CFA Level 3 is where the program finally feels like investment work rather than investment theory. The earlier stages focus on valuation, ratios and quantitative mechanics. At this level, the exam asks candidates to think like portfolio managers who must justify every choice they make for a real client.
Imagine this common scenario.
“A client earns a strong salary, expects a large expense in five years and has a moderate risk appetite.”
You are asked to calculate their return need, recommend an asset mix and justify whether their risk capacity aligns with the proposed strategy.
Each part of the question builds on the previous one, similar to how actual investment committees operate. If you miss one detail, the rest of the reasoning collapses. This is the heart of CFA Level 3. You are no longer proving that you know finance. You are proving that you can use finance logically, responsibly and consistently.
Candidates often describe Level 3 as the stage where everything clicks. You start noticing that portfolio management is not about finding perfect answers. It is about making defensible decisions using incomplete but structured information. That is what the exam tests. And that is what makes it engaging for learners who enjoy real investment problem-solving.
This blog takes you inside the full experience of preparing for Level 3, focusing on the parts of the exam that truly influence performance. You will find practical frameworks for mastering the constructed response section, insights on interpreting IPS narratives, topic weight strategies, efficient study allocation models, revision loops, common error patterns and realistic examples that reflect how actual portfolio decisions are made. Whether you are just beginning your preparation or refining your final weeks, this guide gives you a clearer, more structured path to navigate Level 3 of CFA with confidence.
A Quick Look at What the CFA Program Covers
Before exploring CFA Level 3, readers often search for clarity on what is CFA, especially if they are new to the program structure. The CFA course, offered by the CFA Institute, is a globally recognised pathway that develops investment professionals through a layered learning experience. Each level is designed to sharpen different skills that eventually converge at Level 3.
How the CFA Program Is Structured
The table below provides a simple, high-level view of the three CFA levels and what each one builds.
| CFA Stage | Core Focus | Skills Developed |
| Level 1 | Foundational frameworks | Financial tools, ethics basics, and market understanding |
| Level 2 | Analytical depth | Valuation, quantitative precision, complex case solving |
| Level 3 | Applied portfolio management | Client-oriented decisions, IPS creation, and communication clarity |
This structure makes the final stage feel more practical and decision-driven compared to the earlier levels.
What CFA Training Prepares You For
The CFA course details are not limited to exams. It cultivates professional habits that align with real investment responsibilities. Candidates absorb principles that help them evaluate portfolios, manage risk and maintain ethical judgment in fast-changing market environments.
Key capabilities built across the CFA pathway
- Analysing investments with structured logic.
- Interpreting financial data within broader economic contexts.
- Assessing suitability for different client types.
- Maintaining independent, ethical decision-making.
- Integrating multiple asset classes into coherent portfolios.
All of these capabilities come together meaningfully at CFA Level 3, which expects candidates to demonstrate applied reasoning instead of mechanical recall.
Why This Foundation Matters for CFA Level 3
The CFA is a gateway to leading global finance careers. Level 3 pulls elements from earlier levels into one integrated decision-making environment. Understanding the structure of the CFA Program helps candidates appreciate why Level 3 uses narrative-driven, client-oriented questions.
Key reasons this connection is important
- Return calculations rely on valuation understanding from Level 2.
- Risk tolerance decisions use behavioural concepts introduced earlier.
- Portfolio construction requires familiarity with asset class interactions.
- Ethics influences judgment in nearly every scenario.
This layering prepares candidates to respond like portfolio managers rather than exam takers. This video explains in depth, while giving practical references, as to why the CFA charter has become a gold standard of finance qualifications and one of the best moves for your finance career.
Core Subjects Covered in CFA Level 3
CFA Level 3 focuses on applied portfolio management, and the subject mix reflects this shift. Instead of learning tools in isolation, candidates learn how different asset classes and decision frameworks work together to serve client needs. The curriculum blends analytical skill with judgment, which is why understanding each subject’s purpose becomes essential for exam success.
The table below summarises the major subjects tested at Level 3 along with their core focus areas.
| Topic | What It Covers |
| Individual Portfolio Management | IPS, client constraints, return and risk objectives |
| Institutional Portfolio Management | Pension funds, endowments, insurance portfolios, banks, and foundations |
| Fixed Income Portfolio Management | Key rate duration, curve strategies, interest rate risk, hedging tools |
| Equity Portfolio Management | Factor exposures, manager selection, portfolio structuring |
| Alternative Investments | Private equity, real estate, hedge funds, and real assets in portfolios |
| Risk Management | Risk measures, hedging frameworks, and multi-asset risk evaluation |
| Economics for Portfolio Decisions | Economic growth expectations, market conditions, and macro considerations |
| Derivatives | Hedging, overlays, risk adjustments within portfolios |
| Ethics | Professional conduct, scenario judgement, standards application |
These subjects anchor the analytical and decision-based tasks that appear throughout the Level 3, especially in the constructed response section, where topics often blend into multi-layered portfolio scenarios.
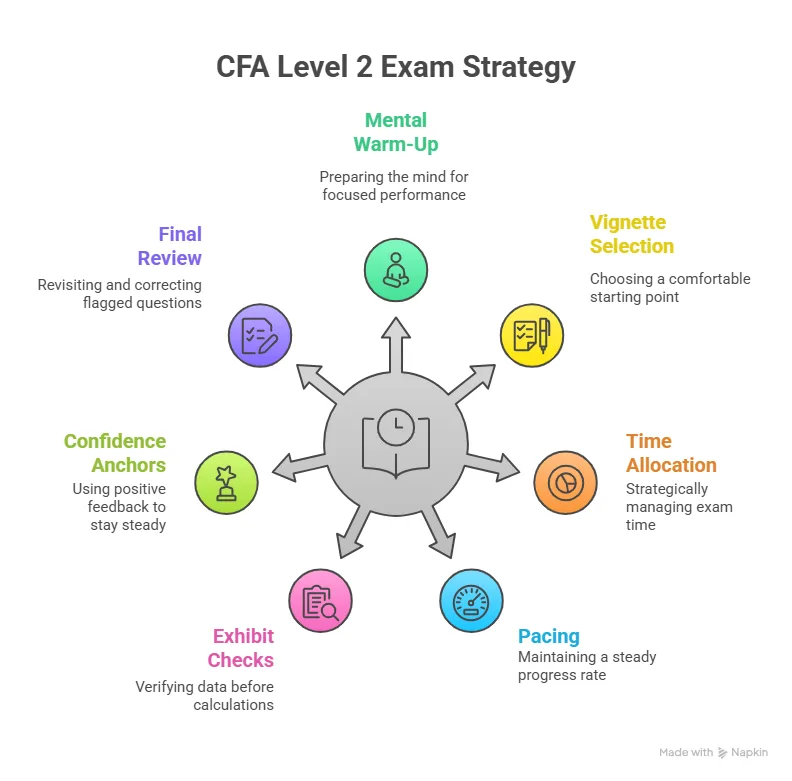
1. How the Constructed Response Session Works
The constructed response section is the signature feature of CFA Level 3. This is the session where many learners lose time by writing excessive explanations or drifting off task. The exam format is built around short, targeted responses that show accurate reasoning. The first step is always recognising what the command word is asking for. Reading the final command words before reading the whole question helps the mind stay anchored.
Understanding What Each Command Word Requires
Below is a detailed explanation to help candidates recognise how different instructions guide the format of the response. This table helps avoid wasting time on long paragraphs that do not gain additional marks.
| Command Word | What It Seeks | How To Answer |
| Calculate | Numeric output | Provide the formula and the final figure, including units |
| Determine | A concrete conclusion | State the final value or decision directly |
| Recommend | A choice or action | Begin with the recommendation, then support it briefly |
| Justify | Explanation of reasoning | Describe the rationale using relevant curriculum logic |
| Identify | A list of points | Provide short bullets that give only the essential ideas |
Practical Method for Constructed Response
Candidates benefit from creating memory templates for different tasks. IPS creation, return calculations, liquidity assessments and constraints can all follow standard patterns. These patterns act as mental scaffolding under time pressure. When a client case mentions a near-term purchase, that detail shapes liquidity and time horizon automatically. Treating client narratives as real people helps keep important elements in focus.
2. Portfolio Management at CFA Level 3
The curriculum of Level 3 focuses heavily on building and managing portfolios rather than valuing individual assets. Competence depends on connecting client details to appropriate strategies. This is often easier when students form mental pictures for each type of investor.
Private Wealth Clients
Private wealth management clients require attention to lifestyle spending, large expenses, income stability and return needs. When reading their investment policy statements, candidates can imagine individuals they know in similar financial positions. This makes risk capacity and liquidity constraints easier to identify.
Institutional Clients
Institutional considerations become much clearer when tied to everyday examples. Pension funds manage obligations to retirees. Endowments support long-term spending commitments. Insurance companies maintain portfolios within regulatory frameworks. These associations act as memory triggers when reading lengthy cases.
Techniques for Portfolio Rebalancing
The CFA Level 3 course includes portfolio rebalancing methods such as constant mix, constant proportion, and buy and hold. These concepts become easier to recall when linked with character traits. Constant mix mirrors a stabiliser mindset. Buy and hold reflects patience. Constant proportion resembles a more assertive risk posture. Using these mental pictures helps candidates recall the behaviour of each strategy under market changes.
3. Mastering Fixed Income at Level 3
Fixed income scenarios in Level 3 involve term structure changes, key rate duration and curve interpretation. A helpful analogy is to imagine the yield curve as a road. Any twist in the road affects certain sections more than others. Key rate duration highlights the segments that respond most. Slope shifts resemble gentle inclines and declines. This story-like approach helps bring structure to formulas and interpretations.
4. Equity Portfolio Concepts
CFA Level 3 moves away from valuing stocks and into analysing equity portfolios. Factor models, risk decomposition and manager selection take centre stage. A useful practice technique is to break every equity strategy into three categories. These are the drivers of returns, the exposure to risk and the suitability for the client. Repeating this habit builds speed during Level 3 prep. The following visual gives a demo strategy that many CFAs use in their daily work for managing equity portfolios with ease:

5. Alternative Investments in Context
Alternative investments become easier to understand due to their real-world links. Real estate cases involve cap rates and rental flows. Private equity questions refer to distribution waterfalls and deal structures. Hedge fund strategies show clear behaviour patterns. Since these ideas connect with market examples, retention improves naturally.
6. Ethics as a Decisive Scoring Component
Ethics holds significant weight in CFA Level 3 outcomes. Historically, candidates near the minimum passing score often shift into pass or fail categories based on Ethics performance. The section relies on scenario interpretation rather than plain recall. Exposure to varied question sources builds sharper instincts. Many learners who enrol in Level 3 classes practice Ethics from multiple providers to prepare for the range of possible contexts.
Common Ethics Themes at Level 3
Below is a summary of the key areas that consistently appear across Ethics questions. Candidates can use this to prioritise the topics that deliver the highest return on effort.
The table provides a focused list of recurring Ethics themes and the core skills needed for each.
| Ethical Area | Often Tested Topic | Key Skill Needed |
| Professionalism | Conflicts of interest | Identifying subtle bias or dual responsibility |
| Integrity of Capital Markets | Use of non-public information | Distinguishing materiality and suitability |
| Duties to Clients | Suitability checks | Aligning recommendations with client conditions |
| Duties to Employers | Loyalty and conduct | Understanding parallel activity concerns |
| Investment Analysis and Recommendations | Research independence | Documenting assumptions properly |
Applying Behavioural and Practical Thinking
The Level 3 curriculum introduces behavioural concepts that influence investor decisions. Loss aversion, framing, regret and mental accounting influence how clients respond to information. Candidates who visualise these tendencies in real people find it easier to apply the theory in case studies. A straightforward method is to recall typical client behaviour from everyday situations. This builds natural recognition when reading behaviour-related vignettes.
Global Presence and Professional Motivation
CFA Level 3 is recognised internationally for its depth in applied portfolio management. Data published by the CFA Institute shows a global presence of charterholders in more than 160 countries through official membership statistics on their website. Many candidates feel a shift in confidence after studying at this level because they begin understanding client-oriented thinking. This mindset often proves useful in interviews for asset management, research and advisory roles.
Building a Practical Strategy for CFA Level 3
Preparation for Level 3 becomes easier when candidates align their efforts with how the exam is actually tested. The content rewards structured thinking and efficient time use. A study approach that blends conceptual understanding with case practice provides the strongest performance. Many candidates who prepare at this level notice that a gentle shift in learning style makes a significant improvement in recall. Instead of covering topics in linear order, the process becomes more thematic. For example, reading private wealth theory first and solving the linked constructed response cases immediately afterwards creates a loop that strengthens understanding.
Constructing an Effective Weekly Study Framework
Candidates who plan their time using blocks rather than daily micro schedules find the approach more flexible. It reduces the pressure of squeezing content into strict calendars. A weekly framework also allows a deeper focus on the Level 3 course without needing constant readjustments.
A Sample Weekly Study Breakdown
Below is a simplified structure learners often use during the main study window. It gives enough flexibility to adjust workload while staying aligned with the curriculum.
This table gives an example of how a typical study week may be organised for CFA Level 3. It creates space for reading, case practice and revision without overwhelming the candidate.
| Day | Focus Area | Purpose |
| Monday | Read one major topic | Build a conceptual base |
| Tuesday | Solve 2 to 3 constructed response cases | Apply new concepts |
| Wednesday | Review errors from the prior day | Understand recurring weak spots |
| Thursday | Cover a secondary subtopic | Maintain syllabus continuity |
| Friday | Solve item set questions | Strengthen analytical speed |
| Saturday | Mixed practice set | Reinforce cross-topic thinking |
| Sunday | Light revision and rest | Maintain long-term recall |
This type of rhythm helps sustain energy across several months and aligns with the intensity needed for CFA Level 3.
Balancing Reading and Practice
One of the common challenges candidates face is determining how much reading is necessary after completing CFA Level 2. Many assume their prior background carries them forward, but Level 3 introduces a strong focus on application. Reading the curriculum helps, yet it is the practice cases that reveal how theory functions in realistic portfolios. For example, reading about return objectives may feel simple, but writing them in a client-specific narrative requires careful thought. When preparing for the Level 3 exam, candidates who alternate between reading and case solving usually achieve faster improvement.
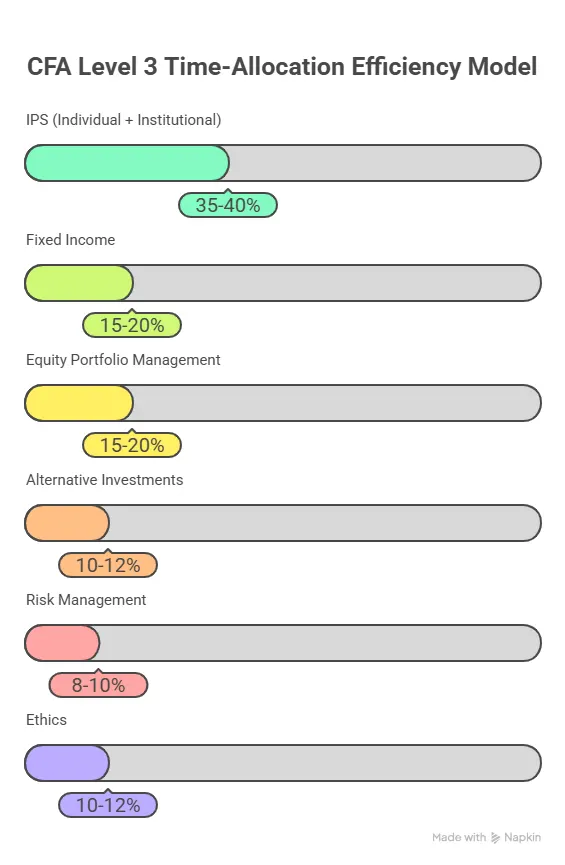
Understanding Topic Weight Distribution
The curriculum groups Level 3 topics into clusters that carry different weights. Recognising these weight patterns helps candidates allocate time effectively during CFA Level 3 prep.
Topic Weight Overview
Below is a general summary of how topics are distributed in Level 3. Although exact weights vary year to year, the structure consistently rewards command over portfolio management. This table outlines the typical weight distribution across Level 3 subjects. Candidates can use this view to make informed study choices.
| Topic | Approximate Weight | Priority Level |
| Portfolio Management (Individual) | High | Essential |
| Portfolio Management (Institutional) | High | Essential |
| Ethics | High | Essential |
| Fixed Income | Medium | Important |
| Equity Portfolio Management | Medium | Important |
| Alternative Investments | Medium | Useful |
| Risk Management | Medium | Useful |
| Derivatives | Low to Medium | Supportive |
| Economics | Low | Supportive |
The table helps learners understand the clear emphasis on portfolio management. A candidate who masters these sections gains stronger overall stability in the CFA Level 3 exam.
Building Case-Solving Skill
Case solving is the heart of CFA Level 3. It involves interpreting client data, prioritising relevant factors and structuring responses clearly. The most frequently tested component is the Investment Policy Statement. Every detail in the narrative often relates to an IPS element. Candidates benefit from learning a step-by-step IPS approach that never changes.
A Simple IPS Pattern to Practice
This method helps maintain consistency under pressure.
These bullets outline a repeatable process candidates can use when creating IPS responses in the CFA Level 3 exam.
- Identify the client type
- Understand their financial situation
- Establish return objectives
- Identify risk capacity and risk tolerance
- Clarify liquidity needs
- Define time horizon
- Identify tax circumstances
- State any legal or regulatory constraints
- Summarise unique considerations
This checklist functions like a safety net. It prevents candidates from missing components that carry marks in the rubric.
1. Learning Through Error Analysis
Error analysis provides one of the deepest learning gains at Level 3. When a candidate solves a case and reviews their mistakes, they uncover patterns. Some candidates frequently miscalculate liquidity. Others miss risk constraints because they skim the narrative too quickly. Creating a separate notebook of recurring errors helps internalise these insights. This method becomes even more effective when paired with feedback from mentors or peers studying for the CFA Level 3 course.
2. Practical Time Management Techniques
Time management influences scores heavily in the constructed response section. Many candidates know the solutions conceptually but struggle to produce them fast enough. To improve speed, candidates can practice solving short scenarios within five-minute capsules. This builds instinctive decision-making. Another method is limiting each answer to a maximum of three bullet points unless the question specifies otherwise. The exam rewards accuracy, not length. Practising under these constraints trains efficiency.
3. How to Approach Item Sets Effectively
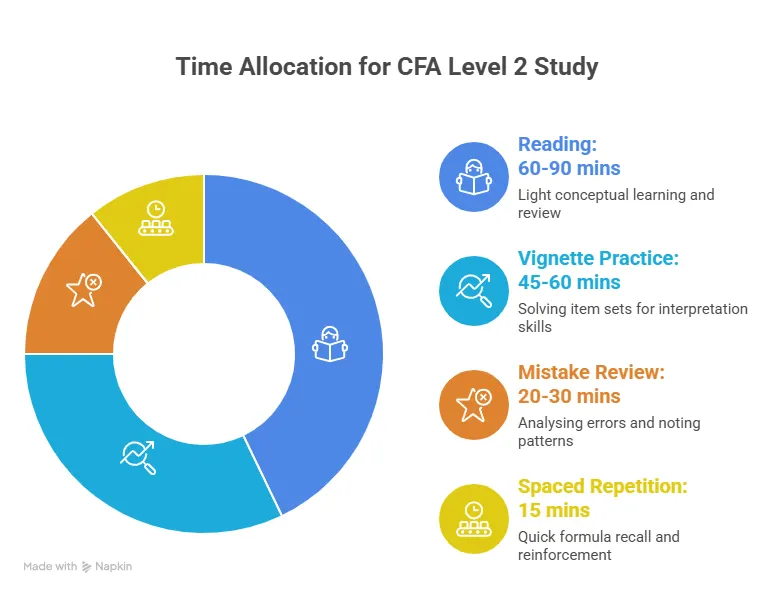
The item set section in CFA Level 3 still relies heavily on careful reading. Although candidates may feel more comfortable with this format after Level 2, the narratives at Level 3 require context-based interpretation. A helpful technique is to read the questions before reading the vignette. It gives the reader clarity on what to look for. While this approach does not work for everyone, many candidates find that it reduces the time spent rereading. Item sets also tend to integrate multiple topics, so interdisciplinary thinking becomes valuable during Level 3 prep.
The following visual gives a strategic breakdown of time allocation techniques based on the subjects of Level 3 for you to plan your preparation effectively:
Understanding the Overall Cost of Preparation
The CFA Level 3 exam dates and fees include registration fees, preparation material and optional classes. Candidates generally calculate their total cost by considering three components. These include exam fees, prep course charges and the cost of mock exams or additional resources. The CFA Institute provides updated exam fee details directly on its official site, and candidates planning their budgets often check these well in advance.
Overview of CFA Level 3 Preparation Costs
Although prices vary depending on geography and provider, the table below provides a general structure to help candidates estimate the cost of the full preparation cycle.
This table outlines the typical cost elements for Level 3 preparation. It includes exam registration, prep providers and supplementary materials.
| Component | Typical Range | Notes |
| Exam Registration | Refer to the official CFA Institute fee schedule | Includes early and standard windows |
| Prep Course | Variable across providers | Depends on live classes, recorded content or hybrid programs |
| Mock Exams | Provider dependent | Quality varies across platforms |
| Books and Supplements | Optional | Useful for revision or extra practice |
| Additional Tools | Minimal to moderate | Includes flashcards, apps or formula sheets |
This overview helps candidates plan the investment required for the Level 3 prep cycle.
Strengthening Revision Cycles for CFA Level 3
Revision at CFA Level 3 works best when it follows a looping structure. Candidates who repeat material in layered intervals retain concepts far better than those who attempt a single heavy revision push. The content at this stage requires practical insight along with theoretical recall. A looping revision pattern allows both to grow steadily. Each cycle improves clarity when solving cases and helps the candidate identify recurring decision frameworks.
1. A Three-Loop Revision Method
This approach gives candidates enough touchpoints with the curriculum without overwhelming their schedules. Each loop builds on the previous one.
The list below outlines how the three-loop revision process works for CFA Level 3 candidates.
- Loop 1: High-level review of all notes and formula sheets
- Loop 2: Constructed response practice under timed conditions
- Loop 3: Mixed item sets, Ethics refresh and error consolidation
Loop 1 creates structure. Loop 2 builds speed. Loop 3 strengthens decision-making across topics.
2. Creating a Personal Level 3 Handbook
Based on the CFA Level 3 results published by the CFA Institute, some candidates benefit from building a personal handbook summarising tricky areas. This helps centre the mind during the final few weeks. A handbook condenses the large curriculum into manageable elements. Most learners include IPS templates, key decision rules, common pitfalls, brief ethics notes and error patterns. During Level 3 prep, this separate document often becomes a quick reference guide that saves time.
Suggested Sections for the Handbook
Below is a recommended structure that many successful candidates use. This list outlines common inclusions in a personal CFA Level 3 handbook.
- Private wealth IPS checklist
- Institutional investor characteristics table
- Fixed income strategy notes
- Equity factor model summaries
- Risk management definitions
- Alternative investments key concepts
- Ethics triggers and grey area examples
- Personal error notes and reminders
This type of handbook helps maintain clarity throughout the final study phase. Watch this video that breaks down some common myths about the CFA exam and helps you build confidence for your preparation journey:
Final Month Strategy for CFA Level 3
The last month before the exam is when refinement happens. At this stage, candidates should feel comfortable navigating the syllabus. The focus shifts to accuracy, speed and confidence. You can also refer to the candidate resources provided by the CFA Institute to strengthen your preparation.
A Structured Plan for the Last 30 Days
Below is a commonly recommended pattern that aligns with how many candidates revise effectively.
This table demonstrates how the final 30 days can be planned while keeping a balance between practice and review.
| Week | Priority | Activities |
| Week 1 | Deep practice | Solve full-length constructed response sets and analyse errors |
| Week 2 | Mixed reinforcement | Complete item sets across varied topics |
| Week 3 | Ethics and weak areas | Revisit problem topics, revise Ethics cases |
| Week 4 | Simulation | Attempt two to three mock exams and revise the handbook |
This approach prepares candidates thoroughly for the Level 3 exam while helping maintain mental clarity.
Common Mistakes Candidates Should Avoid
Avoiding common errors improves performance more than many realise. Level 3 rewards precision and calm thinking, and many mistakes stem from rushing.
This list summarises recurring mistakes that candidates can avoid during the CFA Level 3 journey:
- Skipping Ethics during revision
- Writing long answers in constructed response questions
- Ignoring time management drills
- Misreading client details in IPS questions
- Over-reliance on memorisation rather than application
- Not analysing mock exam errors in detail
- Solving questions without replicating exam conditions
Identifying these patterns early can protect candidates from losing marks unnecessarily. This video gives a practical approach for working professionals to clear the CFA strategically while balancing their work schedules:
FAQs About CFA Level 3
This section addresses the most frequently asked questions about CFA Level 3, offering clear explanations to help candidates understand exam expectations, preparation needs, eligibility requirements and the path that follows after completion.
Is CFA Level 3 tough?
CFA Level 3 is challenging because it focuses on applied thinking rather than memorised formulas. The exam uses complex narratives that require judgment, clarity and realistic portfolio interpretation. Many candidates find this level more mentally demanding because the constructed response format requires concise and accurate writing. Those who join Imarticus Learning benefit from guided case solving, which helps reduce the difficulty significantly.
What is a Level 3 CFA?
A Level 3 CFA candidate is someone who has reached the final stage of the CFA Program. Level 3 of CFA focuses on portfolio management, wealth planning and advanced investment decision making. The exam assesses how candidates apply theory to client-based situations. It blends IPS analysis, fixed income strategy, equity portfolio construction, alternative investments and Ethics. This stage reflects practical investment concepts and prepares candidates to think like real-world portfolio managers.
Who is eligible for CFA Level 3?
A candidate becomes eligible for CFA Level 3 after clearing both CFA Level 1 and Level 2. Anyone who passes the earlier stages can register for Level 3 through the official CFA Institute website. No additional academic or professional eligibility is required. Since Level 3 highlights portfolio management, readiness depends on understanding earlier valuation concepts.
Is CFA higher than MBA?
CFA and MBA programs serve different professional goals. CFA focuses on deep investment knowledge, portfolio construction and ethical decision-making, while MBA programs cover a broad business landscape, including marketing, management and operations. Many professionals pursue both qualifications because they complement each other. Someone preparing for CFA gains analytical depth and investment-specific expertise. Someone pursuing an MBA gains managerial and strategic exposure. The value of each depends on career goals.
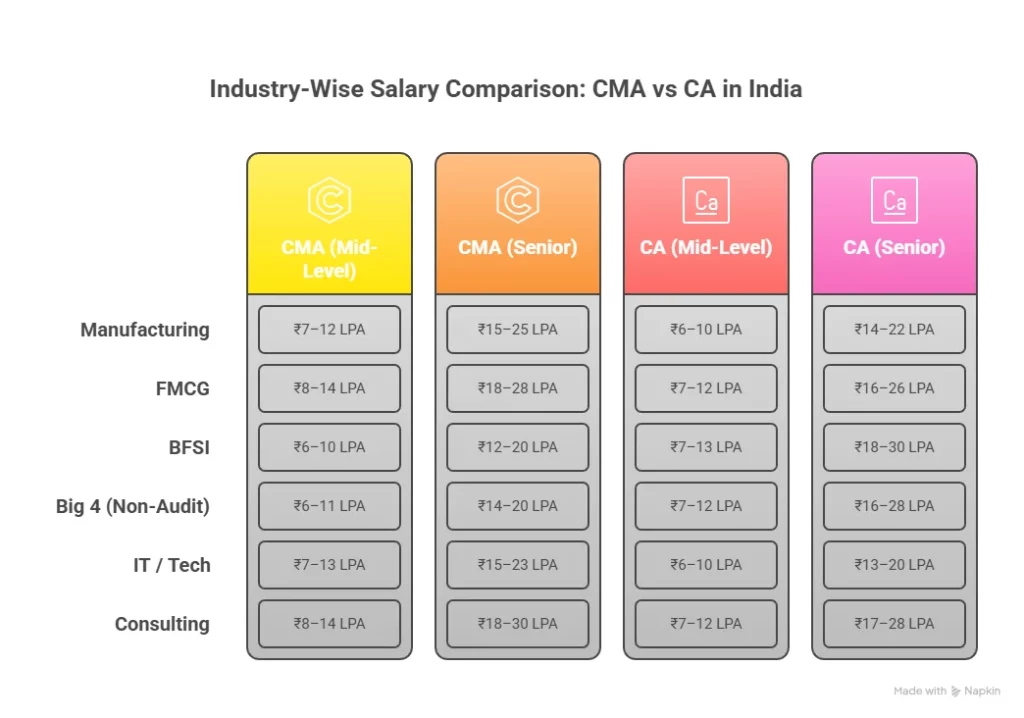
How much is a CFA Level 3 salary?
A CFA Level 3 candidate in India typically earns ₹9 lakh to ₹18 lakh per year in early roles, rising to ₹18 lakh to ₹30 lakh with experience. Professionals with five to ten years in investment roles often earn ₹30 lakh to ₹50 lakh or more. Internationally, experienced professionals commonly earn USD 100,000 to 150,000 per year. Clearing Level 3 strengthens both credibility and compensation potential, especially when supported through structured preparation such as the programs offered by Imarticus Learning.
Can I do CFA without a degree?
Entry into the CFA Program does not always require a completed degree, as the CFA Institute allows registration based on certain alternative criteria. While a degree is not mandatory for progressing through the program, employers in finance often prefer candidates with both academic qualifications and the CFA credential.
How many attempts for CFA Level 3?
The CFA Institute does not limit the number of attempts a candidate may take. A learner can attempt CFA Level 3 as many times as needed. Most candidates refine their approach after each sitting and build stronger familiarity with the exam style. Programs like CFA prep courses often help candidates identify weak areas quickly. Imarticus Learning offers doubt-clearing and structured practice that helps reduce the number of attempts needed.
Is 60 percent enough to pass CFA Level 3?
The CFA Institute does not publish an official minimum passing score. Historically, candidates often reference the idea that around 60% feel close to the passing zone, although this is not a published benchmark. Level 3 scores depend on the overall candidate performance distribution. Providers like Imarticus Learning often guide students on target scoring ranges during mock exams.
How many months to study for CFA Level 3?
Most candidates prepare for Level 3 over four to six months. The timeline depends on work schedules, familiarity with portfolio management concepts and study pace. A typical study cycle includes reading, practice cases, revision loops and mock exams. Candidates with demanding jobs often start early to distribute their workload. Preparing for CFA using structured prep materials with Imarticus Learning helps create an organised path, especially for those balancing multiple commitments while preparing.
What happens after I pass CFA Level 3?
Passing CFA Level 3 puts a candidate on the final stretch toward earning the charter. After completing this stage, candidates need to submit their relevant work experience for approval and complete the professional requirements laid out by the CFA Institute. Once approved, the candidate becomes a CFA charterholder. Many individuals experience a boost in workplace confidence and new opportunities once they clear this milestone.
Bringing Your CFA Level 3 Journey Into Focus
CFA Level 3 brings the entire CFA pathway together and prepares candidates to think like real portfolio managers. The concepts, cases and IPS work all build toward one goal: making clear, defensible investment decisions under realistic conditions. As you move deeper into your preparation, the habits that matter most are steady practice, sharp reading, clean writing and consistent revision. Small improvements in these areas compound quickly.
Many candidates find that structured guidance helps them stay disciplined and confident through the final stretch. If you prefer learning with support, the CFA course prep at Imarticus Learning offers organised case practice, doubt clearing and exam-focused study plans that align well with Level 3 requirements.
Stay patient, stay intentional and treat every practice session as a chance to refine your thinking. With the right preparation path, CFA becomes far more achievable than it first appears.