Table of Contents
If you’re exploring a career in risk management or finance, chances are you’ve already come across FRM. And once you hear about it, the next question usually follows almost immediately: what exactly does the FRM syllabus include?
That’s an important question – because the FRM certification isn’t just another finance course you add to your resume. It’s a specialised, globally recognised qualification designed for people who want to understand how financial risk actually works in the real world. From market fluctuations to credit defaults and financial crises, FRM focuses on how institutions measure uncertainty, manage exposure, and protect capital.
In other words, it’s not a surface-level program. It’s built for those who want to move beyond theory and develop a deeper understanding of how financial decisions are made under risk.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the FRM syllabus clearly and practically. You’ll get a detailed look at the FRM course curriculum, the exam pattern, and the overall course structure – so you can understand what the journey really involves before you begin.
Did you know?
The FRM syllabus is updated regularly to stay aligned with real financial markets and global risk practices. This means what you study isn’t outdated theory – it reflects how banks, investment firms, and financial institutions currently measure and manage risk.
What is FRM?
A lot of students exploring finance careers eventually come across the question: What is FRM, and why is everyone talking about it?
FRM stands for Financial Risk Management, which is a globally respected certification awarded by the Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP). It’s a course designed to help people understand how financial risks work and how organisations manage them.
The program delves deeply into identifying, analysing, and managing various types of risk. The FRM Syllabus covers:
- Market risk
- Credit risk
- Operational risk
- Investment risk.
Because of this, FRM is highly valued in roles across banking, risk analytics, treasury, asset management, and even financial regulation.
If a job involves making financial decisions or protecting companies from losses, FRM syllabus knowledge becomes extremely relevant. Before registering, it’s important to understand the overall FRM fees, including enrolment, exam registration, and study resources, so you can plan your investment clearly.
FRM Course Structure
Before examining the subjects and getting into the FRM syllabus details, it is helpful to understand how the FRM course is actually structured.
The FRM exam curriculum is divided into two levels:
- FRM Part 1 – Focuses on the foundations and tools of risk management. This is where you build strong conceptual clarity in quantitative methods, financial markets, and core risk principles.
- FRM Part 2 – Focuses on practical application. This is where you learn how risk management works inside banks, investment firms, and financial institutions in real-world scenarios.
You need to clear Part 1 before attempting Part 2. The good part? With the right planning and consistent study, many students complete both levels within a relatively short time and start positioning themselves for specialised risk-focused roles.
Watch this insightful video before you dive deeper into preparation, which can give you a clearer picture of how the FRM course works, how the exams are structured, and how the certification can shape your career in risk management and finance.
FRM Syllabus & Topics Breakdown
The FRM Certification syllabus is designed to build strong, practical expertise in financial risk management, not just exam knowledge. The FRM syllabus is carefully structured to help you think and work like a real risk professional from day one.
FRM Part 1 Syllabus
The FRM Part 1 Syllabus is built around four core areas that form the backbone of real-world risk management. This is where you stop thinking like a student and start thinking like a risk professional.
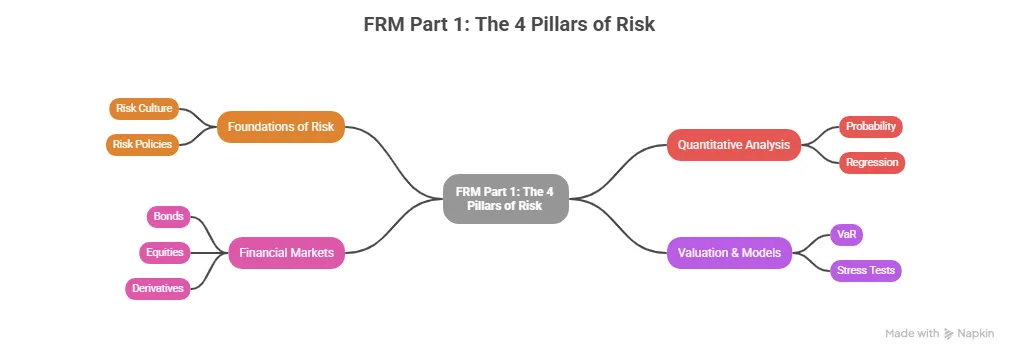
1. Foundations of Risk Management
This is where everything begins. You learn how financial institutions identify, measure, and control risks – from market crashes, credit defaults, liquidity problems, and operational failures. Instead of abstract concepts, you start seeing how risk policies are designed, how limits are set, and how decisions are made in real risk teams.
2. Quantitative Analysis
This is the language of risk. Here you work with statistics, probability, distributions, and regression models. It may sound technical, but this is what allows you to convert uncertainty into numbers that decision-makers can act on. You learn how models predict losses, how confidence levels are built, and why data drives every risk report you see in a bank or investment firm.
3. Financial Markets & Products
This section connects theory with actual financial instruments. You study and understand how bonds, equities, derivatives, futures, and options work, and more importantly, how risk is involved in each product. You understand why a sudden interest rate change impacts bond prices, how derivatives hedge portfolios, and how trading desks manage exposure.
4. Valuation & Risk Models
This is where everything comes together. Here, you learn tools like Value at Risk (VaR), stress testing, scenario analysis, and pricing models. These aren’t academic formulas but the exact frameworks that banks use every day to measure portfolio risk, prepare for extreme market events, and comply with regulatory requirements.
And this is what makes the FRM syllabus different. You’re not memorising chapters to clear an exam. You’re learning the same methods that power:
- Daily risk dashboards in banks
- RBI stress testing frameworks
- Portfolio risk limits
- Hedge fund exposure models
By the time you finish FRM Part 1, you’re not just prepared for an exam. You’re trained to think like someone who manages risk for a living.
FRM Part 2 Syllabus
FRM Part 2 is where you move from understanding risk to managing it. Part 1 builds your foundation. Part 2 puts you in the decision-maker’s seat. This is the level where you start thinking like someone responsible for protecting portfolios, institutions, and capital.
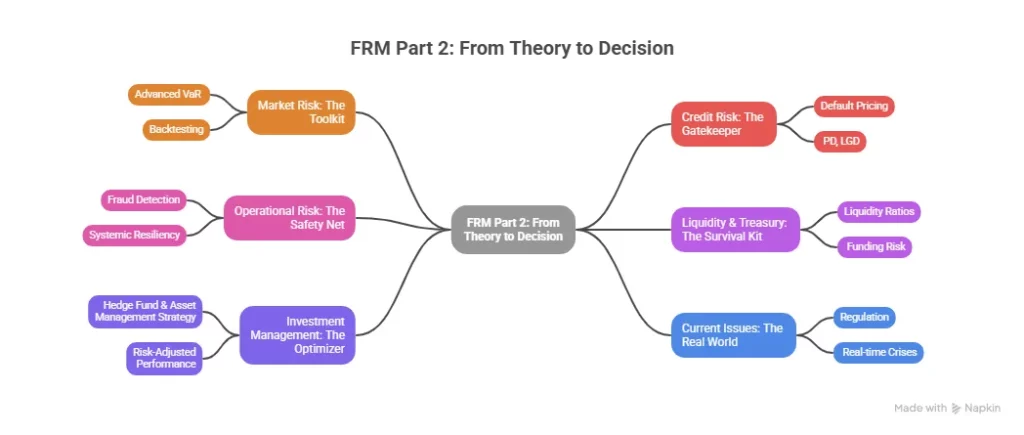
1. Market Risk Measurement & Management
Here, you go deeper into how market risk is actually monitored and controlled. You work with advanced VaR models, backtesting, stress testing, and scenario analysis. You learn how trading desks set risk limits, how breaches are handled, and how banks prepare for extreme market movements. This is the toolkit behind every market risk report that goes to senior management.
2. Credit Risk Measurement & Management
This is one of the most powerful parts of the FRM syllabus. You learn how banks evaluate borrowers, price default risk, and manage large loan portfolios. From probability of default (PD) to loss given default (LGD), you understand how credit decisions are quantified. This is exactly how banks decide whether to lend, how much to lend, and at what risk premium.
3. Operational Risk & Resiliency
Risk isn’t only about markets and credit. This section shows you what happens when systems fail, processes break, or compliance is ignored. You study fraud risk, cyber risk, regulatory risk, and business continuity planning. In today’s digital world, this knowledge is becoming as critical as market risk itself.
4. Liquidity & Treasury Risk Management
This is about survival. You learn how banks ensure they always have enough cash to meet obligations. You study liquidity ratios, funding risk, and stress liquidity planning. This is what prevents institutions from collapsing during financial crises.
5. Risk Management in Investment Management
Here, you step into the world of asset management and hedge funds. You learn how portfolio managers control risk while chasing returns. Concepts like portfolio diversification, risk-adjusted performance, and exposure management become practical tools rather than textbook ideas.
6. Current Issues in Financial Markets
This keeps the FRM syllabus relevant. You study real-world case studies, regulatory changes, and market crises. It connects everything you learn to what is happening right now in global finance.
FRM Part 2 is not about passing another exam. It’s about becoming trusted with responsibility.
This is where you learn:
- How banks protect billions in capital
- How portfolios are defended during market crashes
- How institutions survive financial stress
- How risk teams influence business decisions
After Part 2, you’re no longer just qualified. You’re equipped to sit in real risk roles and make a real impact.
FRM Part 1 tests foundations across four domains. When Indian professionals enrol, they’re not just studying for exams – they’re building frameworks that appear in RBI stress tests, bank risk committees, and hedge fund quant desks across Mumbai, Bangalore, and Delhi.
Did you know?
FRM is considered one of the most specialised finance certifications globally because it focuses entirely on risk, a function every financial institution depends on to survive market uncertainty.
What Makes the FRM Curriculum Unique
One of the biggest reasons the FRM course stands out is its strong focus on real-world application. The FRM course curriculum isn’t designed to just help you clear an exam – it’s designed to help you think and work like a risk professional.
Instead of focusing only on definitions or textbook theory, the FRM exam syllabus prepares you for the kind of situations risk managers deal with every day inside banks, financial institutions, and large corporations. You don’t just learn what risk is; you learn how to identify it, measure it, and respond to it.
Throughout the program, you’ll develop the ability to:
- Interpret risk reports and understand what the numbers actually mean for an organisation.
- Understand regulatory frameworks and how global financial regulations impact decision-making.
- Apply financial models in uncertain environments, where outcomes aren’t always predictable.
- Think like a risk manager, evaluating scenarios rather than memorising formulas.
This practical orientation is exactly why FRM is respected across the financial industry. Employers know that someone who has gone through the FRM curriculum has been trained to analyse risk thoughtfully and make informed decisions – not just perform calculations.
Here’s what to expect in the FRM exam curriculum:
- FRM Part 1 is more quantitative and concept-heavy. It focuses on building your foundation – statistics, financial markets, valuation models, and core risk concepts.
- FRM Part 2 is more application-driven. It tests how well you can use those concepts in real-world situations involving market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and investment risk.
Most serious candidates spend around 200 to 250 hours per part preparing. That may sound like a lot, but when spread across a few months of steady study, it becomes manageable. With the right planning and consistency, most students are able to navigate it successfully.
To help you get a clearer perspective, here’s a quick video that offers a practical look at where FRM stands in 2026 and who benefits most from pursuing it.
FRM Exam Pattern
Understanding the FRM exam structure – including duration, question format, and difficulty level helps you plan preparation more strategically.
The FRM exam is divided into two parts, and both are computer-based. Each part tests not just your knowledge of the FRM syllabus but also your ability to apply concepts under time pressure.
Here’s what the exam pattern generally looks like:
| FRM Exam Component | Details |
| Exam Levels | FRM Part I and FRM Part II |
| Exam Mode | Computer-based exam |
| Duration | 4 hours for each part |
| Question Type | Multiple-choice questions |
| Negative Marking | No negative marking |
| Exam Windows | Conducted multiple times a year (typically May, August, and November) |
FRM Preparation Strategy
Most students take around 4 to 6 months to prepare for FRM Part I. The exam tests your conceptual foundation across quantitative analysis, financial markets, and risk models.
Consistency matters more than long study marathons tocomplete the FRM syllabus. A practical study plan usually looks like:
- 2-3 hours of study on weekdays
- 4-6 hours on weekends
- Regular mock tests and revisions
After clearing Part I, FRM Part II typically takes another 4 to 6 months of focused preparation. This level requires a deeper understanding and application rather than memorisation. You’ll again need consistent daily study, case-based practice, and weekly mock tests to stay exam-ready.
In short: If you register early, pay your fees, plan your preparation calmly, and see FRM fees as a step toward long-term career security, not just another exam expense.
Register early, plan your preparation calmly, and look at FRM fees as an investment in long-term career security rather than just another exam expense.
If you’re evaluating timelines, understanding the FRM course duration also helps you plan preparation realistically alongside work or studies. Most candidates complete both levels within the typical FRM course duration, which depends on study consistency and work commitments.
Also Read: FRM Salary in India: Roles, Pay Scale, and Career Growth
Who Should Pursue FRM?
FRM is a specialised global certification designed for people who want to build careers in financial risk management, banking, analytics, and strategic finance roles. It goes beyond textbook finance and focuses on how banks, investment firms, and financial institutions identify risks, measure them, and control them.
If you’re wondering whether the FRM course aligns with your background and career direction, this table will give you clarity.
| Qualification / Background | Is FRM a good fit | How FRM Helps |
| CMA | ✅ | Moves you into risk and strategic finance roles. |
| CA | ✅ | Moves you into risk and strategic finance roles. |
| ACCA | ✅ | Adds risk expertise to global finance roles. |
| CPA | ✅ | Useful for advisory and financial analytics roles. |
| CFA | ✅ | Useful for advisory and financial analytics roles. |
| MBA (Finance) | ✅ | Useful for advisory and financial analytics roles. |
| BCom Graduates | ✅ | Helps you specialise early in finance and risk. |
| MCom Graduates | ✅ | Adds practical, industry-focused skills. |
| Engineering/Math/Statistics Background | ✅ | Ideal for risk analytics and quant finance roles. |
| Banking & Finance Professionals | ✅ | Helps move into risk and treasury roles. |
| Commerce Students Exploring Finance | ✅ | Builds strong finance and market understanding. |
| Students Focused Only on Taxation/Audit Practice | ❌ | FRM is specialised in risk and financial markets. Those focused purely on taxation or audit practice may find other qualifications more aligned with their goals. |
| Non-Finance Creative/Non-Analytical Career Paths | ❌ | FRM is analytical and finance-heavy. It suits those interested in numbers, markets, and financial decision-making rather than creative or non-finance roles. |
Professionals who complete FRM often see strong growth in FRM salary packages globally, especially in banking, consulting, and risk analytics roles.
Did you know?
FRM Part 1 builds technical foundations, while Part 2 focuses heavily on real-world application, which is why employers often value candidates who clear both levels.
Why Students Choose Imarticus Learning for FRM Preparation
By the time most students finish understanding the FRM syllabus, a new question usually comes up: “Where should I prepare for it properly?”
The FRM program is built with a focus on application. At Imarticus Learning, topics are explained in a way that helps you actually understand risk concepts – not just memorise formulas.
You get:
- Structured coverage of the FRM syllabus.
- Focused preparation for FRM Part 1 and Part 2.
- Alignment with the FRM exam pattern.
- Regular mock tests and exam readiness.
- Integrated Sectional tests, Full-length mocks, Revision sessions, and Doubt-solving support.
- Guidance beyond just syllabus completion.
- Designed for students and working professionals.
- A preparation approach aligned with real careers.
Ultimately, FRM isn’t just about passing an exam. It’s about building a career in risk, banking, analytics, and finance. A structured program helps you move from understanding the FRM course to actually using it for career growth.
For students who want clarity, discipline, and consistent support, the Imarticus learning experience is designed to make the FRM journey far more organised and achievable.
FAQs About FRM Syllabus
Before starting your preparation, it’s natural to have questions about the FRM syllabus. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions to help you plan your study schedule better and approach the course with clarity and confidence
Who should consider doing FRM?
FRM is ideal for finance students, CA, CMA, or ACCA aspirants, MBA finance graduates, banking professionals, and anyone interested in risk management, investment analysis, or financial markets.
How should I study the FRM syllabus effectively?
Start by understanding concepts instead of memorising them. Once a topic is clear, practice as many questions as possible. Revision is extremely important because the syllabus is vast. A simple routine of daily study, weekly revision, and regular mock tests works well for most students. You can enrol in reputed training institutes like Imarticus Learning for structured preparation.
What does the FRM syllabus actually teach you?
The FRM syllabus is designed to teach you how financial risk works in the real world. You’ll learn how organisations protect themselves from market crashes, credit defaults, operational failures, and liquidity problems. By the end of the syllabus, you start thinking less like a student and more like someone working in a risk team.
How long does it take to complete the FRM syllabus?
Most students take around 4 to 6 months to complete each level’s syllabus with consistent preparation. If you study regularly for a few hours each day and practise mock tests, you can comfortably cover the syllabus without feeling rushed. Institutes like Imarticus Learning offer training that helps you gain key skills and master the FRM concepts.
Does the FRM syllabus change every year?
The FRM syllabus doesn’t change every year. However, some small updates are introduced to keep the syllabus aligned with industry trends and global financial developments. This ensures that what you study stays relevant to real-world finance and risk management.
Which topics in the FRM syllabus are considered the toughest?
Quantitative Analysis in Part 1 can feel challenging initially because it involves statistics and probability. In Part 2, the market risk and credit risk sections are often seen as the most detailed. However, once you understand the logic behind them, these subjects become much easier and even enjoyable.
Is the FRM syllabus useful for real jobs in finance?
Yes, very much. The concepts you study – like Value at Risk (VaR), stress testing, credit risk models, and portfolio risk are used daily in banks, consulting firms, and investment companies. This is why FRM is valued globally. It teaches skills that are directly applicable in risk and finance roles.
Can beginners in finance handle the FRM syllabus?
Yes, beginners can manage it with the right approach. You may need extra time in the beginning to understand basic finance and quantitative concepts, but many non-commerce and engineering students complete FRM every year with disciplined preparation.
How Difficult Is the FRM Syllabus?
Let’s be honest, the FRM syllabus is not easy. But it’s also not unmanageable. It’s a rigorous program because risk management itself is a field of high responsibility. The FRM exam syllabus is designed to test your conceptual clarity and application ability in realistic scenarios.
Take Your First Step Toward a Risk Career with the FRM Syllabus
The FRM syllabus is not designed to be easy – it’s designed to be relevant. Something that actually adds value to your career and helps you move into more specialised, meaningful finance roles.
Every topic you study connects directly to how financial institutions measure risk, protect capital, and make high-stakes decisions. That’s what makes FRM different from general finance courses. It doesn’t just teach concepts; it prepares you for responsibility.
What makes FRM worth considering today is how relevant it has become. As financial systems grow more complex and regulated, companies need people who understand risk deeply – not just at a theoretical level, but in a practical, decision-focused way. That’s exactly the kind of thinking FRM develops.
So if you see yourself working in roles where analysis, strategy, and financial decision-making matter, the FRM course is still a strong and relevant choice. Take that first step now and shape your career.

