Have you ever wondered why some finance professionals seem to fast-track their careers, landing top roles, commanding high salaries, and being relied upon for the most pivotal business decisions? For many, the key isn’t just intelligence or a fancy degree – it’s a three-letter credential, the CMA Certification that’s quietly revolutionising the financial landscape of Indian business.
Today, Certified Management Accountants are rewriting the rules for what’s possible, not just in the world of salaries, but in how much influence, respect, and strategic authority a finance professional can earn in India’s fast-evolving marketplace.
Let’s walk through the CMA-certified professional’s salary journey – real numbers, real stories, and real insight you won’t get anywhere else.
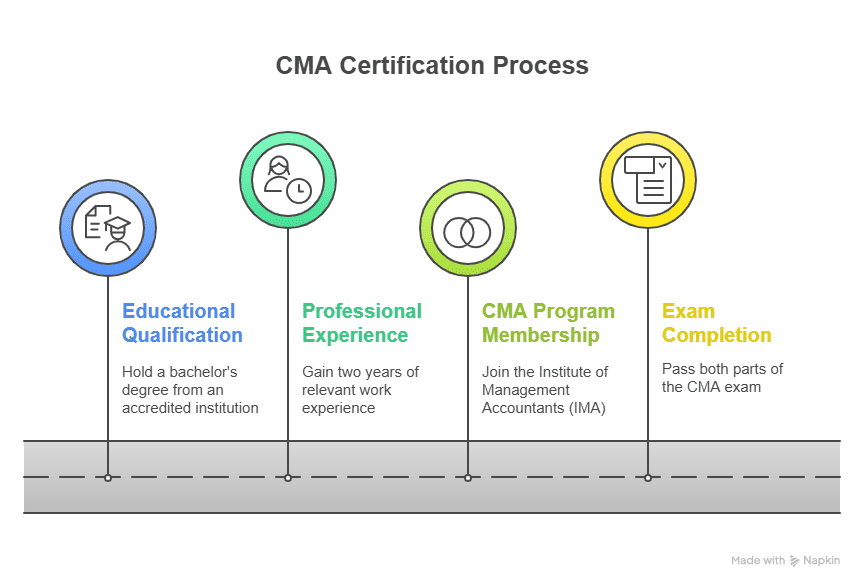
What is CMA? Credentials That Command Respect
The CMA credential, awarded by global bodies like the Institute of Cost Accountants of India (ICMAI) and the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), USA, is the highest cost and management accountancy qualification. It prepares professionals for roles in budgeting, cost control, financial planning, business analysis, and strategic leadership skills now prized in boardrooms and startups alike.
If you’re new to this, here’s a quick look at what is CMA and why it’s so valued.
According to ICMAI, CMAs in India earn 30-40% more than non-certified finance professionals.
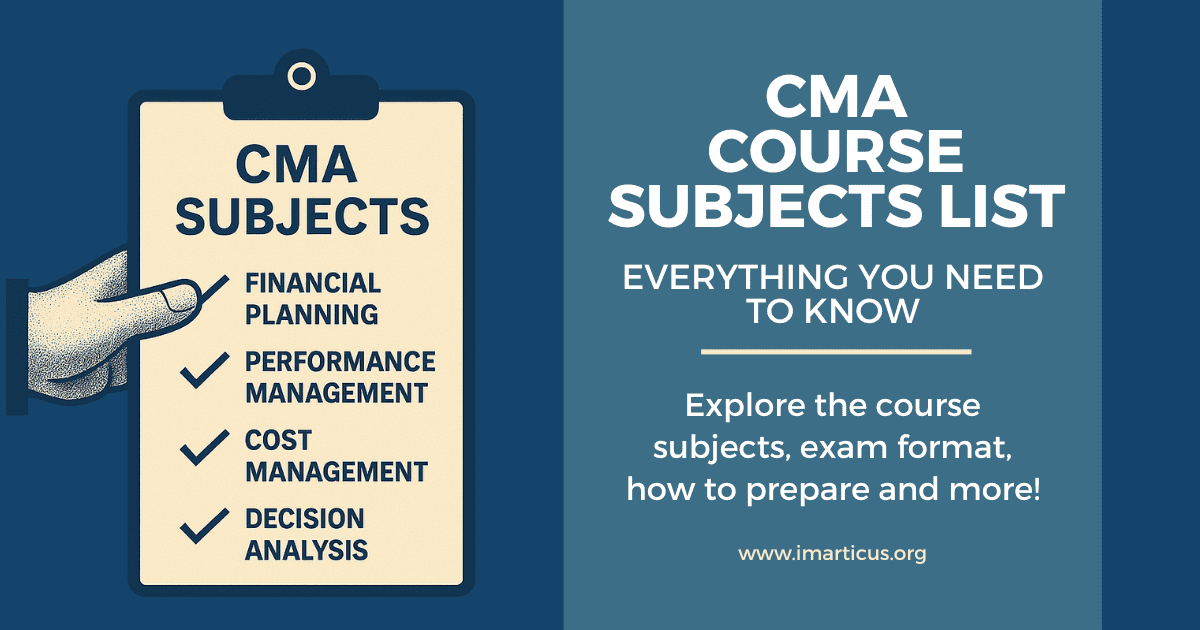
What Does a CMA Professional Actually Do?
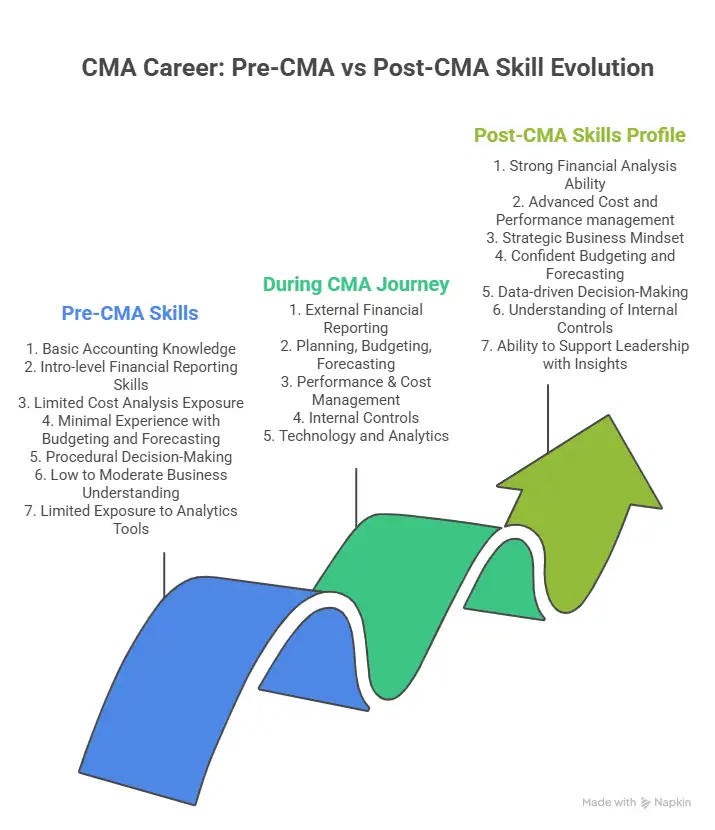
A CMA adds value by blending accounting knowledge with strategic insight – supporting budgeting, cost management, pricing decision analysis, financial analysis and risk evaluation. The role has evolved far beyond recordkeeping; today’s CMAs are expected to influence operational efficiency, market competitiveness, and senior management strategy.
The CMA Career & Salary Trajectory: Years 1-15+
As CMAs progress, salary growth accelerates – early experience fuels managerial promotions, while analytics and strategy expertise propel leadership roles.
| Years of Experience | Roles | Annual SalaryIn LPA (lakhs per annum) | Key Milestones |
| 0-2 | Analyst, Jr. Accountant | ₹4-7 LPA | Training, first promotions |
| 3-5 | Sr. Analyst, Deputy Mgr | ₹7-12 LPA | Specialisation, certifications |
| 6-10 | Financial Manager, Team Lead | ₹12-20 LPA | Strategy, team leadership |
| 11-15+ | Senior/CXO | ₹20-40 LPA+ | Board roles, executive |
If you’re exploring the US CMA course, this quick video breaks down everything you need to know.
CMA Freshers Salary in India: What to Expect When You Start Out
Starting your CMA journey? The good news is – even as a fresher, you’re stepping into one of the most rewarding finance careers out there.
On average, CMA freshers in India earn between ₹4-12 LPA, which works out to roughly ₹33,000-₹98,000 per month. Your exact package, however, depends on where you start and how you position yourself.
Here’s what really influences your first CMA offer and how you can make it count:
- Your city matters: If you’re starting in Mumbai, Bengaluru, or Delhi, expect better pay – these cities are where most top finance and consulting firms hire from.
- Your industry choice: Finance, consulting, and manufacturing roles usually offer a stronger start compared to traditional accounting or back-office profiles.
- Your academic edge: Great CMA scores or degrees like B.Com, M.Com, or MBA can instantly put you ahead in salary negotiations.
In short, where you work, what you do, and how well you’ve performed academically – all three can make a big difference in how your CMA journey begins. CMA lets you advance your accounting career and reach newer heights in the business world.
Interesting Fact– Employers today are willing to pay a clear premium for CMA-certified professionals – not just for their financial expertise, but for their ability to translate numbers into strategy.
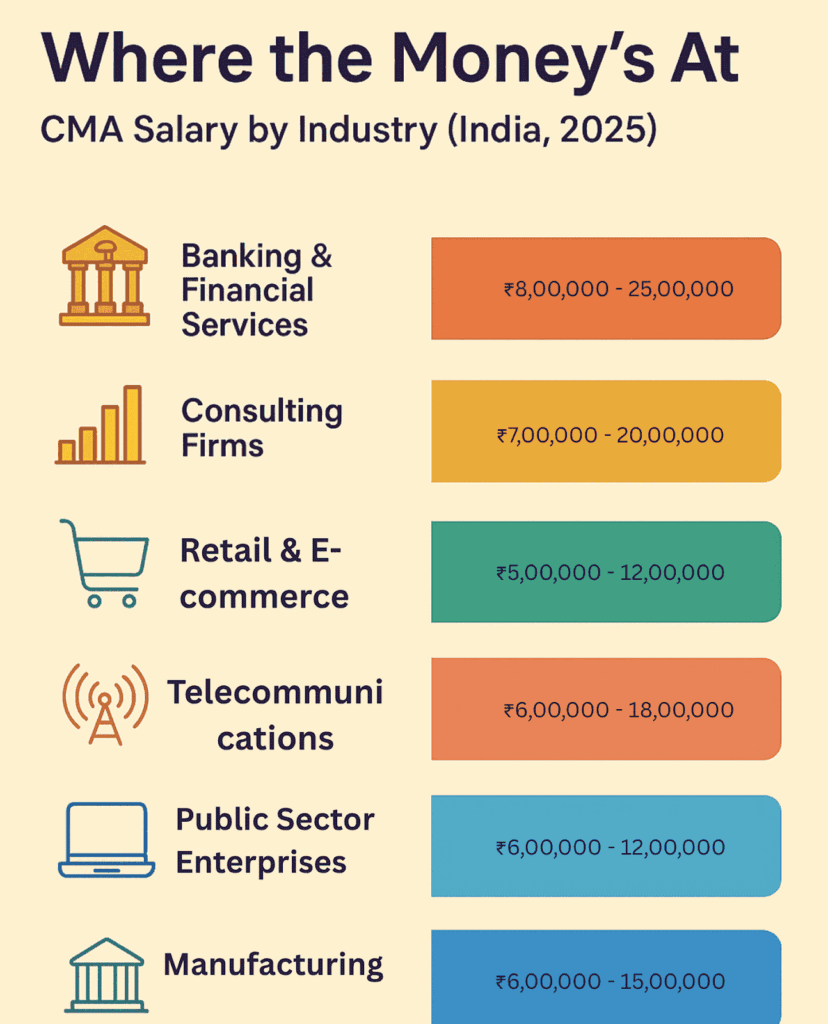
Which Industries Hire CMAs?
From banking and consulting to IT, manufacturing, and startups – CMAs are now indispensable wherever financial analysis, strategy, efficiency, and compliance meet innovation.
Here’s a breakdown of CMA salaries across industries in India, based on 2025 hiring data and campus placement insights.
| Industry | Top Employers |
| Banking & Financial | HDFC, SBI, ICICI, Axis, Barclays |
| Consulting & Big 4 | Deloitte, EY, PwC, KPMG |
| Manufacturing & FMCG | Tata, Reliance, Mahindra, ITC, HUL |
| IT & Tech | Infosys, Flipkart, Amazon, Accenture |
| Startups & Unicorns | Paytm, Razorpay, CRED |
| Public Sector/Government | Railways, PSUs, and Auditing bodies |
Demand spans well beyond banks and corporates – recent ICMAI campus placement data reveal top-tier brands actively recruiting CMAs at new highs.
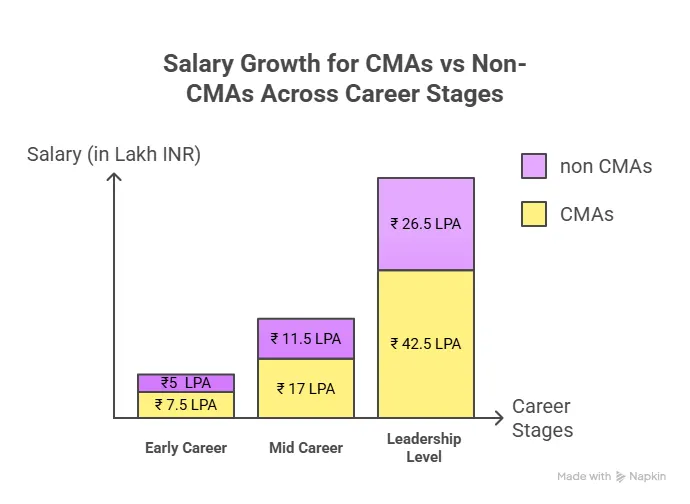
Experience Brings Rewards: CMA Salary Growth Journey
Each career milestone brings exponential pay jumps for CMAs as experience compounds, so does strategic influence and earning power.
What is the real value in a CMA career? Upward mobility.
According to Naukri’s 2025 salary analytics, CMA professionals in mid-level finance roles earn nearly 28% more than their non-certified peers – primarily due to the combination of financial acumen and strategic decision-making skills.
| Experience Level | Average Starting Salary | Common Roles |
| 0-2 Years | ₹4-7 LPA | Cost Accountant, Analyst |
| 3-5 Years | ₹7-12 LPA | Senior Analyst, Deputy Manager |
| 6-10 Years | ₹12-20 LPA | Financial Manager, Commercial Lead |
| 10+ Years | ₹20 LPA & above | Head of Finance, Senior Manager |
| Senior/CXO | ₹25 LPA – 1 Crore | CFO, Controller, Director |
Salary jumps grow steeper with every stage. Every new level brings sharper increases – especially for those who specialise, take on digital roles like ERP, analytics, and demonstrate leadership.
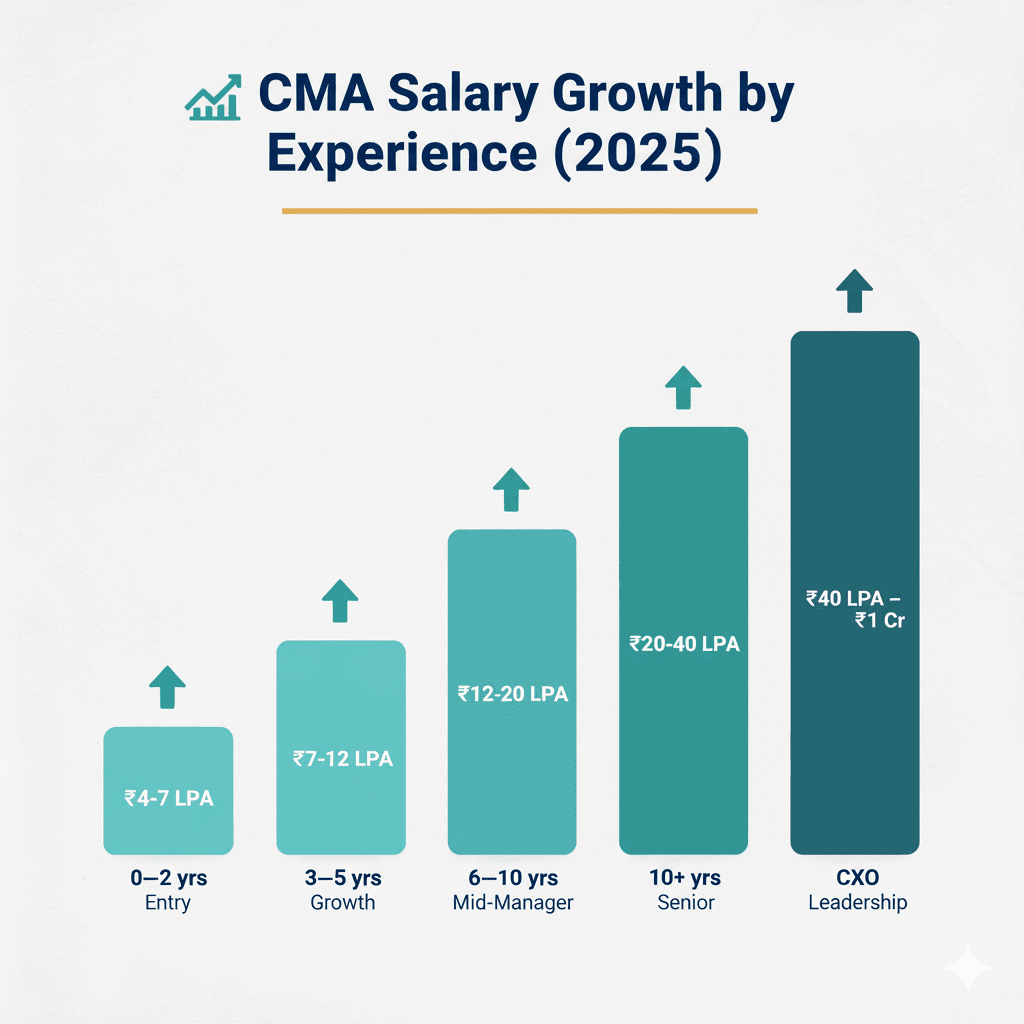
CMA Salary Increases: A Long-Term Perspective
A CMA career isn’t just lucrative – it’s built for consistent, long-term growth. Here’s what your salary journey could look like as you progress through different stages:
- Years 1-2: This is your learning curve – where you build your foundation, sharpen your technical edge, and start earning a solid base with a starting salary between ₹4-7 LPA.
- Years 3-5: The stage where things really start moving. You specialise, get noticed for your expertise, and step into roles that reward you with ₹7-12 LPA.
- Years 6-10: You’re now leading teams, making key business calls, and driving strategy – your salary grows in stride, reaching around ₹12-20 LPA.
When you combine your CMA credential with continuous learning, strong networking, and skill upgradation, you don’t just grow in numbers – you build a career trajectory that compounds over time.
What’s driving CMA salaries in India today? Watch this video for a clear breakdown of pay trends, salary benchmarks and how Indian CMA professionals stack up in the world.
Highest CMA Salary in India: 2025 Milestones
In 2025, the highest campus placement salary reported by ICMAI is ₹26 LPA – new records are being set each placement season. For senior CMAs with leadership portfolios, the apex is ₹80 LPA to ₹1 crore annually, usually at multinationals or listed companies.
| Industry | Typical Salary Range | Freshers | Mid-Level | Senior |
| Banking & Finance | ₹8-25 LPA | ₹6-8 LPA | ₹12-18 LPA | ₹20-25 LPA+ |
| IT & Technology | ₹10-22 LPA | ₹7 LPA | ₹14-18 LPA | ₹20 LPA+ |
| FMCG/Manufacturing | ₹8-18 LPA | ₹6 LPA | ₹10-15 LPA | ₹18 LPA+ |
| Consulting Firms | ₹7-20 LPA | ₹7 LPA | ₹12-18 LPA | ₹20 LPA+ |
| Oil/Gas/Heavy Industry | ₹6-20 LPA | ₹6 LPA | ₹10-14 LPA | ₹15 LPA+ |
| Healthcare/Pharma | ₹10-22 LPA | ₹7-9 LPA | ₹14-18 LPA | ₹20 LPA+ |
| E-commerce/Retail | ₹5-12 LPA | ₹5 LPA | ₹8-12 LPA | ₹12 LPA+ |
| Government/Public Sector | ₹6-12 LPA | ₹6 LPA | ₹10 LPA | ₹12 LPA |
Banking, IT, and multinational consultancies lead the pack, with consulting often matching CXO pay for strategy experts.
Did You Know?
The highest CMA campus placement in 2025 hit ₹26 LPA (ICMAI Data). This marks a 30% jump from pre-pandemic figures, highlighting the rising premium for management accountants with digital and strategic skills.
City-Wise CMA Salary Insights
Salaries vary widely with city, with Mumbai, Gurgaon, Chennai, and Bengaluru offering premium packages (senior CMAs often earn over ₹20 LPA here), while tier-2 cities see fresher and mid-level offers toward the lower median (₹5-7 LPA).
| City | Freshers | Mid-Level | Senior |
| Mumbai | ₹7-10 LPA | ₹15-20 LPA | ₹25 LPA+ |
| Bengaluru | ₹7-9 LPA | ₹12-18 LPA | ₹20 LPA+ |
| Delhi NCR | ₹6-8 LPA | ₹12-16 LPA | ₹18 LPA+ |
| Chennai | ₹5.5-7.5 LPA | ₹12-15 LPA | ₹18 LPA+ |
| Tier-2 | ₹5-7 LPA | ₹10-14 LPA | ₹15 LPA+ |
Metro locations offer steeper salary acceleration due to the concentration of MNCs, banks, and consultancies. Relocation and remote work options also expand pay packages for the right candidate.
Interesting Insight!
Cities with strong corporate clusters (Mumbai, Bengaluru) offer up to 30-35% higher pay than tier-2 locations.
Non-Salary Perks: Why Total CMA Take-Home Is Higher
Modern Indian employers sweeten the pay package for high-demand finance roles:
- Performance-based bonuses (often 15-100% of base)
- ESOPs, especially in startups and listed companies
- Healthcare, executive travel, and perks
- International exposure and relocation
Senior-level CMA professionals often get extensive benefits and, at the C-suite, negotiation power for stock and variable components.
Hidden Pay Boosters
Even when base salaries seem similar, CMA-certified professionals enjoy stronger total compensation through:
- Stock options and profit-sharing plans (especially in listed companies)
- Annual retention bonuses in the consulting and manufacturing sectors
- Paid professional development (ERP, analytics certifications)
- Relocation assistance and flexible work perks
2025 CMA Salary Trends: What’s Driving Growth?
The financial year 2025 provides a new marketplace for CMA compensation:
- Demand Spike: Post-pandemic market expansion and digital transformation have skyrocketed strategic cost and management accountancy needs.
- Premium for US CMA & Global CMAs: Dual credentials (CMA India + CMA USA) fetch higher salaries, especially with multinationals and export-driven firms.
- Placement Records Rising: ICMAI campus placement packages are breaking previous records, and some freshers report up to ₹26 LPA in 2025.
- Inflation Impact: Salary hikes for finance professionals have outstripped inflation – numbers up 10-15% compared to the previous three-year average.
Pro Tip!
Pairing your CMA qualification with an ERP or analytics certification, such as SAP, Power BI, or Python for Finance, can push your pay scale up by 20-30% within 2-3 years.
Popular CMA Job Roles & Pay Scales
The spectrum is broad, giving aspirants multiple pathways with above-market rewards for core finance expertise. Here are some popular job roles for CMAs with their salary ranges.
| Job Role | Salary Range |
| Accountant | ₹3-8 LPA |
| Financial Analyst | ₹6.5-12 LPA |
| Management Accounting | ₹5-10 LPA |
| Senior Financial Analyst | ₹10-18 LPA |
| Finance Manager | ₹11-16.5 LPA |
| Tax Manager | ₹7-15 LPA |
| Internal Auditor | ₹5-10 LPA |
| CFO | ₹20-40 LPA+ |
| Senior Finance Manager | ₹17-21 LPA+ |
| Financial Consultant | ₹7-10 LPA+ |
Did You Know?
Mid-career growth is rapid; combining the CMA with digital and analytics skills unlocks higher packages faster.
How Do Indian CMA Salaries Compare Globally?
Indian CMAs are rapidly closing the global pay gap, with dual CMA (India + USA) holders leading salary jumps in multinational and consulting sectors.
- USA CMAs in India: Typically report ₹6-10 LPA as freshers, with mid-career pros at ₹12-20 LPA, and senior professionals up to ₹25-35 LPA (MNCs, Big 4).
- Global CMA average: Asia-Pacific CMA salaries typically trail the US and Europe by 30-40%, but a rapid rise is evident in Indian placements in 2025.
Are you curious about how CMA salaries in India stack up against global pay scales?
Watch this video to uncover what the CMA qualification truly means, how it transforms careers, and where Indian CMAs stand on the world stage.
Top CMA Employers in India
Global giants, Big 4 firms, and leading Indian corporates actively seek CMAs for finance transformation roles that demand precision, foresight, and leadership.
- Big 4 Consulting (EY, PwC, Deloitte, KPMG)
- MNC Corporations (Tata, Reliance, Aditya Birla, HUL, ITC)
- Leading Banks & NBFCs (HDFC, ICICI, SBI)
- Tech and E-commerce (Infosys, Flipkart, Amazon, Accenture)
- Startups and Unicorn enterprises
Fact: Industry reports indicate CMAs in India earn 25-35% higher on average than non-certified finance professionals, particularly in strategy and cost leadership roles.
Average CMA Salary in India
Before we dive into the numbers, let’s understand what the average CMA salary in India really reflects – it’s not just about the paycheque, but the value that strategic financial expertise brings to businesses today.
| Source | Reported Average CMA Salary (2025) | Sample Base |
| ICMAI Campus Report | ₹10.2 LPA | Fresh Graduates |
| Glassdoor | ₹12.5 LPA | Mid-Level Professionals |
| AmbitionBox | ₹14.8 LPA | 800+ User Entries |
| 6Figr | ₹18.5 LPA | Senior Roles (10+ yrs) |
According to Payscale, CMA salaries range from ₹4 LPA as freshers to over ₹1 crore at senior-level careers. With packages like these, the CMA certification can provide a good ROI and tools for success, especially with Imarticus Learning by your side.
Skills That Amplify Your CMA Salary
Employers now expect CMAs to combine financial foresight with analytical fluency.
| Skill Domain | Impact on Salary | Recommended Tools/Certifications |
| Financial Analytics | +25% | Power BI, Tableau |
| ERP & Automation | +20% | SAP, Oracle, TallyPrime |
| Strategic Costing | +18% | CMA Advanced Modules |
| ESG & Compliance | +15% | ICAI/ICMAI ESG Framework |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | +22% | Python, SQL, Excel Advanced |
Technical expertise alone isn’t enough – CMAs who master analytics, ERP systems, ESG, and automation see pay hikes up to 30% faster than peers.
Watch this realistic EY mock interview for US CMA candidates – a step-by-step guide to cracking technical, behavioural, and situational questions with expert-backed strategies.
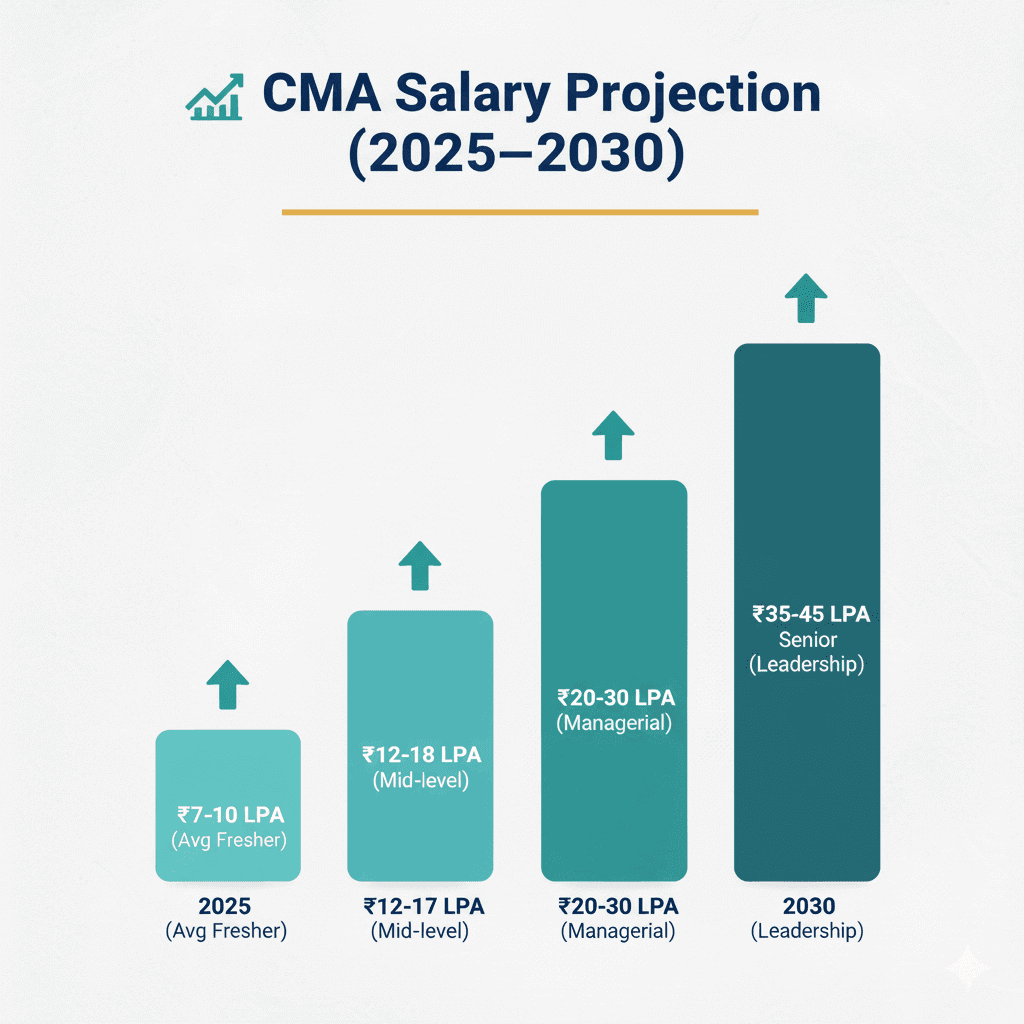
CMA Salary Outlook 2025-2030: The Decade of Strategic Finance
If you are wondering can CMA lead to a high paying finance career?
Between 2025 and 2030, CMA salaries in India are expected to soar, with data-driven and strategic roles commanding the highest compensation tiers.
Imagine this: by 2030, an entry-level CMA starting at ₹6 LPA today could be earning ₹20-25 LPA, not just through promotions, but by moving into analytics-driven roles and leadership tracks that didn’t even exist five years ago.
If the last few years have taught us anything, it’s that CMAs have outgrown the label of “number crunchers.” They’ve become the strategic partners every business needs – the ones turning data into direction and finance into foresight.
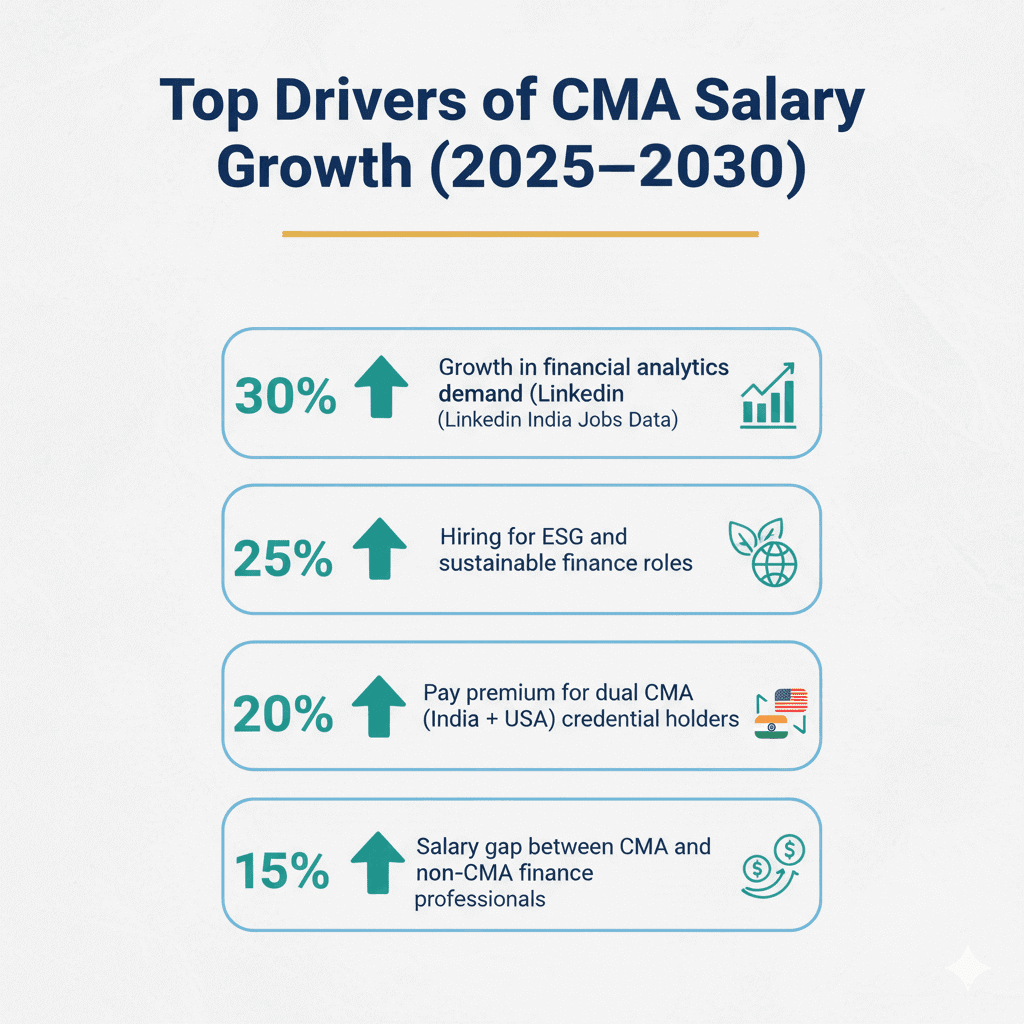
As per recent hiring trends and ICMAI insights, the demand for CMA professionals in India is expected to climb 25-30%, powered by the push toward digital finance, smarter cost management strategies, ESG compliance, and the growing need for finance leaders who can think strategically, not just technically.
Salaries are projected to increase by another 20-25% across mid-senior levels, especially for professionals skilled in data analytics, ERP, automation, and strategic cost leadership.
Companies aren’t just rewarding technical accounting expertise anymore – they’re paying premiums for CMAs who can interpret data, influence strategy, and create measurable business impact with professional ethics.
By 2030, India is likely to see CMA salaries at par with global averages, particularly in industries like fintech, consulting, and manufacturing transformation. In other words, the next five years won’t just determine how much CMAs earn – but how much influence they hold in shaping India’s corporate future.
The takeaway!
CMAs who continuously upskill, embrace technology, and align finance with strategy will define the new benchmarks for compensation and leadership by 2030.
Comparing CMA with Other Top Finance Certifications
When it comes to choosing the right finance qualification, the options can feel endless – from CPA to CFA to ACCA. But if you’re aiming for the perfect mix of global recognition, strong ROI, and faster career growth, here’s how the CMA stacks up against other leading certifications:
| Factors | CMA | CPA | CFA | ACCA | FRM |
| Global Recognition | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Salary Potential (India) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Industry Demand (2025) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Difficulty Level | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Duration | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Exam Flexibility (Online) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Growth Potential (2030) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| ROI / Payback Period | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Overall Rating (2025) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
FAQs About CMA Salary in India
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions students and professionals ask when exploring the CMA salary in India, from monthly pay scales to long-term growth and industry demand.
What is the salary of a CMA in India per month?
If you’re just starting, a CMA in India can expect to earn anywhere between ₹33,000 to ₹58,000 per month – depending on where you work, your industry, and the size of your company. As you gain experience, that figure can comfortably cross ₹1 lakh a month, especially once you move into mid-level or managerial roles.
Can a CMA earn ₹1 lakh per month?
Yes, and quite realistically too. Most CMAs hit the ₹1 lakh/month milestone within 5-7 years, particularly those in consulting, finance, or multinational companies where strategic and analytical roles are highly valued.
Who earns more, CA or CMA?
Both qualifications open doors to lucrative careers; it really depends on your area of expertise. CAs tend to dominate in audit, tax, and assurance, while CMAs usually take the lead in Business Strategy, Cost Management, and Financial Planning & Analysis roles. In corporate and manufacturing, CMAs often have the edge.
Which CMA has the highest salary?
Top-level CMAs in leadership roles – like CFOs, Finance Directors, or Controllers- can earn anywhere between ₹50 LPA and ₹1 crore annually. These roles are usually with large corporations, multinationals, or high-growth startups where strategic finance drives business decisions.
Is CMA in demand?
Yes, more than ever. With companies focusing on cost efficiency, digital transformation, and strategic finance, CMA-certified professionals are seeing 25-30% higher demand across industries compared to previous years.
Turning Your CMA into a Career Power Move
The CMA credential is globally recognised and respected across industries, giving you the flexibility to pursue diverse career paths, whether in corporate finance, strategy, or consulting. Completing the CMA course demonstrates not just technical proficiency but also your commitment to continuous professional growth, setting you apart in today’s competitive job market.
A CMA isn’t just another accounting certification – it’s your gateway to becoming the kind of finance professional who doesn’t just report numbers but drives decisions. Whether you’re starting or aiming for leadership, the CMA builds your confidence, credibility, and strategic edge – the kind that makes people turn to you in the boardroom.
And as India’s financial landscape keeps evolving, one thing’s certain – the demand and rewards for skilled CMAs are only climbing. So if you’re ready to turn your financial expertise into real influence, now’s the time to invest in your CMA journey.
At Imarticus Learning, we know that today’s finance aspirants don’t just want to pass an exam – they want to build a career that grows with them. Our CMA program is designed exactly for that – to help you master the concepts, apply them through real-world cases, and confidently step into high-impact finance roles.
When you join the CMA program at Imarticus, you’re not just preparing for an exam. You’re stepping into a global finance career that’s built to evolve, lead, and last. Enquire now!