begin to merge, thus making it very important for all to know more about global markets and foreign exchange risk. This is because such challenges will be unavoidable to the companies which will go global.
- Data Analytics: Big data provides a new approach to the traditional ways of financial estimating and making decisions. With the assistance of data analytics, it becomes possible for such organizations to assess the state of the market and to apply the most efficient strategic approach towards it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, no one can underestimate the importance of corporate finance to the achievement of any corporation. From understanding the fundamentals of corporate finance to appreciating the need for corporate finance and implementing more corporate finance strategies enables businesses to navigate the stormy waters of finances quite easily.
Additionally, the quest for knowledge by undertaking courses such as those offered at IIM Lucknow is bound to improve one’s appreciation and skills in the subject under discussion. In view of the changing dynamics vis-a-vis the financial environment, always being in the know and being flexible will be paramount in making it in corporate finance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary focus of corporate finance?
The primary focus of corporate finance is on the long-term growth of the business and, in the process, the effective and efficient growth of the business equity as a result of proper financial management.
What are the main components of corporate finance?
The main components comprise capital budgeting, capital structure, working capital management, financial analysis, risk management, etc.