Mathematical implementation and mathematical functionality play a key role in understanding the workings of various physical entities. Creating mathematical models and mathematical measurements is essential to give shape to the theories and concepts. It also plays a vital role in writing code and new-age Machine learning algorithms.
Measurement:
Any attribute of an object that can be assigned with a meaningful number to observe, assess or understand the item is called Measurement. This measurement can be broadly divided into two types:
- Scalars
- Vectors
Scalars:
The measurement of the attribute of the objects doesn’t depend on the direction of the item.
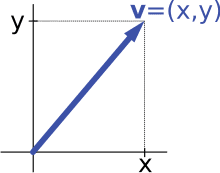 To illustrate the definition let us consider the length between two points. The span between these two points doesn’t change depending on the direction as the size remains the same.
To illustrate the definition let us consider the length between two points. The span between these two points doesn’t change depending on the direction as the size remains the same.
Vectors:
The measurements of the attribute of the objects depend on the direction of the attribute too.
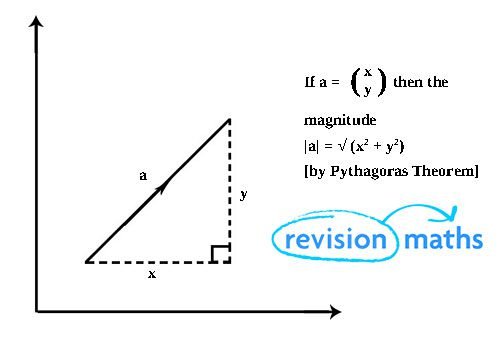
This can be understood by taking the example of force. Force needs a path with the numerical to comprehend the measurement
Vectors are denoted by an Arrow (entirely→).
The direction where the vector points are called the vector’s direction.
Types of Vectors:
- Zero Vector or Null Vector: A zero vector is the vector consisting Zero-Length and no direction
- Unit Vector: A vector that has a magnitude of 1 with a set direction.
- Collinear Vector: If the vectors are parallel to each other or on the same line irrespective of their direction.
- Coplanar Vector: All vectors that lie in the same plane
- Equal Vector: If the vectors have the same magnitude and direction
- Position Vector: A point that can be constituted as a constant point regarding other vectors
Implementation of vectors in Python:
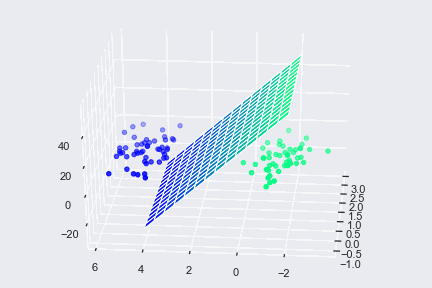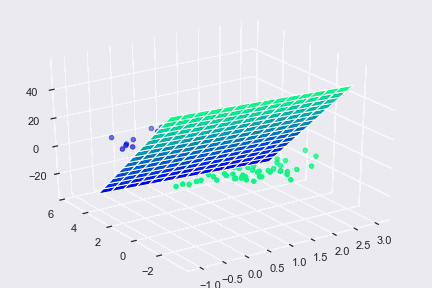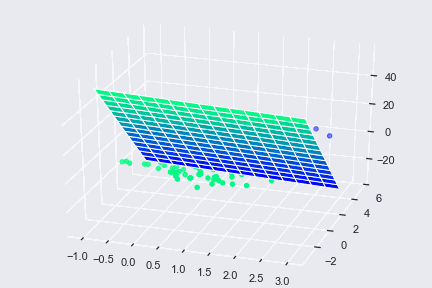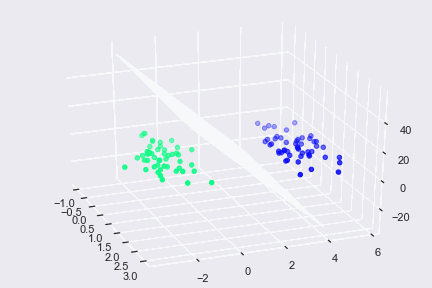
Vectors are a beneficial component not only in computer languages but also in machine learning. Decision-making is one of the most critical aspects of machine learning and vectors, in particular, is used in one such algorithm called Support Vector Machine (SVM). An SVM is used to analyze the given dimensional space for finding optimal hyperplane. The concept of vector/Euclidean distance is used to know the distance between data points and hyperplane.
 To achieve this through machine learning, we use Python as the programming language using libraries such as NumPy, Pandas. Python and the array operations in Python are useful to perform many algorithms such as SVM.
To achieve this through machine learning, we use Python as the programming language using libraries such as NumPy, Pandas. Python and the array operations in Python are useful to perform many algorithms such as SVM.
Therefore, having a prior Python Training is valuable and essential to get a grip on how vector functionalities are applied in more advanced topics such as Machine Learning.
Implementation in Python:
Vector Implementation can happen through arrays in Python. All the vector functionality can be done through libraries like NumPy. Using a simple code, we can implement various basic vector functionalities such as
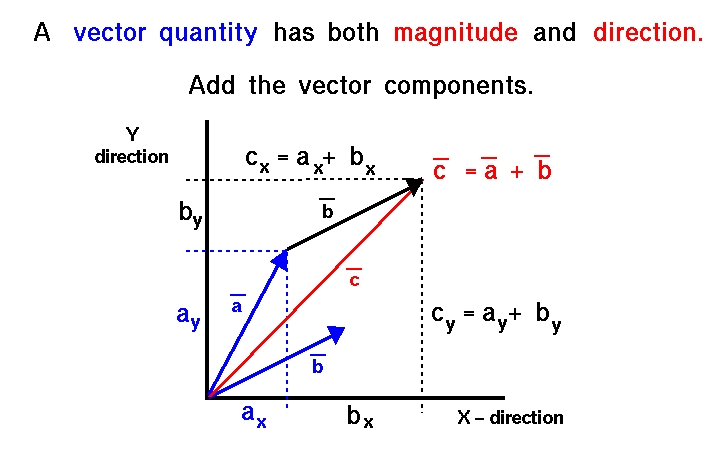
- Vector Addition: The addition of two vectors through Python can be seen here:
import numpy as np #pip install numpy
a=np.array([2,1,3])
b=np.array([4,5,3])
print(a+b)
Output: [6,6,6]
- Vector Subtraction: Subtraction of two vectors through Python can be seen here:
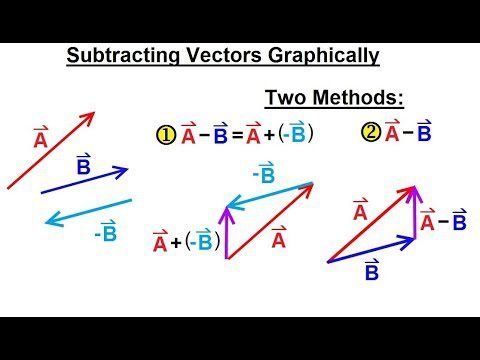
import numpy as np
a=np.array([2,3])
b=np.array([1,-1])
print(a-b)
Output: [1,4]
- Scalar Multiplication: Multiplying a scalar to vector is given below:
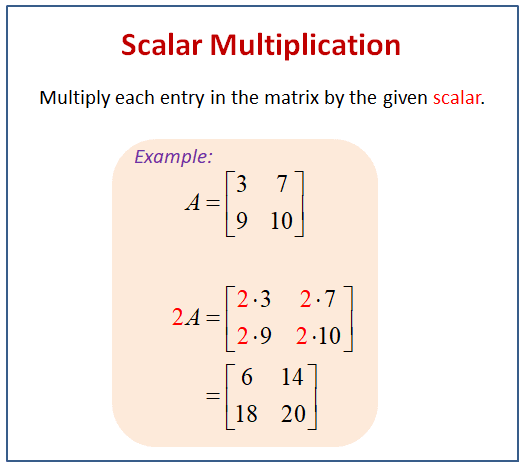
import numpy as np
a=np.array([3,5])
print(3*a)
Output: [9, 15]
- Euclidean Distance calculations: In Euclidean distance calculation the distance is measured between two points and can be done in Python as follows:
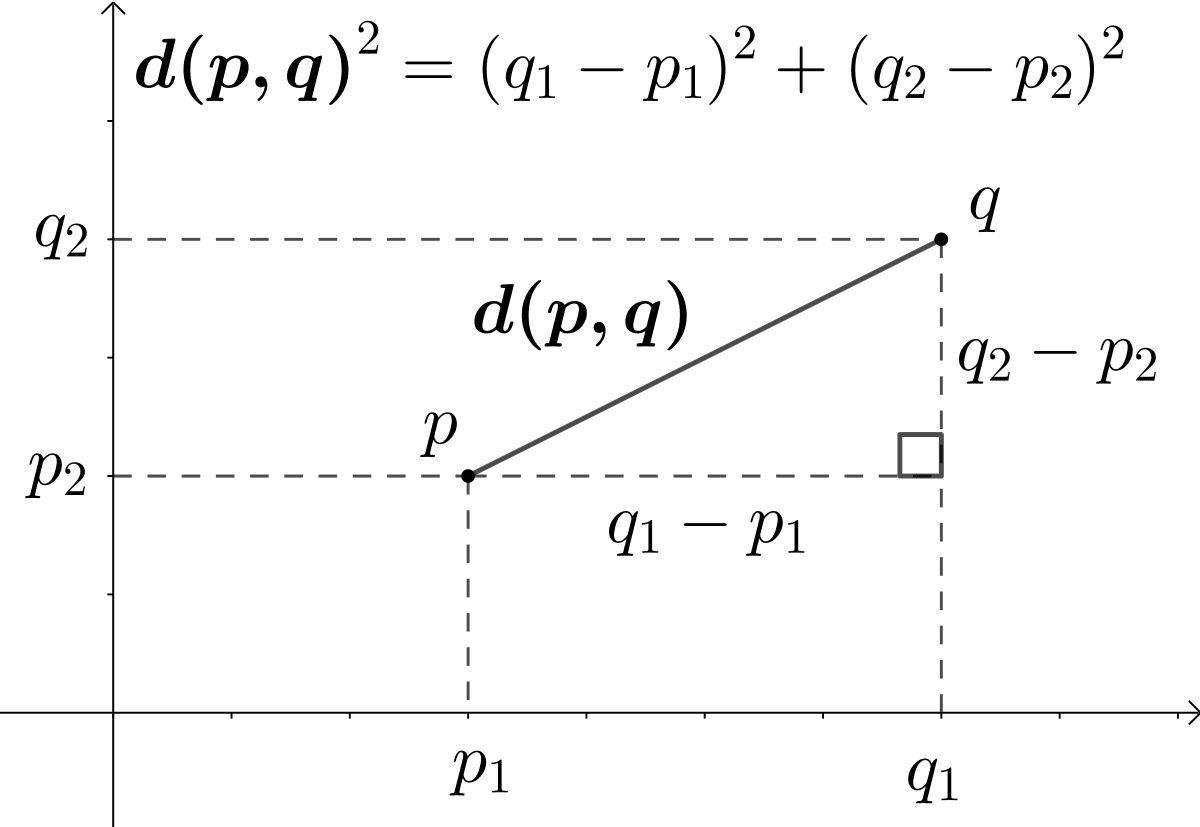
import NumPy as np #pip install NumPy
a=np.array([4,6])
b=np.array([7,-2])
print(np.linalg.norm(a-b))
Output: 8.0622577
These are some of the implementations of vectors in linear algebra using Python. Python is an essential language to understand advanced topics such as machine learning. Therefore, basic Python Training is the best step to ensure a great career.