Financial Accounting transforms transaction information into concise, precise statements to support sound judgment in decision-making to improve profitability.
This article covers financial accounting fundamentals, demonstrates how enterprise operations accounting supports strategy development, and explains how precise accounting drives improved profits.
You will learn valuable insights in everyday life to improve business financial reports, how to improve profits with accounting, financial reporting impact, how to keep businesses financially healthy, and use accounting and profitability as a business tool.
Financial Accounting Fundamentals: Getting Down to Basics
What Is Financial Accounting?
Financial Accounting is the journalising, summarising, and reporting of business transactions that impact a firm’s financial status.
Following standards like IFRS or GAAP prevents inconsistency, ensures transparency, and comparability of a company’s financial reports.
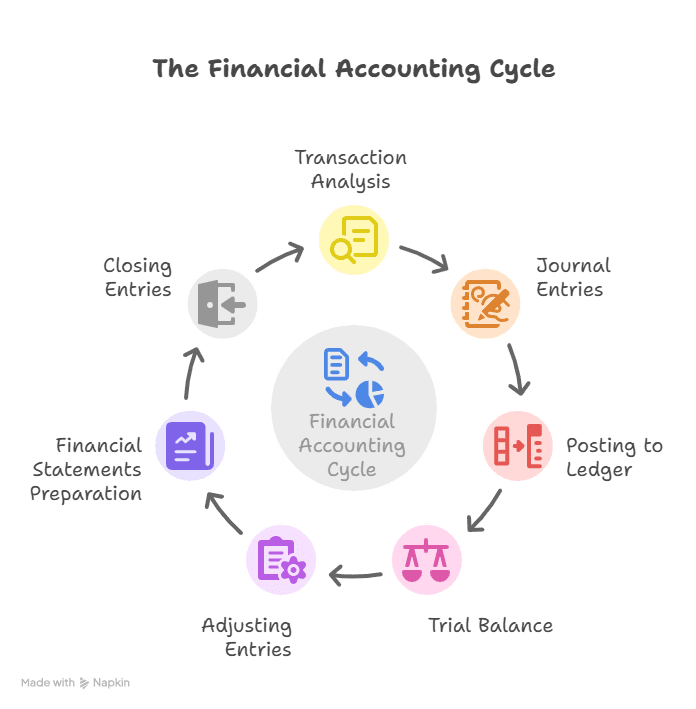
Principles in financial accounting involve recording invoices, journalising to ledger accounts, preparing trial balances, and preparing financial statements.
The orderly procedure of accounting for business transactions ensures consistency and helps create a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial position.
Core Accounting Principles of Financial Accounting Basics
It is important to have knowledge of the major principles of fundamental financial accounting since such principles influence the recognition and presentation of transactions:
Accrual Concept
Accrue revenues when incurred and expense against respective periods in order to represent performance properly.
Matching Principle
Match expenses against respective revenue to disclose the profitability of goods or services.
Materiality
Disclose items which are likely to affect users’ decisions; items such as immaterial do not need to be disclosed.
Prudence (Conservatism)
Do not overestimate revenues or assets; credit expenses and liabilities should be incurred.
Consistency
Use the same accounting policies in each period to ensure comparability.
These standards form a foundation for good accounting and profitability analysis, which instils confidence and enables decision-making by stakeholders.
Why Financial Accounting Matters
Good financial accounting is not just a mere ritual of compliance; it is a foundation for strategic decision-making.
Trend Analysis
Comparison to earlier data enables businesses to record growth patterns and anticipate change within the market.
Resource Allocation
Spending decisions by finance are based on financial information, which invests in the most feasible options.
Compliance with Regulation
Profitability ratios and accounting levels with compliance reduce the risk of penalty, audit, and loss of reputation.
Those businesses which excel at these basics have a strong financial base and a clear route to long-term growth.
Business Financial Reports and Their Function
Business financial reports transform accounting information into beneficial tools for stakeholders. The key reports are:
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Statement of Changes in Equity
Each of the reports has a separate function, yet collectively they provide an overall indication of the finances.
Income Statement: The Profit & Loss Barometer
Profit and loss account or income statement contains revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and net profit or loss for an interval. Major items are:
- Revenue
- Gross Profit (Revenue – COGS)
- Operating Expenses (Marketing, R&D, Administration)
- Net Profit
Managers utilise the income statement to determine high-margin products, track cost drivers, and compare with the competition. For instance, an unexpected spike in COGS could be an indicator that there are inefficiencies in supply that should be cleaned up immediately.
Balance Sheet: Snapshot of Financial Position
A balance sheet shows assets, liabilities, and equity holders’ funds at one point in time with the following equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The most significant accounts are:
- Assets (Current and Non-Current)
- Liabilities (Current and Non-Current)
- Equity (Common Stock, Retained Earnings)
Liquidity is studied by analysts through the use of ratio measures, such as the current ratio (Current Assets / Current Liabilities). An equilibrium balance sheet fosters investor confidence and possesses a high credit rating, ultimately enhancing the company’s overall financial health in the long term.
Cash Flow Statement: Subsequent Cash Flows
Although profitability is the key element, cash flow gives the capacity to meet future obligations. The statement of cash flows categorises cash flows in three ways
- Operating Activities (Cash from core business)
- Investing Activities (Buying or selling assets)
- Financing Activities (Issuance of equity or debt, dividend payments)
With cash inflows and outflows monitored, owners gain a sense of whether the operations are generating sufficient cash, whether dividends can be paid, and when external borrowing can be requested.
Statement of Changes in Equity
This statement records the changes in owners’ equity for a time period. It contains:
- Retained Earnings
- Net Income (or Loss)
- Dividends Paid
- Issuance or Repurchase of Shares
Investors refer to this statement in order to view the way in which profit is shared or reinvested, and this influences growth strategy and dividend policy.
Business Financial Reports Role in Decision-Making
Successful business financial reports play a very significant role in the planning of strategies. CEOs and CFOs make use of such reports for:
- Optimal capital allocation
- Identifying those segments that do not perform well for sale
- Easier merger and acquisition decisions
- Make Projections of Future Performance
For instance, while net profit improves when operating cash flow remains steady or declining, managerial investigation of the causes of working capital management issues is a case in point illustrating how analysis of financial reporting influences provokes remedial action.
Increase Profits with Accounting: Effective Strategies
Manages Expenses Using Cost-Effective Expense Tracking
Another very useful way of maximising profits through accounting is maintaining rigid controls on costs. Separating costs into fixed, variable, direct, and indirect categories enables organisations to identify inefficiencies and optimise their spending. Key activities are:
Automate Expense Reporting
Utilise cloud-based applications to scan receipts, automate expenditure approvals online, and quickly enter data into accounting programs.
Analyse Variance Reports
Compare month-to-month actual vs. budgeted costs and identify overruns quickly and correct them on time.
Negotiate with Vendor Agreements
With sophisticated cost segmentation, accounting functions can negotiate multi-service contract packages, payment terms, or quantity discounts.
These cost-reduction efforts reduce wasteful expenditures and combine profit margins, representative of the value of accounting to business efficiency.
Optimising Revenue Recognition
Accurate revenue recognition posts sales during the appropriate period, eliminating earnings misstatement. Best practices are:
Adhere to Industry Standards
Construction, manufacturing, or software industries might implement specialised techniques (e.g., percentage-of-completion).
Conduct Periodic Revenue Audits
Ensure that all invoices, credit notes, and returns are properly posted; audits will catch any differences or potential fraud.
Embrace Automation
ERP system revenue recognition modules minimise errors and maintain compliance with changing rules.
Truly accurate levels of revenues allow companies to present an honest financial condition picture, engender investor trust, and facilitate fundraising.
Improved Inventory Handling
Inventory prices directly impact the cost of goods sold (COGS) and gross margin percentages. Maximise inventory by:
Selecting the Appropriate Costing Method
FIFO, LIFO, or Weighted Average Cost impacts margins and tax exposure differently.
Implement Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory
Saving on holding costs and obsolescence makes working capital available for growth efforts.
Implement Inventory Analytics
Track stock days, turnover, and slow movers; rebalance reorder points with demand forecasting.
These inventory disciplines are the building blocks of profitability as well as accounting, releasing cash not locked up in overstock.
Strategic Tax Planning
Financial accounting cannot be separated from tax planning. Most effective strategies include:
Recognise Eligible Credits and Allowances
Investigate R&D tax reliefs, capital allowances, and industry-specific allowances to minimise taxable profit.
Postpone Revenue & Depreciate Early
Delay revenue recognition to a subsequent fiscal year or bring forward depreciation benefits to achieve maximum taxation cost.
Investigate Transfer Pricing Strategies
Make sure intercompany transactions comply with local as well as foreign regulations to avert penalties.
Tax compliance in day-to-day accounting decreases liabilities, improves cash flow, and optimises after-tax profitability.
CPA Talent Deficiency
The biggest threat to the accounting profession is the upcoming talent shortage of qualified CPAs. It’s estimated that 75% of existing CPAs are retiring in 15 years, and 2023 yielded the lowest CPA applicants for over 16 years (Becker’s CPA Salary Insights). Organisations can steer clear of this threat by:
- Investment in Training and Development
- Offer sponsored CPA study leaves, mentoring schemes, and regular professional courses.
- Imposing Outsourced Expertise
- Collaboration with existing accounting systems or individual CPAs to offer a stable financial reporting pull.
- Technology Solution Adoption
- Install AI-based accounting software to execute repetitive work so accountants have time for strategic analysis.
- CPA shortage planning offers accounting careers and facilitates profitability.
Business Accounting Tips for Profitability
Enforce Cloud-Based Accounting Programs
Access to real-time information, automatically performed reconciliations, and streamlined integration with CRM, payroll, and inventory modules enhance accuracy.
Perform Monthly Reconciliations
Perform frequent bank, credit-card, and sub-ledger reconciliations to identify differences in a timely fashion and prevent material misstatements.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Monitor gross profit margin, current ratio, ROE, and debt-to-equity ratio to analyse the company’s financial position and make decisions accordingly.
Improve Internal Controls
Segment tasks, impose approval controls, and perform regular audits to minimise fraud risk and provide data integrity.
Implement Cash Flow Forecasting
Develop short- and long-term cash flow projections to forecast working capital requirements and prevent liquidity deficiencies.
Use Scenario Analysis
Evaluate the effect of recession, price volatility, or regulatory environment variations on profitability, utilising budgeting scenarios.
Subcontract Non-Core Functions
Subcontract payroll, accounts payable, or tax return preparation to eliminate overhead and improve efficiency.
Invest in Continuous Training
Encourage employees to obtain ACCA or CPA certification and stay up-to-date with changing accounting standards and technological advancements.
Comparison of Financial Statements
| Financial Statement | Purpose | Impact on Bottom Line |
| Income Statement | Displays revenues, expenses, and net profit/loss | Differentiates profitable units and highlights key cost drivers |
| Balance Sheet | Shows assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity | Reflects liquidity and solvency, influencing investment decisions |
| Cash Flow Statement | Tracks cash flows from operations, investing, and financing | Demonstrates ability to meet obligations and sustain operations |
This analysis emphasises the way in which each of the reports serves strategic decision-making as well as guarantees the financial health of the company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the fundamental concepts of financial accounting?
Fundamental principles of financial accounting consist of the accrual concept, matching principle, materiality, prudence, and consistency, making the financial reports of the business a true representation of performance as well as financial stability.
How does financial accounting increase profitability?
Through examination of business accounting books, firms establish cost centres, enhance expense reporting, maximise revenue recognitions, and implement cost-cutting measures.
Why are accounting reports of a business useful to investors?
They facilitate transparency on revenues, cash flows, and debt, allowing investors to compare company financial well-being, growth potential, and risk.
How frequently must a company release financial statements?
In the past month or quarter, for monitoring internally and year-end accounts for reporting purposes to report for statutory reasons. Reporting timely provides visibility in real-time into profitability and cash position.
Is accounting outsourcing a way to improve profitability?
Payroll processing, bookkeeping, or tax return preparation outsourcing lowers overhead costs, minimises errors, and allows internal employees to dedicate time to strategic analysis.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Financial Accounting is not merely a compliance; it’s a strategic asset. From simple financial accounting principles to tax planning and stock management, business operations are fueled by financial accounting, creating solid decision-making, cost containment, and continued growth.
Key Takeaways
- Clarity Brings Trust: Proper business finance reporting builds stakeholder confidence and brings in investments.
- Insights Optimise Profits: In-depth financial accounting identifies sources of inefficiency, allowing for focused cost-reduction strategies.
- Talent Shortage Plan: With an impending CPA shortage on the horizon, technology and training investments are necessary to bring stability to profitability as well as accounting stability.
Ready to lock down your financial accounting systems and seal up your bottom line? Join Imarticus Learning’s Certified Public Accountant course and gain hands-on skills, industry credibility, as well as the ability to drive your organisation to greater profitability.




