Delhi NCR runs on deals. New startups raise funds. Family businesses plan exits. Global funds enter India every year. Each deal needs people who understand valuation, financial models, and strategy. That is where investment bankers step in.
Many students first come across the field in small ways. A classroom discussion on mergers. A news article about a funding round. A curiosity about how investors decide the value of a company. Questions like these explain why interest in Investment Banking in Delhi has steadily grown among commerce students, MBA aspirants, and early career professionals.
Delhi NCR has gradually become an important centre for corporate and advisory activity. Several large companies run their strategy and finance teams from the region. Gurugram hosts consulting firms and financial advisory offices that work closely with businesses across North India. For someone considering a career in finance, this environment makes learning the field more practical, and that is the point where many learners start looking more closely at Investment Banking Courses in Delhi.
This guide takes a closer look at Investment Banking Courses in Delhi and how they connect with real career opportunities in the region. You will see what these programs usually teach, how course fees vary, what skills employers expect from fresh analysts, and which investment banks in Delhi NCR and advisory firms actively hire in the market. The blog also explores internships, entry-level roles, and the types of financial work students can expect once they step into the industry.
Did you know?
The demand for trained analysts has grown sharply in the last decade. According to the India Brand Equity Foundation, India’s financial services sector is expected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2025. A large part of this growth sits inside advisory, private equity, and mergers.
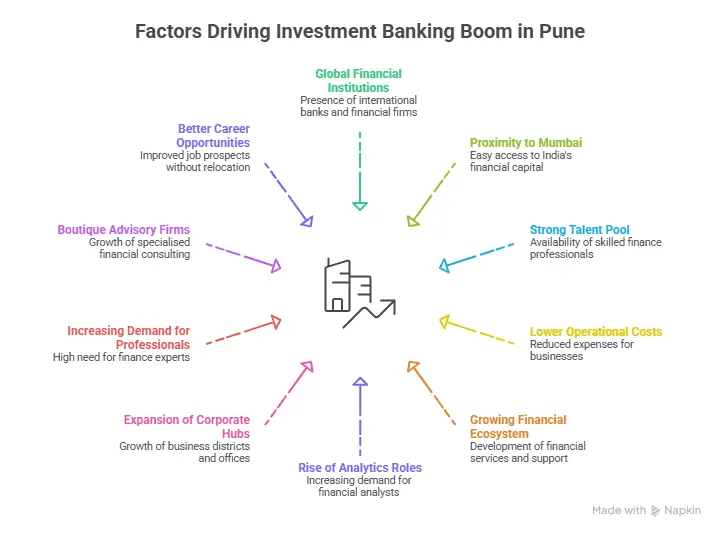
The Rise Of Delhi NCR As An Investment Banking Ecosystem
Many people assume Mumbai runs the finance industry. That is partly true. Yet Delhi NCR has quietly built its own investment advisory ecosystem. Large consulting firms operate from Gurugram. Private equity funds have offices here. Corporate groups also maintain strategy teams in the region.
For someone exploring finance careers, this environment reveals something important about the industry. Investment banking is not only about global financial centres or large Wall Street firms. If you have ever wondered: What is investment banking, looking at the activity around Delhi NCR offers a practical lens into how the field actually functions.
A student who studies close to this environment sees how finance works in the real world. Before looking at training programs, it helps to understand why the region attracts deal advisory activity.
Corporate Headquarters And Advisory Firms
Delhi NCR hosts several corporate headquarters. Many companies prefer to keep strategy teams close to leadership. You will find many investment banking firms in Delhi NCR advising on acquisitions, capital raising, and restructuring. Some firms work with large corporations. Others support mid-sized companies.
Startup Funding Activity
Startups across North India often operate from Gurugram or Noida. Venture capital funds regularly scout deals here. This activity increases demand for professionals who understand valuation.
For example, when a food delivery startup raises funds, investors want to know the company’s worth. Someone must analyse revenue, market size, and projections. That task often goes to analysts working inside investment banking companies in Delhi NCR.
Presence Of Boutique Advisory Firms
Large banks handle billion-dollar deals. Yet many mid-market transactions happen through smaller advisory firms. These firms specialise in sectors such as healthcare, technology, or manufacturing. You will find many boutique investment banking firms in Delhi working with growing companies that need funding or strategic advice.
For many people entering finance, investment banking is one of those terms that appear often but are not always clearly understood. Understanding the role, responsibilities, and the type of work involved can make the industry far easier to grasp for anyone considering a career in this space.
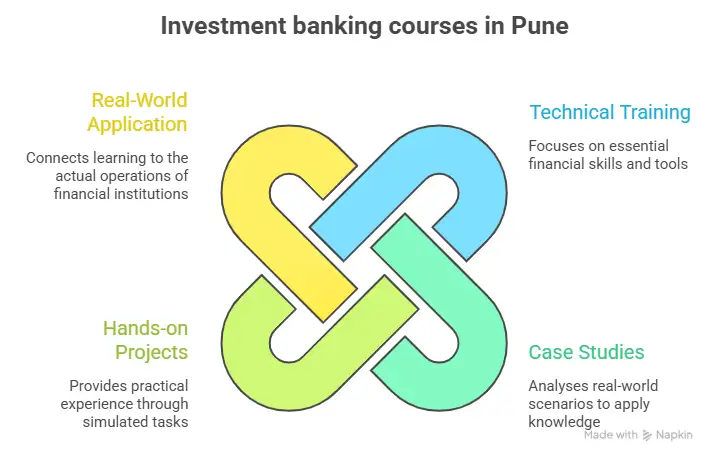
What Investment Banking Courses Actually Teach
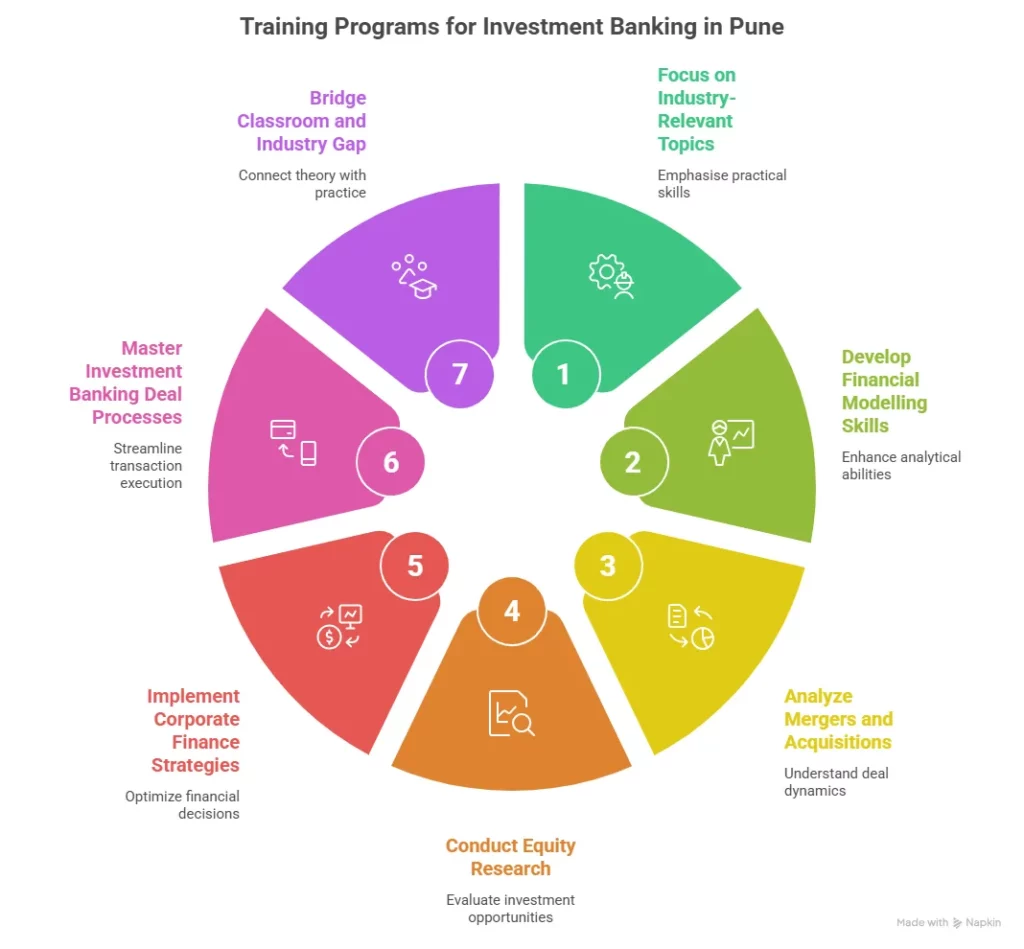
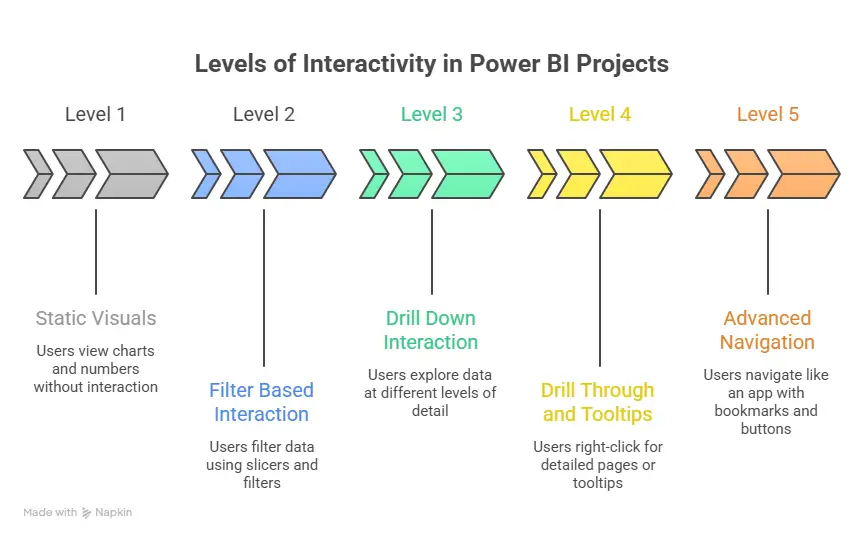
The phrase “investment banking” sounds intimidating. Yet most programs revolve around a few core skills. The goal is to train students to analyse companies and understand deals. Students enrolling in investment banking classes in Delhi usually encounter four important areas of training for investment banking exams.
Think of it like learning how a doctor reads medical reports. Finance professionals learn to read balance sheets, revenue patterns, and industry data.
Financial Modelling
Financial modelling forms the backbone of investment banking. A model is simply a structured spreadsheet that forecasts a company’s future.
Imagine you want to estimate the revenue of a coffee chain over the next five years. You consider store expansion, pricing, and customer growth. All these factors sit inside a financial model. Analysts working inside investment banking companies in Delhi rely heavily on such models.
Business Valuation
Every deal needs valuation. Suppose a manufacturing firm wants to sell a 30% stake to investors. Buyers will first ask one question: What is the company worth?
Courses teach valuation methods such as:
- Discounted cash flow
- Comparable company analysis
- Precedent transactions
These methods help analysts estimate the fair value of a business.
Deal Structuring
Deals rarely move in a straight line. Some involve equity. Some involve debt. Others mix both. Training programs explain how deals are structured. This knowledge becomes useful when working with investment banks in Delhi NCR that handle acquisitions or capital raising mandates.
Excel And Data Analysis
Many new students underestimate this skill. Excel remains the primary tool for financial analysis. Learning shortcuts, formula logic, and model structuring saves enormous time during real projects. Professionals working inside top investment banks in Delhi often build models that run across thousands of spreadsheet cells.
Also Read: What Should Beginners Know About Investment Banking Operations?
Types Of Investment Banking Courses Available In Delhi
Programs vary widely in duration and focus. Some students want quick certification. Others prefer longer career programs. A quick overview helps you decide what suits your goals.
| Program Type | Duration | Key Focus | Who Usually Enrols |
| Short Term Certification Programs | 3-6 months | Valuation, financial modelling, deal analysis | Students preparing for investment banking jobs in Delhi for freshers |
| Financial Modelling Bootcamps | 2-4 months | Excel-based financial modelling and analysis | Commerce graduates, MBA students, and corporate finance professionals aiming for investment banking jobs in Delhi NCR |
| Postgraduate Career Programs | 9-12 months | Technical training, internships, and career guidance | Students seeking structured preparation and industry exposure |
You will find several boutique investment banks in Delhi working closely with growing companies. Such work often takes place within teams working at investment banks in Delhi NCR or advisory firms across Gurugram.
Also Read: How BCom Graduates Can Secure a Job in Investment Banking?
Investment Banking Course Fees In Delhi
Cost varies based on program length and the institute’s reputation. Students exploring investment banking course fees in Delhi often see a wide range. Before looking at numbers, it helps to understand why fees differ. Programs offering internships, case studies, and placement support usually charge more.
| Course Type | Duration | Average Fees |
| Certification Programs | 3 to 6 months | ₹50,000 to ₹1.5 lakh |
| Financial Modelling Bootcamps | 2 to 4 months | ₹30,000 to ₹90,000 |
| Postgraduate Programs | 9 to 12 months | ₹2 lakh to ₹6 lakh |
Students should evaluate curriculum depth, industry exposure, and faculty expertise before deciding.
Also Read: Do Investment Banking Courses Deliver Real Career Value?
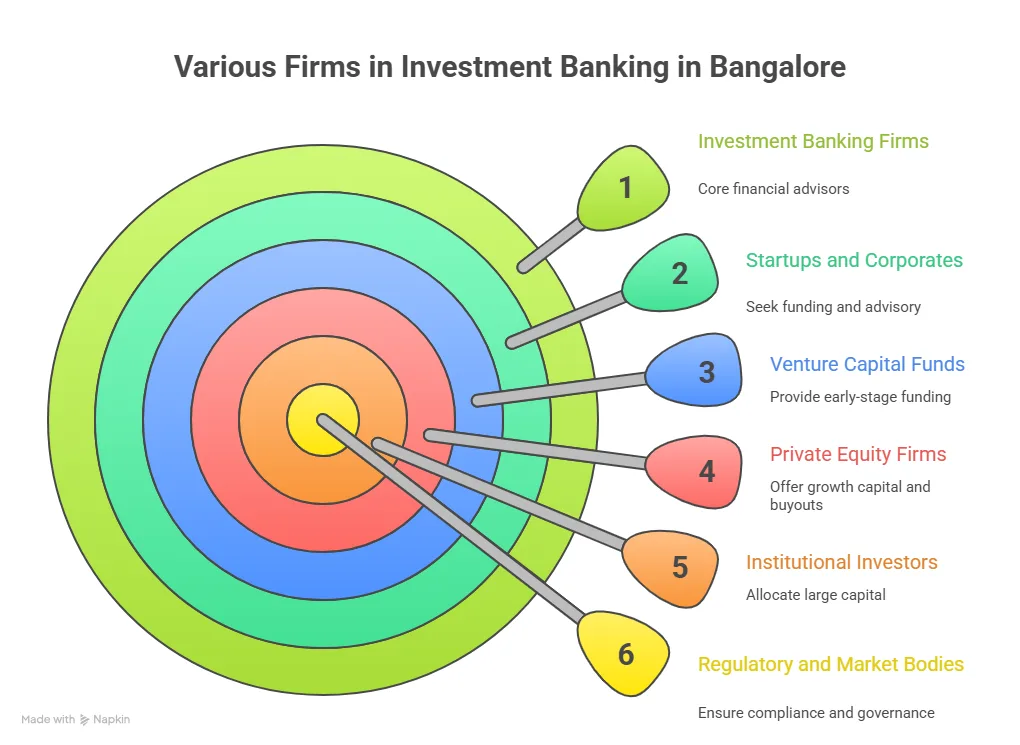
A Quick Look At Investment Banking Firms In Delhi NCR
Before students choose training programs, many also explore the firms operating in the region that hire for high-paying investment banking jobs. The presence of advisory firms increases the chances of internships and analyst roles.
Below are examples of organisations operating across the NCR ecosystem.
| Firm Type | Examples |
| Global Banks | Citi, HSBC, Barclays |
| Indian Investment Banks | Axis Capital, ICICI Securities |
| Advisory Firms | Avendus Capital, JM Financial |
| Boutique Advisors | Singhi Advisors, O3 Capital |
These organisations form part of the broader list of investment banks in Delhi NCR that work on deals across sectors such as infrastructure, technology, and consumer businesses. Many of these firms recruit analysts through internship pipelines. Students who complete industry-oriented Investment Banking Courses in Delhi often target these opportunities as their first step into the field.
Industries Driving Investment Banking Activity In Delhi NCR
Delhi NCR hosts several sectors that attract private equity and corporate investment. These sectors generate advisory work for investment banking companies in Delhi NCR and propel you in your investment banking career.
| Industry | Why It Attracts Investment Banking Activity |
| Technology and Startups | Gurugram and Noida host many startups and tech firms seeking capital to scale. |
| Infrastructure and Energy | Large infrastructure projects require structured financing and investor participation. |
| Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals | Healthcare chains and pharma companies are expanding across India and attracting investors. |
| Financial Services and Fintech | Delhi NCR has many fintech startups and financial service firms attracting investors and strategic partners. |
| Consumer and Retail | Consumer brands and retail chains often expand through partnerships, acquisitions, and investor funding. |
| Manufacturing and Industrial Companies | Many mid-sized manufacturers in North India seek capital to expand production and enter new markets. |
Advisory firms within the list of investment banking companies in Delhi NCR often structure these transactions.
Also Read: How to Become an Investment Banker in India?
Top Investment Banks In Delhi NCR
The classroom teaches concepts. The industry shows how those concepts work in real deals. Many students who explore Investment Banking Degree in Delhi also want to understand which firms operate in the region.
Delhi NCR hosts a strong mix of global banks, domestic institutions, and advisory boutiques. These firms handle mergers, capital raising, restructuring, and private equity transactions.
Boutique Investment Banks In Delhi And Their Role
Large banks usually focus on billion-dollar transactions. Mid-sized companies also need advisory support. That gap is filled by boutique firms. These firms specialise in focused advisory services such as:
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Private equity fundraising
- Corporate restructuring
- Strategic advisory
Many entrepreneurs prefer boutique advisors because the teams are smaller and more specialised. The experience often feels like working with a trusted financial architect who designs a deal from scratch.
Below is an example overview.
| Boutique Advisory Firms | Core Focus |
| Singhi Advisors | Mergers and acquisitions |
| O3 Capital | Mid-market advisory |
| Uniqus Advisory | Strategic finance |
| Allegro Advisors | Growth capital transactions |
These firms also appear on the list of boutique investment banks in Delhi that support companies across North India. Students who join industry-focused Investment Banking Courses in Delhi sometimes secure internships with such advisory firms because boutique firms often value hands-on modelling skills.
Did You Know?
A report from Grant Thornton’s Dealtracker shows that India recorded over 1500+ private equity and venture capital deals in a single year. Each deal requires analysts who build models, prepare investor documents, and support transaction teams.
Investment Banking Internship Opportunities In Delhi NCR
Internships often act as the first step into the industry. Many advisory firms hire interns who can assist with research, financial models, and presentation materials. These internships give students a close look at how deals unfold. Students pursuing Investment Banking Courses in Delhi frequently aim to secure an investment banking internship in Delhi NCR during or after their training.
→ Think of it like working behind the scenes of a film set. The audience sees the final movie. Interns observe the editing, scripting, and production stages.
Internship responsibilities may include:
- Financial statements analysis
- Valuation modelling
- Industry research
- Preparing pitch decks
Internships can last between two and six months. Some institutes partner with advisory firms to help students access these opportunities. Others encourage students to apply independently to firms listed in the list of investment banks in Delhi.
Breaking into investment banking can feel competitive at first, especially for students who are just beginning to explore finance roles. This perspective walks through the practical steps and preparation strategies that often help aspiring professionals move closer to opportunities in the investment banking industry.
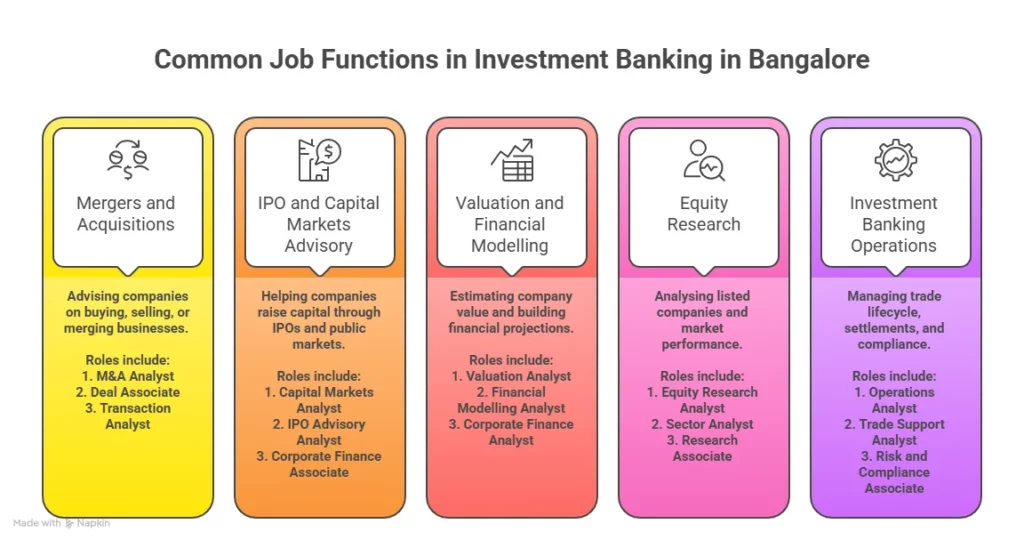
Investment Banking Jobs In Delhi NCR
Many graduates worry about job availability before enrolling in professional training. Delhi NCR offers a growing range of roles across advisory firms, consulting companies, and corporate finance teams. Students who complete practical training often apply for investment banking jobs in Delhi or related analyst roles.
Below are common entry-level roles.
| Entry Level Role | Typical Work |
| Investment Banking Analyst | Financial modelling and deal research |
| Valuation Analyst | Company valuation projects |
| Corporate Finance Analyst | Strategy and financial planning |
| Deal Advisory Associate | Transaction support |
Fresh graduates often start with analyst positions. Over time, they move toward associate and vice president roles. Many organisations across investment banking firms in Delhi NCR also recruit graduates through internship pipelines.
Investment Banking Jobs In Delhi For Freshers
Freshers usually enter the industry through analyst or research roles. These roles may exist within investment banks, consulting firms, or corporate strategy teams. Graduates applying for investment banking jobs in Delhi for freshers should focus on building three capabilities.
- Financial modelling
- Valuation analysis
- Strong Excel skills
A simple example illustrates why. Suppose a technology startup plans to raise funds from private equity investors. Analysts may need to forecast future revenue. They will study customer growth, product pricing, and operating costs.
Also Read: Should You Choose Investment Banking or Commercial Banking?
Investment Banking Salaries In Delhi NCR
Investment banking salary expectations depend on role, experience, and firm size. Analysts usually earn less during the first year. Pay increases quickly as experience grows. Below is a general salary overview.
| Role | Experience Level | Typical Salary Range |
| Investment Banking Analyst | 0-2 years | ₹8 – 15 LPA |
| Senior Analyst | 2-3 years | ₹12 – 20 LPA |
| Associate | 3-6 years | ₹18 – 35 LPA |
| Vice President (VP) | 6-10 years | ₹35 – 70 LPA |
| Director / Executive Director | 10-15 years | ₹60 LPA – 1.2 Cr |
| Managing Director (MD) | 15+ years | ₹1.5 Cr – 3 Cr+ |
These numbers vary across organisations listed among the top investment banks in Delhi and advisory firms across NCR.
Also Read: How Does Investment Banking Pay Compare to Other Finance Jobs?
How To Choose The Right Investment Banking Course In Delhi
Many students search for training options without knowing how to judge course quality. Brochures often highlight placement numbers or software tools. What matters more is how the program prepares you for real analytical work. Students exploring Investment Banking Courses in Delhi should focus on programs that combine theory with practice.
Curriculum Depth
A good program covers the full lifecycle of a transaction. This includes financial modelling, valuation methods, and deal structuring. Students who want to work with investment banking firms in Delhi should ensure the curriculum includes mergers and acquisitions case studies.
Real Financial Models
Excel models are the backbone of the profession. Programs should include detailed modelling exercises using real company data. This practice prepares students for investment banking roles across companies in Delhi NCR.
Industry Exposure
Some programs collaborate with advisory firms for guest lectures or project work. This exposure helps students understand how deals move from discussion to execution. Courses connected with professionals working in top investment banks in Delhi often provide stronger industry insights.
Internship Opportunities
Internships provide the first real experience of financial advisory work. Programs that assist students in securing an investment banking internship in Delhi NCR create a smoother transition into professional roles.
Students pursuing B.Com often spend the first few years focused on exams and theory, without always seeing how those subjects connect to real careers in finance. As graduation approaches, questions about the next step become more urgent. This discussion looks at the choices B.Com students are increasingly considering as they plan their career paths before the year comes to a close.
Skills That Employers Value Most In Investment Banking
Technical knowledge matters. Yet recruiters also evaluate how candidates think. Analysts often work under tight deadlines. They must interpret financial data quickly and present insights clearly. A student aiming for investment banking jobs in Delhi NCR should build the following skills.
| Skill | Why It Matters In Investment Banking |
| Financial Curiosity | Analysts constantly study businesses, markets, and financial data to understand how companies grow and generate revenue. |
| Attention to Detail | Even small numerical errors can affect valuation models and deal analysis. Precision is critical during financial modelling. |
| Communication Skills | Analysts must present financial insights clearly to clients, investors, and senior deal teams. |
| Structured Thinking | Complex deals involve many variables. Analysts must organise data logically to support clear recommendations. |
These abilities become essential when applying for investment banking jobs in Delhi for freshers.
Also Read: How Can You Master the Investment Banking Career Path?
Why Choose Imarticus Learning For Your Investment Banking Certification
When exploring Investment Banking Courses in Delhi, the institute you choose often makes a significant difference. Learners today choose the Investment Banking in Delhi certification from Imarticus Learning because of their practically oriented curriculum. The course is designed to bridge the gap between theoretical finance education and the operational skills required in investment banks and financial institutions.
Here are some of the key aspects that make the program stand out for students who want structured training before entering the investment banking industry.
- 100% Job Assurance With Interview Opportunities: The program offers job assurance support and helps learners secure interviews with hiring companies. Students receive a minimum of seven guaranteed interview opportunities with investment banking and financial services firms.
- Industry Relevant Skill Development: The curriculum focuses on core skills used in investment banking operations, including securities operations, wealth and asset management processes, and financial market workflows.
- Structured Program Duration: The program typically runs for around three months full-time or six months part-time, making it a relatively fast pathway for learners who want to enter investment banking operations roles quickly.
- Strong Placement Record: The program has historically reported around an 85% placement rate with salaries reaching up to ₹9 LPA, reflecting its industry alignment.
- Real-World Investment Banking Operations Curriculum: The course covers areas such as securities, derivatives, financial markets, AML, and risk management, which are critical for roles in investment banking operations divisions.
The course aims to prepare learners for leading careers in investment banking operations teams, treasury divisions, and financial services firms.
FAQs About Investment Banking Courses in Delhi
Clarity matters before choosing any finance program. A few frequently asked questions around eligibility, career paths, and certifications are discussed below that come up while researching Investment Banking Courses in Delhi. The answers below bring clarity to these areas.
Which Is The Best Course For Investment Banking?
Students usually evaluate programs based on curriculum, faculty expertise, and industry exposure. Among the many Investment Banking Courses in Delhi, structured career programs that include financial modelling, valuation training, and real transaction case studies tend to offer stronger preparation for analyst roles. Imarticus Learning have developed programs designed to bridge classroom learning with the expectations of firms operating across the NCR financial ecosystem.
What Is The Best Course For Financial Modeling In Delhi?
Financial modelling programs that focus on real company data and deal scenarios often deliver the best learning outcomes. Many professionals who work with investment banking companies in Delhi NCR rely heavily on Excel-based financial models. Training programs offered by Imarticus Learning emphasise hands-on modelling practice, which helps students prepare for technical interviews within advisory firms and consulting organisations.
Which Is The Best Investment Banking Course For Working Professionals?
Working professionals often prefer flexible programs that allow evening or weekend learning. Some Investment Banking Courses in Delhi are designed specifically for professionals who want to transition from accounting, consulting, or corporate finance roles into deal advisory careers. Programs offered by Imarticus Learning combine online learning with case studies so professionals can develop practical modelling skills without leaving their current jobs.
What Is The Best Certification Investment Banking Course?
Certification programs focusing on valuation, financial modelling, and deal structuring often provide the fastest entry point into the industry. Many institutes offer short-term certifications, yet the most effective Investment Banking Courses in Delhi include practical projects that simulate real advisory transactions. Imarticus Learning’s courses include case studies and industry projects that mirror the workflow followed by analysts in investment banks.
Is CFA Only For Investment Banking?
The Chartered Financial Analyst program covers investment management, portfolio analysis, and financial markets. While many professionals working in asset management pursue this qualification, it also supports roles within investment banking firms in Delhi NCR that require strong financial analysis skills. However, candidates often complement CFA studies with specialised Investment Banking Courses in Delhi to build practical modelling and deal advisory capabilities.
Who Is Eligible For Investment Banking Course?
Most training programs accept graduates from commerce, business, engineering, or economics backgrounds. Students interested in corporate finance or deal advisory careers often enrol in Investment Banking Courses in Delhi after completing undergraduate studies. Institutes Imarticus Learning also admits MBA students and early career professionals who want to develop advanced financial modelling skills before applying for analyst roles.
Is Investment Banking A Good Career?
Investment banking offers strong financial rewards and exposure to strategic business decisions. Professionals working within investment banks in Delhi NCR participate in mergers, acquisitions, and capital raising deals that shape corporate growth. Students who complete rigorous Investment Banking Courses in Delhi and build strong analytical skills often find rewarding opportunities across advisory firms, consulting companies, and private equity organisations.
Which Is Better, MBA Or Investment Banking?
An MBA provides a broad management education covering marketing, operations, and leadership. Specialised Investment Banking Courses in Delhi focus specifically on financial modelling, valuation analysis, and deal structuring. Many professionals combine both pathways by completing an MBA and then pursuing specialised training with Imarticus Learning to prepare for roles within investment banking companies in Delhi NCR.
Where Your Journey With Investment Banking Courses In Delhi Can Begin
By now, you probably see investment banking a little differently. It stops looking like a distant Wall Street idea and starts to feel like a real career path that people build step by step. Delhi NCR has become a good place to learn this craft. Many companies keep their strategy and finance teams here. When you begin to notice this ecosystem, it becomes clear why many students look for Investment Banking Courses in Delhi when they want to step into the field.
For students who want that kind of practical learning, Investment Banking in Delhi offered by Imarticus Learning focuses on hands-on modelling, valuation techniques, and projects inspired by real corporate transactions. The aim is simple. Help learners move from understanding finance concepts to applying them in situations that resemble the real world of advisory firms and corporate finance teams.
Every career in investment banking begins in small ways. A spreadsheet that finally makes sense. A valuation exercise that clicks after several attempts. A case study that suddenly shows how a company’s strategy connects with its numbers. If those moments interest you, exploring the right investment banking jobs in Delhi is the step that turns that curiosity into something far more meaningful over time.