Considering the intricacy of today’s financial environment, the role of CRA has emerged as a crucial one for well-informed investors.
Credit Research Analysts (CRAs) give valuable insights into a borrower’s creditworthiness, aiding in risk aversion and portfolio management.
Through analysing financial statements, industry trends, and macroeconomic considerations, CRAs inform investment decisions based on evidence-based suggestions.
What is the role of a Credit Research Analyst?
A Credit Research Analyst (CRA) analyses credit risk on corporate or sovereign debt securities. The functions of a credit research analyst are:
- Financial statement analysis and ratio analysis
- Industry and macroeconomic analysis
- Monitoring of credit rating changes and market sentiment
- Creation of detailed reports and investment suggestions
These functions ensure that investors are aware of potential threats before investing capital, thereby optimising portfolio stability.
Why Is Credit Analysis Important in Investments?
Credit analysis in investment forms the backbone of fixed-income portfolio management. By analysing a borrower’s capacity for debt servicing, CRAs protect investors from defaults and downgrades. Major advantages are:
- Risk Mitigation: Weak credit profiles are caught early on, avoiding heavy losses.
- Yield Optimisation: Investors are provided with the convenience of controlling risk and return through selecting the right credit spreads.
- Informed Decision-Making: In-depth analysis enables portfolio managers to make informed decisions ahead of time.
How CRAs Conduct Credit Risk Analysis for Investors
The investor credit risk analysis takes a disciplined path:
- Quantitative Analysis: Examination of financial ratios like debt-to-equity, interest coverage and free cash flow.
- Qualitative Analysis: Analysis of management quality, corporate governance and industry outlook.
- Scenario Analysis: Stress-testing balance sheets under adverse economic conditions.
- Comparative Benchmarking: Comparing credit metrics versus peers to pinpoint relative strengths or weaknesses.
Responsibilities and Duties of a Credit Analyst Job Role
A typical Credit analyst job includes:
- Obtaining information from annual reports, bond prospectuses and financial databases
- Cash flow forecasting and debt servicing ability
- Interfacing with corporate management teams and rating agencies
- Publishing credit research notes, risk ratings and recommendation memos
- Tracking contemporaneous credit events and market announcements
- These responsibilities assist in ensuring investors have updated information, allowing for timely portfolio rebalancing.
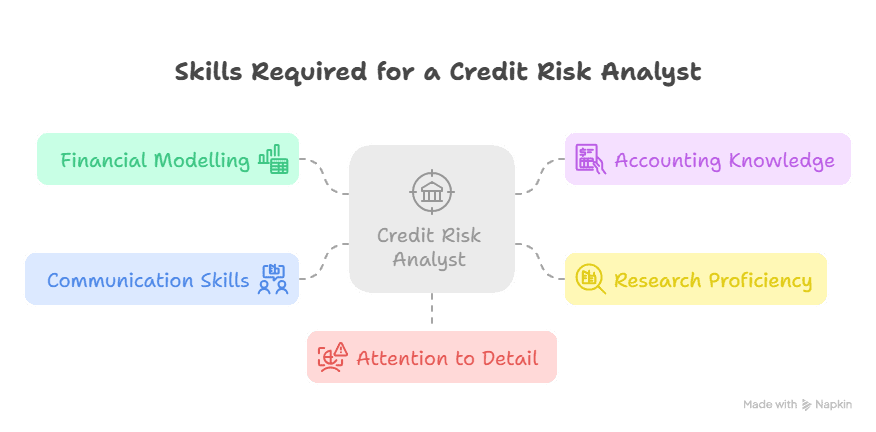
Skills and Qualifications to be a CRA in Financial Markets
It takes both technical and soft skills to be a CRA in financial markets. These are some of the primary requirements:
- Financial Modelling: Excel, VBA or Python skills for forecasting and ratio analysis.
- Accounting Knowledge: Familiarity with balance sheets, income statements and cash flow statements.
- Research Proficiency: Capacity to analyse industry reports, economic data and regulatory filings.
- Communication Skills: Capacity to compose short research reports and communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Attention to Detail: Identifying insignificant credit risks that could impact ratings.
Some potential CRAs aim to acquire the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) certificate as a way of increasing their credentials. For example, the Imarticus Learning CFA Certification Program trains applicants with greater insight into credit fundamentals, portfolio management and ethics.
The Importance of Credit Research in Financial Markets
The significance of credit research cannot be exaggerated. Investors depend on CRAs for
- Early distress or default warning indicators
- Geography versus sector comparisons
- Identification of overpriced or mispriced debt securities
- Macro and regulatory trend data
- Lacking strong credit research, portfolios can become vulnerable to concealed threats, ultimately diluting investment returns.
Salary Expectations: Credit Research vs. Companion Functions
Career planning cannot ignore compensation trends. This is a table of salary details of professionals who are taking credit-related courses such as the CFA. These figures are used as a reference for CRAs and similar roles:
| Designation | Average Annual Salary (₹) |
| CFA Level 1 Candidate | ₹9,80,000 |
| CFA Level 2 Candidate | ₹13,50,000 |
| CFA Level 3 Candidate | ₹17,50,000 |
| Charter Pending (Level 3 cleared) | ₹20,70,000 |
| CFA Charterholder | ₹44,40,000 |
These figures—borrowed from The Wall Street School—emphasise earning power upon going through CFA levels, emphasising the importance of higher certifications for CRAs and credit investors.
Process to become a Credit Research Analyst
Getting successful in the CRA in financial markets entails candidates normally going through:
- Education: Bachelor’s degree in finance, accounting or economics.
- Certifications: Obtaining certifications like the CFA, Financial Risk Manager (FRM) or specialist credit courses.
- Practical Experience: Junior analysts or interns at banks, rating agencies and asset management firms.
- Networking: Establishing connections with industry professionals using LinkedIn, conventions and finance forums.
- Continuous Learning: Updating oneself on market trends, regulatory updates and enhancing credit methods.
Most of these candidates also join the Imarticus Learning CFA Certification Program to access a comprehensive learning framework, mentorship, and case study exposure, preparing them for the challenging task of credit research.
What is Credit Risk Analytics? – #KnowledgeBytes | Imarticus Learning
Table: Main Responsibilities vs. Essential Skills
| Responsibility | Essential Skill/Tool | Result |
| Financial Statement Analysis | Excel, Financial Ratios | Correct cash flow projections |
| Industry Research | Bloomberg Terminal, Bloomberg Industry Analysis | Awareness of sector-specific risks |
| Credit Report Writing | Word Processing, Data Visualisation | Accurate and concise investment advice |
| Monitoring Macroeconomic Trends | Economic Indicators, News Feeds | Timely risk assessment adjustments |
| Working with Rating Agencies | Communication, Networking | Current knowledge of rating adjustments |
New Lens: ESG Metrics in Credit Analysis
Over the past years, Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) metrics have gained increasing importance in the Significance of credit analysis. New CRAs take into account:
- Environmental Risks: Effect of climate change on a firm’s capacity to pay its debts.
- Social Factors: Labour practices and community relations influence creditworthiness.
- Governance Standards: Board composition, transparency and executive incentives.
Incorporating ESG factors provides a comprehensive view of credit risk, attracting socially responsible investors and reflecting new regulatory trends worldwide. Such an innovative approach distinguishes forward-looking CRAs from conventional analysts and provides investment houses with a competitive advantage.
External Resources and Further Reading
To learn more, refer to the following reliable sources:
- Investopedia: Credit Analysis – Comprehensive overview of credit analysis techniques.
- S&P Global Ratings – International credit rating procedures insights.
- Moody’s Investors Service – Credit approaches and research reports.
- International Monetary Fund Publications – Macroeconomic publications shaping credit markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the underlying role of CRA in investment decisions?
A CRA analyses a borrower’s credit risk based on financial reports, market data and industry trends. Their studies inform investors about default risk and facilitate bond portfolio construction.
What is the difference between credit analysis in investment and equity research?
Credit analysis is concerned with debt servicing ability, cover of interest and repayment. Equity research, by contrast, is concerned with growth prospects, profitability ratios and share valuations.
Why is CRA in financial markets important during periods of economic downturn?
During a downturn, default risk increases as cash flows are reduced. CRAs spot weaker issuers early to enable investors to re-allocate capital and minimise losses.
What are the tools that credit analysts most typically use?
CRAs employ Bloomberg Terminals, S&P Global data feeds, Excel financial modelling, Python or VBA automation, and database subscriptions such as FactSet or Capital IQ.
Can a non-CFA holder still be a successful CRA?
Yes. While CFA credentials are highly prized, practical experience, proper accounting ability, and a research mind can also get one into a successful CRA role.
How do ESG factors impact credit risk assessment for investors?
ESG factors enable CRAs to analyse long-term sustainability risk. For example, weak governance can imply higher default probabilities, while environmental liabilities can burden cash flows.
What is the difference between a CRA and a credit rating agency?
A CRA typically functions as part of an asset management or investment bank, conducting in-house analysis. Standalone credit ratings by credit rating agencies such as S&P or Moody’s are often adopted by most CRAs as a reference point.
What does a credit analyst’s job role include?
Most companies prefer a bachelor’s in finance, accounting or economics. CFA, FRM or specialised credit courses certification makes the candidate better.
How does credit research influence bond yields?
Good credit research constricts spreads and yields since risk perception is reduced. Poor forecasts, however, widens spreads since yields increase to compensate investors for assuming higher risk.
Where does one get training in advanced credit analysis techniques?
Places like the CFA Institute, Risk Management Association and professional training with Imarticus Learning provide thorough training in credit analysis.
Conclusion
Credit Research Analysts have a critical function in influencing investment decisions through in-depth Credit analysis of investments and risk appraisal. Whether you are an aspiring analyst or a seasoned portfolio manager, the nuances of credit research can do much to better your decision-making. Using stringent methodologies, ESG data and sophisticated tools, CRAs enable investors to make better-informed decisions when they enter the debt market.
Key Takeaways
- CRAs Assess Credit Risk: They examine financial, industry and macroeconomic data to estimate default probabilities.
- ESG Additions Enhance Value: Environmental, social and governance additions contain a broad credit analysis in their inclusion.
- Certification and Experience Are Important: Seeking qualifications like the CFA and getting experience “hands-on” are essential for a career in CRAs.
If you’re ready to embark on a rewarding career as a Credit Research Analyst or enhance your credit analysis skills, explore the Imarticus Learning CFA Certification Program today. Gain the industry-relevant knowledge and hands-on experience needed to excel in financial markets.
