Investment banking is a dynamic and rewarding field. It offers numerous career opportunities and the potential for high earnings.
To succeed, you need the right skills and knowledge. Investment banking courses can provide this foundation.
These courses are designed to equip you with essential skills. They cover topics like financial modelling, valuation, and risk management.
Many courses also offer placement support. This helps students secure jobs after completing their studies.
The CIBOP course is a popular choice in India. It is known for its comprehensive curriculum and placement support.
CIBOP centres are located in Pune, Mumbai, and Bangalore. Each location offers unique advantages and opportunities.
Understanding the details of these courses is crucial. It helps you make informed decisions about your education and career path.
This guide will explore various investment banking courses. It will highlight their benefits, structure, and placement opportunities.
Whether you’re a student or a professional, this information can help you advance your career in investment banking.
Understanding Investment Banking: An Overview
Investment banking is a cornerstone of the financial industry. It plays a crucial role in capital markets.
Investment banks act as intermediaries. They assist clients in raising capital through the issuance of securities.
They also provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions. This involves strategic advice and valuation services.
Investment bankers assist clients in navigating complex financial transactions. Their expertise is vital for major business decisions.
Investment banks offer diverse services. These include trading securities, asset management, and risk management.
A career in investment banking requires strong analytical skills. Communication and negotiation abilities are equally important.
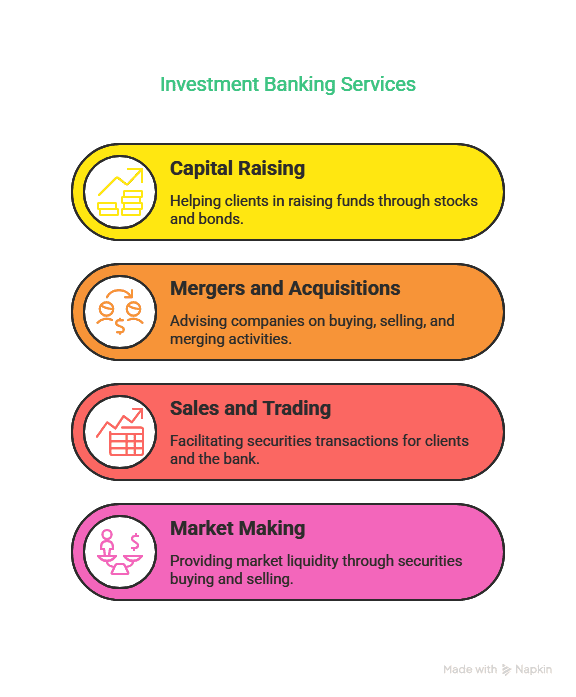
Key Functions of Investment Banking:
- Capital Raising: Assisting companies with issuing stocks or bonds.
- Advisory Services: Providing strategic advice for mergers and acquisitions.
- Trading and Sales: Facilitating the buying and selling of securities.
- Asset Management: Managing investment portfolios for clients.
The fast-paced nature of investment banking attracts ambitious individuals. It offers challenging work and the potential for high financial rewards.
The industry requires ongoing learning and adaptation to remain competitive. As markets evolve, investment bankers must stay informed and flexible.
Understanding the fundamentals of investment banking is essential. It can help you decide if this career path aligns with your aspirations.
Why Choose Investment Banking as a Career?
Choosing a career in investment banking is a decision driven by many factors. It’s known for its lucrative salary packages and bonuses.
A career in this field offers significant career growth. Young professionals can rapidly climb the corporate ladder.
Investment banking provides exposure to high-profile deals. This allows professionals to work with top-tier clients.
The work is intellectually challenging. It requires problem-solving skills and strategic thinking.
Benefits of a Career in Investment Banking:
- High Earning Potential: Attractive salaries with performance-related bonuses.
- Career Progression: Rapid advancement opportunities within the firm.
- Client Exposure: Work on transactions with leading businesses and influential clients.
- Skill Development: Develop a diverse skill set that is valuable across various industries.
Investment banking enhances analytical and technical skills. It fosters a competitive and fast-paced work environment.
This sector offers networking opportunities with industry leaders. Building connections can be beneficial for long-term career success.
Ultimately, investment banking provides a compelling career path. It combines financial rewards, professional growth, and dynamic work experiences.
What to Look for in Investment Banking Courses
Selecting the right investment banking course is essential for achieving career success. Various factors should guide this decision.
Course content is paramount. It should cover financial modelling, valuation, and risk management.
Practical training offers hands-on experience. This bridges the gap between theory and practice.
Key Components to Consider:
- Curriculum Depth: Covers core subjects like M&A, trading, and asset management.
- Industry Connections: Partnerships with financial firms can enhance learning.
- Practical Exposure: Includes case studies, simulations, and real-world projects.
Faculty expertise plays a vital role. Learning from industry veterans can provide valuable insights.
Accreditation is another factor to consider. Accredited courses are more likely to be recognised by employers.
Placement support is essential. Courses with high placement rates offer a significant advantage.
Additional Factors to Assess:
- Class Size: Smaller classes allow personalised attention.
- Alumni Network: A strong network can aid in job placement and career progression.
- Technology Integration: Training in financial software and tools is crucial.
Evaluate the course’s duration and flexibility in scheduling. This ensures it aligns with your current commitments.
A good investment banking course should offer competitive fees. Consider the return on investment in terms of career opportunities.
Research extensively before enrolling. A well-chosen course can set the foundation for a prosperous investment banking career.

The Importance of Placement Support in Investment Banking Courses
Placement support is a key factor when selecting investment banking courses. It provides a stepping stone into the industry.
The competition for investment banking roles is fierce. Courses offering placement support help bridge the gap.
Placement support often includes resume building and interview preparation. These services increase your hiring prospects.
Being industry-ready is crucial. Courses with strong placement records prepare candidates for the real-world challenges.
Benefits of Placement Support:
- Structured Job Searches: Organised processes help locate and secure roles faster.
- Networking Opportunities: Connections with alumni and firms enhance employment prospects.
- Soft Skills Training: Tailored sessions on negotiation and communication enhance employability.
Partnerships with financial institutions add value. Many courses secure placements through their connections.
Placement support increases your return on investment. The career opportunities offset the course costs.
Programs with high placement rates often have strong reputations. This attracts both students and employers.
Understanding the details of these services is vital. Different courses offer varying levels of support and resources.
Investment banking aspirants should prioritise courses with robust placement services. This support can be instrumental in launching and furthering one’s career.
Spotlight on CIBOP: Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional
The CIBOP course is a prominent option in the field of investment banking education. It focuses on operations and processes.
Designed for aspiring finance professionals, CIBOP addresses the core aspects of banking operations. It caters to both beginners and experienced candidates.
As the financial world evolves, this course stands out for its practicality. It provides students with a competitive edge.
Graduates of CIBOP acquire the skills necessary for back-office roles in investment banks. This includes settlements, trade life cycle, and risk management.
CIBOP is offered by Imarticus Learning, a leading provider known for its industry connections. Their training aligns with global banking standards.
Key Features of CIBOP:
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers a wide range of investment banking operations.
- Practical Training: Hands-on learning and real-world case studies enhance understanding.
The course also emphasises soft skills. Effective communication and problem-solving are essential in banking roles.
Recognised by the finance industry, CIBOP is highly regarded by employers. It increases job prospects significantly.
Alumni of CIBOP benefit from strong networking opportunities. These connections can be invaluable for advancing one’s career.
Students can also take advantage of Imarticus Learning’s placement support services. This includes resume workshops and interview coaching.
What is the CIBOP Course?
The CIBOP course is tailored for those entering the banking industry. It focuses on investment banking operations.
The course is intensive and highly detailed. It provides students with a comprehensive understanding of financial processes.
CIBOP prepares candidates for crucial roles in back-office operations. This includes trade settlement and compliance.
Core Areas Covered:
- Trade Life Cycle: Understanding each step from trade execution to settlement.
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing potential financial risks.
The curriculum is thorough. It prepares students for the dynamic investment banking sector. More than technical skills, it fosters a deep understanding of the industry’s operations.
CIBOP Course Details: Curriculum, Duration
The curriculum of CIBOP is comprehensive. It spans various aspects of banking operations.
Modules include trade execution, risk management, and financial regulations. Each topic is vital for operational roles.
The duration of the CIBOP course varies. Typically, it spans several months, blending theoretical learning with practical insights.
Students gain from interactive sessions. These sessions include real-world case studies.
Course Duration:
- Duration: Usually between 3 months, full-time.
Fees can influence choice. However, the return on investment is often justified by the resultant job opportunities.
Hands-on training complements theoretical knowledge. It prepares students for actual workplace challenges.
Imarticus Learning, the offering institution, is known for its commitment to quality education. They ensure that students are industry-ready upon completing the course.
CIBOP Course Locations: Pune, Mumbai, and Bangalore
CIBOP courses are available in major Indian cities. This includes Pune, Mumbai, and Bangalore.
These locations are financial hubs. They offer students ample opportunities for networking and employment.
Each centre offers a unique experience, tailored to its local environment. Facilities in these cities are world-class.
CIBOP centres in these cities are strategically situated. This ensures students have access to industry resources.
Location Details:
- Pune: Offers a blend of academic and cultural exposure.
- Mumbai is known as the financial capital, providing vast opportunities.
- Bangalore: IT and finance blend, ideal for tech-savvy finance professionals.
Proximity to prominent financial institutions benefits students. It enhances learning and job placement potential.
CIBOP Certification and Industry Recognition
Completing the CIBOP course leads to certification. This credential is highly valued in the banking sector.
The course’s reputation and extensive alumni network enhance its value. Employers recognise the course’s rigorous training.
Advantages of CIBOP Certification:
- Industry Recognition: Respected by top banks and financial institutions.
- Credibility: Demonstrates comprehensive knowledge and operational skills.
CIBOP certification opens doors to numerous career opportunities. It signifies a readiness for the demanding world of investment banking operations.
Reasons for Opting for the CIBOP Course
Candidates choose CIBOP for various compelling reasons. The course offers a unique blend of knowledge and practical experience.
Its comprehensive curriculum covers essential banking operations. Students appreciate its depth and breadth.
Imarticus Learning’s reputation adds to the course’s appeal. Its strong ties with the financial industry are a major plus.
Key Reasons to Consider:
- Industry-Relevant Curriculum: Tailored to current banking trends and needs.
- Placement Support: Valuable services that enhance employment prospects.
Many are drawn by the practical training. It equips students with actionable skills for the job market.
CIBOP graduates benefit from networking opportunities. Connections made during the course can be instrumental in launching careers.
Placement Support: Imarticus CIBOP Placements and Success Stories
Imarticus Learning offers robust placement support for CIBOP graduates. This support is vital for a successful career transition.
Their placement program is comprehensive and tailored to each individual. It includes several resources to prepare students for the job market.
Imarticus facilitates resume building and interview preparation. These services help refine candidates’ professional presentation.
A dedicated placement team connects students with leading financial institutions. This network is a significant advantage for job seekers.
Many students land positions in prestigious investment banks. They find roles that align with their skills and ambitions.
Core Services in Placement Support:
- Resume Workshops: Enhance Your Resume for Banking Roles.
- Mock Interviews: Practice simulating real interview scenarios.
Imarticus has a track record of successful placements. Graduates share their journeys and achievements as part of the community.
Success Stories Include:
- Placement in top-tier banks such as JPMorgan Chase.
- Roles secured in critical operations functions.
The support extends beyond course completion. Imarticus alumni can access networking events and continued guidance.
Success stories are numerous. Alumni speak highly of the practical training and dedicated placement services provided.
These stories reflect Imarticus’ commitment to student success. They inspire new students to pursue their career goals energetically.
The reputation of Imarticus Learning’s placement program elevates its status. It’s a critical component of the CIBOP experience, promising a bright future for graduates.
Other Top Investment Banking Courses with Placement Support in India
India offers several renowned investment banking courses. These programs are tailored to equip students with industry-relevant skills.
Many courses provide robust placement support. This feature is crucial for students seeking a seamless transition into a career.
A variety of institutions offer these courses. They boast strong connections with prominent banks and financial firms.
Key Features of These Courses:
- Industry-Linked Curriculum: Courses are designed in collaboration with experienced professionals.
- Networking Opportunities: Extensive alumni networks that facilitate job placements.
Institutes often provide hands-on training. They include practical case studies and real-world scenarios.
Many programs focus on essential skills. Topics often include financial modelling, valuation, and risk management.
Participants benefit from personalised career guidance. This includes resume workshops and interview coaching sessions.
Graduates from these courses often secure competitive roles. Positions range across various departments, including M&A, equity research, and asset management.
Notable Institutions Include:
- National Institute of Securities Markets (NISM)
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) Institute
Completion of these courses often leads to job offers from leading banks. Career advancement becomes more accessible with these endorsements.
Investment Banking Courses in Bangalore
Bangalore offers several top-tier investment banking courses. Known for its tech-savvy environment, the city provides a dynamic learning experience.
Courses in Bangalore focus on practical skills. They often integrate technology with financial strategies.
Highlights of Bangalore Programs:
- Innovative Teaching Methods: Courses use blended learning techniques.
- Strong Industry Ties: Partnerships with local fintech firms for placements.
Graduates benefit from extensive networking opportunities. The city’s vibrant business landscape offers numerous opportunities for career growth.

Investment Banking Courses in Mumbai and Pune
Mumbai, the financial capital, is home to acclaimed banking courses. Pune also hosts respected programs with strong academic foundations.
Courses in these cities offer a diverse range of learning opportunities. They align with the current demands of the financial market.
Notable Features:
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers a range of investment banking topics.
- Placement Support: High placement rates with top financial institutions.
Graduates find roles in major banks and investment firms. Mumbai and Pune remain attractive cities for aspiring bankers.
Online Investment Banking and Finance Courses
Online investment banking courses provide a flexible learning platform. They cater to both beginners and experienced professionals.
These courses encompass a broad range of topics. Participants learn about financial modelling, analysis, and corporate finance principles.
Benefits of Online Courses:
- Self-Paced Learning: Adjust your schedule to your lifestyle.
- Cost-Effective: Often cheaper than traditional classroom courses.
The convenience of online learning cannot be overstated. Students engage with interactive materials through various digital tools.
Courses typically offer comprehensive support. This includes forums, video lectures, and direct communication with instructors.
Graduates of online courses often hold the same qualifications as their traditional peers. Completion of these courses can open doors to various finance-related roles.
Networking opportunities are offered through virtual meetings. Alumni and industry connections facilitate career advancements.

Finance Courses Online: Flexibility and Value
Finance courses online are highly flexible and affordable. They make quality education accessible to a global audience.
These courses focus on essential finance skills. Topics include accounting principles, investment strategies, and risk management.
Key Features:
- Interactive Content: Includes quizzes and practical assignments.
- Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced finance professionals.
Students can fit study time into their busy schedules. This flexibility enhances learning without compromising work or personal commitments.
Investment Courses Online: What to Expect
Investment courses online equip learners with the crucial knowledge needed for investing. Participants gain skills to succeed in various financial environments.
Expect courses to combine theory with practice. The curriculum often includes portfolio management, stock analysis, and studies of the global market.
Core Components:
- Real-Time Simulations: Gain practical experience in simulated markets.
- Case Studies: Analyse real-world financial scenarios.
By completing these courses, learners become well-versed in investment strategies. This knowledge is vital for making informed financial decisions in professional roles.
Corporate Finance Training and Financial Analysis Courses
Corporate finance training is vital for understanding organisational finance management. It covers key areas like capital structure and financial planning.
Participants develop skills to make strategic financial decisions. These decisions help optimise corporate growth and profitability.
Core Elements of Corporate Finance Training:
- Capital Budgeting: Evaluating investment opportunities.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks.
On the other hand, financial analysis courses focus on data interpretation. They teach students how to assess the economic health of a business.
This involves a detailed examination of financial statements. Learners explore balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow analysis.
Benefits of Financial Analysis Courses:
- Decision-Making: Improving analytical skills for better financial decisions.
- Valuation Skills: Learning to evaluate company value accurately.
Both types of courses are beneficial for those aiming to enhance their financial acumen. They offer a practical understanding of complex financial concepts.
Completing these courses equips you with the skills to tackle real-world finance challenges. Graduates often pursue roles in financial planning and investment analysis.
Banking Certification Programs: Boosting Your Credentials
Banking certification programs can significantly enhance your career prospects. They provide recognised credentials that validate your skills in finance.
These programs cater to various banking sectors. Whether you aim for a career in retail, corporate, or investment banking, certifications can guide your path.
Certified courses often cover a wide range of banking operations. They might include regulatory compliance, financial management, and customer service.
Advantages of Banking Certification Programs:
- Credibility: Gain recognised credentials in the banking industry.
- Networking Opportunities: Connect with professionals in the finance industry.
- Skill Development: Acquire up-to-date banking practices.
Such programs are particularly beneficial for career transitions. They assist those entering the banking field for the first time.
By completing a certification, you signal commitment and competence. These aspects are valued by employers seeking skilled professionals.
Investing time in certification pays off with better job opportunities. It positions you as a knowledgeable candidate in a competitive field.
CIBOP Salary in India and Career Prospects
The CIBOP (Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional) course offers a solid foundation in investment banking. It enhances employability within the competitive finance sector.
Upon completion, CIBOP graduates can expect competitive salaries in India. Compensation varies based on experience and location.
Entry-level roles often start with attractive packages. As professionals gain experience, their salary potential increases significantly.
Factors Influencing CIBOP Salary:
- Experience Level: Higher salaries with increased experience.
- Location: Metro cities often offer better compensation.
- Industry Demand: Fluctuates based on market needs.
CIBOP certification opens diverse career paths. Graduates can explore roles in banking operations, risk management, and financial analysis.
Prospects for career advancement are substantial. CIBOP alumni benefit from extensive industry networking opportunities.
Ultimately, investment in CIBOP not only enhances initial salary prospects but also lays the groundwork for long-term career growth. Consistent skill development further enhances these opportunities.
Why Choose Imarticus for CIBOP™?
Imarticus Learning stands out as a trusted name in finance education, with over 12 years of legacy and more than 50,000 learners trained. Their CIBOP™ program offers 100% job assurance with top investment banks, including J.P. Morgan, Capgemini, and BNP Paribas, through a network of over 1,000 hiring partners. The curriculum is designed by industry experts, ensuring real-world relevance and practical application through hands-on training, simulations, and the development of essential soft skills. With flexible learning formats, globally recognised certification, international placement track record, and an average salary package of ₹4 LPA (going up to ₹8 LPA), Imarticus combines expert instruction with guaranteed career outcomes, making it the top choice for aspiring investment banking professionals.

Frequently Asked Questions about Investment Banking Courses
Investment banking courses often raise questions for first-time learners. Below are clear, concise answers to help you understand the essentials of Imarticus Learning’s CIBOP program.
What is investment banking?
Investment banking is a specialised area of finance that helps organisations raise capital and manage complex financial transactions. It plays a crucial role in processes such as IPOs, mergers, acquisitions, and stock issuance.
What are investment banking operations?
Investment banking operations involve the back-end processes that support financial transactions. This includes trade settlement, risk management, clearing, and compliance, ensuring all deals are executed smoothly and accurately.
What will I learn in this course?
The CIBOP course provides over 180 hours of training, focusing on investment banking products, trade life cycles, KYC, AML, and settlement operations. It also includes aptitude and soft skills training for placement readiness.
Does this course include placement support?
Yes. The CIBOP program offers 100% job assurance, along with seven guaranteed interviews, industry-aligned skill training, and soft skills development to ensure you’re fully prepared for placement opportunities.
Who is eligible for this program?
This course is ideal for recent graduates or early professionals (with 0–3 years of experience) from finance, commerce, or business backgrounds. A minimum of 75% attendance and 60% scores in all modules are required for placement eligibility.
Frequently Considered Factors:
- Industry recognition: Ensure the program is accredited and respected.
- Networking opportunities: Consider programs that foster valuable connections within the industry.
Understanding these aspects can help in selecting the right investment banking course that aligns with your career objectives.
Conclusion: Taking the Next Step Toward Your Investment Banking Career
Embarking on an investment banking career can be a transformative experience. It’s essential to choose the right course that aligns with your goals.
Consider factors like placement support, curriculum depth, and industry recognition. Each plays a crucial role in your decision.
A well-chosen investment banking program can provide the skills and network needed for success. Whether you’re starting or transitioning, the right course can make a significant difference.
Next Steps to Consider:
- Research and compare courses: Focus on those with proven placement records.
- Evaluate personal goals and circumstances: Match courses to your career objectives and learning preferences.
- Begin your application process by preparing the necessary documents and gathering any required recommendations.
Taking these steps can lead you toward a successful career in investment banking.