There’s something fascinating about watching numbers unfold over time: salaries, markets, costs, everything that frames a finance career. When I speak with ACCA aspirants, the questions eventually converge on the same theme: “What does the earning journey look like?”
These ACCA Salary Insights are meant to simplify exactly that. When you can see how compensation grows in different regions, how capability compounds, and how employers value global mobility, planning a career path becomes far more strategic.
Before we move across India, the UK, UAE, Canada, and Australia, let’s build a baseline for what governs the ACCA salary insights, because ACCA doesn’t operate in a vacuum. Every number is a product of industry behaviour, economic temperament, demand-supply cycles, and the maturity of finance ecosystems.
A Quick Breakdown of What ACCA Really Is
Before exploring deeper into ACCA Salary Insights, it’s important to start with the foundation: what is ACCA? The Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) is a globally recognised professional qualification built around one core idea: creating finance leaders who can adapt to different regulatory systems, economic environments, and business models.
Unlike region-restricted accounting credentials, the ACCA course carries mobility across more than 180 countries, which is why its earning patterns look so different from one market to another. The qualification combines financial reporting, audit, taxation, performance management, ethics, and business strategy in a way that prepares candidates for both traditional accounting roles and modern analytical or advisory positions.
What makes ACCA stand out is the structure of learning itself. Students progress through skill-based and strategic-level papers while simultaneously developing practical experience through real-world roles. This pairing of theory + applied exposure is exactly what employers look for when deciding salary bands, both in entry-level hiring and in mid-career progression.
As we move forward into the detailed ACCA Salary Insights across India, the UK, UAE, Canada, and Australia, this context becomes important. Salary behaviour is shaped not only by geography, but by how organisations perceive ACCA-trained professionals, as globally adaptable, analytically strong, and prepared for increasingly hybrid finance roles.
This understanding lays the groundwork for why salary growth happens the way it does, and why ACCA remains one of the most internationally relevant qualifications for finance aspirants today. Watch this video to get a ground-up understanding of the ACCA course structure:
Understanding the Modern ACCA Earnings Landscape
Before we look at specific countries, it helps to understand the economic forces shaping the ACCA pay scale worldwide. The global finance industry has entered a new era where the definition of “accounting” has expanded beyond compliance and audit.
Today’s ACCA professionals are transitioning into hybrid roles: finance business partnering, enterprise risk analysis, sustainability reporting, digital finance transformation, and strategic performance management.
Recruiters repeatedly mention that roles requiring analytical judgment, scenario modelling, and real-time reporting are seeing the sharpest salary expansions. When cross-border experience is added, the ACCA earning potential grows at a steady pace, almost like a compounding graph.
A Snapshot Indicator of Global Salary Trajectories
(Description: A simple line graph showing salary growth curves across five countries from entry level to senior level. The slope is steepest for Australia and UAE, moderate for the UK and Canada, and stable but upward for India.)
If someone were to map the median salary growth of ACCA talent over a 10-year lens, three broad patterns emerge:
- High-growth countries (Australia, UAE): Accelerated jumps because of strong financial services ecosystems and shortages of qualified accountants.
- Mature markets (UK, Canada): Consistent but stable increments driven by structured corporate ladders.
- Emerging markets (India): Steady upward curve aligned with digital finance expansion, GCC outsourcing, and the rise of captive finance centres.
These broad forces act as the foundation for the ACCA salary comparison across our five focus countries. Here is a visual overview of the ACCA salary insights across the 5 countries we are going to discuss in detail ahead:
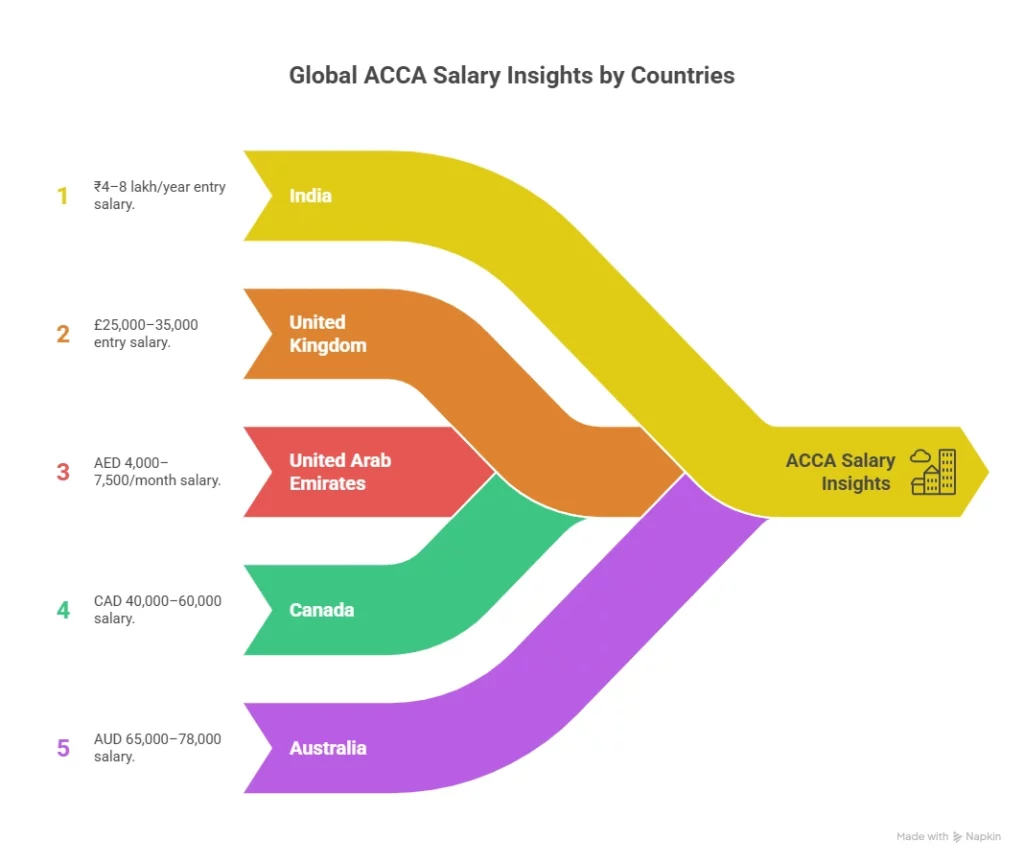
ACCA Salary Insights for India (2025)
India is experiencing one of the most interesting transitions in global finance. Over the last decade, the country shifted from being a back-office engine to a strategic global finance hub. Consultancies, MNCs, fintech companies, global capability centres, and Big Four firms are all restructuring teams to align with the IFRS-based reporting environment.
This demand expansion is reflected directly in the ACCA global salary benchmarks set for professionals working in India.
To better understand the landscape, let’s break down earnings across levels, roles, and industries.
- ACCA Salary Structure in India: Level-by-Level
A structured breakdown of ACCA salaries and career prospects in India across each career stage, showing how earnings progress from entry-level roles to senior finance positions.
ACCA Salary Structure in India (2025)
| Career Stage | Typical Roles | Average Annual Salary |
| Entry Level (0-2 years) | Audit Associate, Accounts Executive, Analyst | ₹4-8 LPA |
| Mid Level (3-6 years) | Financial Analyst, Internal Auditor, FP&A Analyst | ₹8-14 LPA |
| Senior Level (7-12 years) | Finance Manager, Senior Auditor, Compliance Lead | ₹14-22 LPA |
| Leadership (12+ years) | Finance Controller, Head of Finance | ₹25-40+ LPA |
(Source: AmbitionBox, Michael Page India Salary Guide, Glassdoor India)
These numbers anchor the Indian ACCA Salary Insights narrative. The shift from mid to senior levels is especially pronounced in India because of the scarcity of IFRS-trained, ACCA-qualified seniors who can lead multi-country reporting.
- Sector-Wise Salary Breakdown
Different industries value ACCA skill sets differently. For example, a role in internal controls for a bank demands a completely different skill orientation compared to an FP&A analyst in a tech company.
Below is an overview that reflects industry-wide salary behaviour:
ACCA Salary by Sector (India)
| Sector | Salary Range | Hiring Demand Level |
| Big Four Consulting | ₹6-22 LPA | Very High |
| Large MNCs / GCCs | ₹6.5-23 LPA | High |
| Banks & NBFCs | ₹5-18 LPA | High |
| Tech & IT Services | ₹4.5-16 LPA | Moderate |
| Manufacturing & FMCG | ₹4-14 LPA | Moderate |
The rise of GCCs (Global Capability Centres) significantly influences the Indian ACCA pay scale. Over 1,600+ GCCs operate in India, with new ones opening every year, and finance is one of the dominant verticals.
- ACCA Salary Growth Path in India
A finance professional’s early years often feel chaotic: learning, adjusting, absorbing frameworks, and mastering practical judgment. ACCA students tend to peak faster because the qualification trains them for competency-based application rather than pure theoretical learning.
ACCA Salary Insights for the United Kingdom (2025)
The UK is the birthplace of the ACCA qualification and one of the most mature accounting markets in the world. Its salary graph is shaped by a stable economy, high regulatory standards, and deep financial systems.
Because ACCA members in the UK often progress into specialised roles in audit, risk, advisory, tax, and banking, the ACCA global salary framework in this region is fairly structured and predictable.
Salary Snapshot: UK
Here is a structured look at how compensation evolves by experience level:
ACCA Salary Structure: UK (2025)
| Level | Average Annual Salary | Typical Roles |
| Entry Level | £25-35K | Audit Associate, Finance Assistant |
| Mid Level | £40-60K | Financial Analyst, Internal Auditor |
| Senior Level | £65-90K | Senior Accountant, Audit Manager |
| Leadership | £95-130K+ | Finance Controller, Partner-track roles |
(Source: Reed UK Salary Guide, ACCA UK Insights, Glassdoor UK)
The UK remains one of the strongest destinations for ACCA international jobs due to its structured hiring systems and the size of its financial sector (London alone hosts 300,000+ finance roles).
London’s salaries are significantly higher because many global banks, hedge funds, and consulting firms base their European HQs there.
Skills That Trigger Salary Growth in the UK
A unique trait of the UK market is the premium placed on specialised technical knowledge. ACCA professionals with mastery over:
- Sustainability reporting
- IFRS 9 and IFRS 16
- Investment accounting
- Risk and regulatory frameworks (Basel III, Solvency II)
UK Job Market Stability
The UK has maintained a consistently high demand for ACCA professionals even during periods of economic uncertainty. Roles in audit, internal control, and compliance remain evergreen because regulatory governance forms the backbone of the UK corporate environment.
ACCA Salary Insights for the UAE (2025)
The UAE is one of the most attractive global destinations for ACCA professionals because of its tax-free compensation, multi-sector finance ecosystem, and steady creation of regional headquarters. Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah have emerged as multinational finance hubs, each with its own employment pattern.
What stands out in the UAE’s ACCA salary structure is speed: the time taken for a career to accelerate is much shorter compared to Western economies. Large corporate structures move quickly, markets expand rapidly, and companies are constantly on the lookout for professionals with IFRS fluency.
Salary Overview: UAE
Below is a region-specific breakdown that represents the 2025 hiring landscape:
ACCA Salary Structure: UAE (2025)
| Level | Salary Range (Per month) | Typical Roles |
| Entry Level | AED 4,000 – 7,500 | Junior Accountant, Analyst |
| Mid Level | AED 8,000 – 15,000 | Financial Analyst, Internal Auditor |
| Senior Level | AED 16,000 – 25,000+ | Finance Manager, Audit Manager |
| Leadership | AED 28,000 45,000+ | CFO Track Roles, Finance Controller |
(Source: Bayt.com, GulfTalent UAE Report)
These ranges reflect both free-zone and mainland structures. Free-zone entities typically offer slightly higher salary bands due to international exposure and demand for global frameworks.
Why ACCA Salaries Grow Quickly in the UAE
The UAE’s salary acceleration is shaped by five structural advantages:
1. Tax-Free Income
A finance professional earning AED 17,000 per month in Dubai retains nearly the entire amount, a significant advantage.
2. Abundance of Multinational HQs
Dubai is home to 70%+ of the Middle East’s regional headquarters for global corporations.
3. Compliance-Heavy Environment
The UAE’s push toward global regulatory alignment (IFRS, FATF compliance, AML standards) increases demand for ACCA-trained professionals.
4. Rapid Sector Diversification
Banking, logistics, tourism, energy, fintech, and free-zone operations all contribute to job creation.
5. Employer Preference for Global Certifications
ACCA is seen as a “plug-and-play” qualification in the UAE market because the curriculum aligns with IFRS, the UAE’s official reporting framework.
All of these contribute directly to upward-moving ACCA Salary Insights for the region.
Most Common Roles for ACCA Professionals in the UAE
The market strongly favours professionals with a blend of accounting fundamentals, business understanding, and analytics capability:
- Junior Accountant
- Accounts Payable/Receivable Analyst
- Audit Associate
- Financial Analyst
- Internal Auditor
- Management Accountant
- Treasury Analyst
- Senior Accountant
- Finance Manager
- Compliance & Risk Roles
Finance managers and senior auditors in the UAE often handle cross-country portfolios for KSA, Qatar, Oman, and Kuwait, making the region one of the most globally connected markets for ACCA members.
ACCA Salary Insights for Canada (2025)
Canada’s financial job market is structured, stable, and deeply influenced by regulatory expectations. Unlike the UAE’s rapid-growth model, Canada rewards consistency and specialisation.
Where ACCA fits into this system is quite interesting: even though ACCA is not recognised as a “Chartered Accountant” designation in Canada, it is widely accepted for corporate finance roles, controllership tracks, banking, and FP&A roles.
What makes Canada particularly appealing is the clarity of its pay scale and the importance given to structured progression, something ACCA candidates find empowering.
Salary Overview: Canada
An at-a-glance view of how ACCA salaries progress across experience levels in Canada, offering a structured look at earnings from entry roles to senior finance positions.
ACCA Salary Structure: Canada (2025)
| Level | Salary Range (Per year) | Typical Roles |
| Entry Level | CAD 40K-60K | Analyst, Junior Accountant |
| Mid Level | CAD 65K-90K | Senior Accountant, FP&A Analyst |
| Senior Level | CAD 100K-125K | Finance Manager, Audit Manager |
| Leadership | CAD 130K-170K+ | Finance Controller, Director of Finance |
(Source: Glassdoor Canada, Indeed Canada, Randstad Canada Finance Report)
These figures represent corporates, banks, and public-sector entities combined.
Did you know? Ontario, home to Toronto, the financial capital, consistently leads the country’s salary scales.
Canadian Hiring Preferences That Affect ACCA Salaries
1. Hybrid Roles Are Highly Valued
Companies increasingly seek professionals who understand both financial reporting and business analytics.
2. Strong Premium on IT Skills
Good command over SAP, Oracle, Power BI, and financial modelling tools significantly improves the ACCA earning potential in Canada.
3. Public Sector Stability
Government and non-profit organisations often hire ACCA professionals for compliance and budgeting roles.
4. Corporate Finance Focus
Canada’s finance teams value consolidation, forecasting, and risk management abilities, areas where ACCA training strengthens the candidate profile.
ACCA Salary Insights for Australia (2025)
Australia presents a compelling mix of strong finance demand, immigration pathways, and high-quality living. Melbourne and Sydney dominate the accounting employment landscape, and both cities consistently rank in global liveability indices.
Australia’s labour shortage for skilled financial professionals has widened over the last decade. This shortage directly strengthens the ACCA global salary benchmarks in the region.
ACCA Salary Structure: Australia (2025)
| Level | Salary Range (Per Year) | Typical Roles |
| Entry Level | AUD 65K-78K | Graduate Accountant, Analyst |
| Mid Level | AUD 80K-100K | Senior Accountant, Financial Analyst |
| Senior Level | AUD 105K-130K | Finance Manager, Audit Manager |
| Leadership | AUD 140K-180K+ | Finance Controller, Senior Manager |
(Source: Hays Australia Salary Guide, Seek Australia Salary Data, Michael Page Australia)
These ranges are representative across industries: banking, energy, tech, and professional services.
Why ACCA Professionals Thrive in Australia
Five forces shape Australia’s strong salary performance:
1. Skilled Migration Routes Are Clear: ACCA members often qualify under skilled occupation lists, aiding relocation.
2. High Shortage of Senior Accountants: Australia faces one of the sharpest shortages of qualified finance talent, pushing salaries upward.
3. Technology-Driven Finance Ecosystems: Analytics-heavy workplaces prefer internationally trained professionals.
4. Strong Governance Standards: Australian companies emphasise robust internal controls and consolidation; key strengths of ACCA training.
5. Multi-Industry Exposure: Mining, agriculture, fintech, education, and healthcare all maintain steady finance hiring cycles.
City-Wise ACCA Salary Comparison in Australia
A quick breakdown of how ACCA salaries vary across major Australian cities:
Salary Ranges by Major Cities
| City | Salary Range (Per year) |
| Sydney | AUD 80K-155K |
| Melbourne | AUD 75K-150K |
| Brisbane | AUD 70K-140K |
| Perth | AUD 72K-145K |
Sydney and Melbourne dominate finance roles, but Perth’s mining-driven financial ecosystem is also expanding.
Global ACCA Salary Insights: Understanding Patterns Across 5 Countries
By now, we’ve walked through the five regions individually. What ties them together is not just the numbers, but the behavioural patterns behind those numbers.
When professionals look at long-term earning arcs, they often focus on the headline figure of a country. What matters just as much is why a country pays the way it does, and how salary decisions are shaped under the hood.
This section is crafted to give a holistic view that ties together India, the UK, UAE, Canada, and Australia, linking patterns that can guide a 10-year finance career.
Global Salary Patterns That Shape ACCA Careers
Across all the salary datasets, three clear salary behaviours emerge.
1. The “Early Complexity” Reward Curve
Countries reward ACCA professionals for handling complex tasks early in their careers.
Examples include:
- Consolidation
- Audit planning
- IFRS application
- Due diligence
- Financial modelling
- Controls testing
Countries like the UAE and Australia accelerate salaries faster because juniors handle regional or multi-entity exposure earlier than usual.
This is a driving force behind the ACCA Salary Insights framework across geographies.
2. The “Middle Years Premium” (Years 3–7)
This is the golden window for ACCA salary growth globally. By year 3, an ACCA candidate is usually:
- Confident with IFRS
- Exposed to real audits
- Familiar with financial systems
- Capable of leading modules
- Able to mentor juniors
This period brings the steepest jump everywhere, from India to the UK to Canada.
3. The “Specialisation Multiplier” After Year 7
Whether a professional grows slowly or exponentially after year 7 depends on their niche.
High-value niches globally include:
- business performance & FP&A
- ESG reporting
- enterprise risk
- treasury & liquidity management
- M&A support
- digital finance transformation
A mid-career professional with one strong niche consistently outperforms the generalist track in every region.
Essential Skills That Influence ACCA Salaries Globally
Here are the skills that consistently lift earning potential across all five countries.
- Financial Reporting Excellence: Mastery of IFRS remains the strongest salary enhancer. Multi-country entities and listed companies prioritise IFRS-ready talent.
- Strategic & Commercial Finance: Companies reward ACCA professionals who can interpret numbers rather than simply prepare them. These roles include:
- FP&A
- business partnering
- financial modelling
- scenario simulation
- Digital & Data Skills: Every salary dataset shows a premium for professionals skilled in:
- Power BI
- SQL basics
- SAP/Oracle/NetSuite
- Automation tools (Alteryx, UiPath)
- Governance, Risk & Controls: Regulations tighten each year. Professionals with GRC experience rise faster.
- ESG & Sustainability Reporting: One of the fastest-growing areas linked to salary jumps in the UK, Australia, and Canada.
Watch this video to find out the various high-paying job roles you can explore after completing your course, as well as the associated ACCA salary insights:
ACCA International Jobs: Global Mobility Advantage
Mobility is one of ACCA’s strongest traits.
Professionals with this qualification often receive interview opportunities across borders because the curriculum aligns with IFRS, the global language of reporting.
Some of the most active international markets for ACCA in 2025 include:
- UAE
- UK
- Singapore
- Canada
- Australia
- Qatar
- Ireland
- Malaysia
This mobility directly influences the ACCA salary comparison across countries, because moving to a higher-paying geography becomes a strategic option. The following visual captures the various job roles you can explore for global finance roles with your ACCA certification.
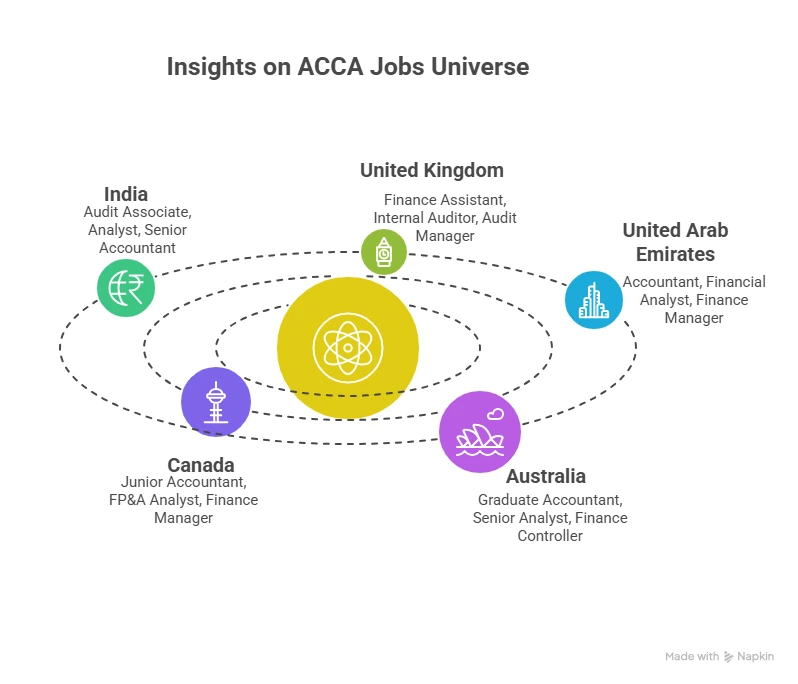
FAQs on ACCA Salary Insights
This section addresses the most frequently asked questions surrounding ACCA Salary Insights, helping learners understand real earning trajectories, global opportunities, and long-term career value.
Can ACCA earn 1 crore?
Yes, reaching the 1-crore annual mark is achievable for ACCA professionals when viewed through long-range ACCA Salary Insights. In India, domestic packages alone rarely reach this number unless the individual is in a senior leadership role in a large conglomerate. Senior finance managers, controllers, and specialist roles in regions like the UAE, Australia, and the UK can cross the 1-crore equivalent once currency conversion is considered.
What is the 7-year rule in ACCA?
The 7-year rule states that students must complete all Strategic Professional exams within seven years after passing their first Strategic Professional paper. The purpose is to maintain current knowledge and ensure qualification relevance. For employers evaluating ACCA candidates, this timeline signals commitment and consistency. Students preparing through structured programs such as those at Imarticus Learning typically complete their exams well before this window closes.
Can you make $500,000 a year as an accountant?
From an ACCA Salary Insights perspective, $500,000 per year sits at the leadership tier of global finance roles. It is an achievable range for CFOs, finance directors, senior partners in consulting firms, and specialists working in investment-heavy industries such as private equity, energy, or multinational banking. While mid-career ACCA professionals generally fall below this bracket, those who progress into executive roles, especially in markets like the US, UK, or Australia, can move toward the $500,000 range as total compensation, including bonuses, stock options, and performance incentives.
Is ACCA a high-paying job?
Yes, ACCA careers align strongly with high-paying global finance roles, which is visible across all ACCA Salary Insights discussed in this article. The earning trajectory begins modestly in emerging markets but rises rapidly with experience, sector transitions, and international exposure. Countries like the UAE and Australia offer significantly higher median salaries compared to local roles in India.
Is ACCA closing in 2026?
There is no indication within any ACCA Salary Insights, ACCA Global publications, or industry reports that the qualification is closing in 2026. ACCA is currently expanding into newer domains like sustainability reporting, digital finance, and global regulatory compliance. The qualification has sustained relevance for over a century and is continuously updated to reflect the needs of global employers. Professionals enrolling today are entering a long-term, globally evolving pathway.
Are ACCA jobless in India?
The concern that ACCA professionals are jobless in India is not supported by any hiring trends or ACCA Salary Insights data. India’s finance ecosystem is expanding rapidly through global capability centres, Big Four firms, consulting companies, fintech players, and multinational corporations. While freshers may need targeted guidance during early job searches, trained candidates, especially those supported by placement ecosystems like Imarticus Learning, secure employment across audit, accounting, analysis, and compliance roles.
Will ACCA be replaced by AI?
AI will transform the nature of finance work, but ACCA will not be replaced. In fact, ACCA Salary Insights show higher demand for professionals who can blend analytical reasoning with digital literacy. Automation handles repetitive tasks, but strategic thinking, interpretation, regulatory judgment, scenario planning, and advisory responsibilities remain human-driven. ACCA regularly updates its curriculum to align with emerging technologies, ensuring that members stay relevant in AI-integrated environments. Roles that combine accounting knowledge with digital tools are witnessing the strongest salary increases globally.
Do Google hire ACCA?
Companies like Google hire for finance, audit, compliance, and FP&A roles, many of which align with ACCA competencies. While ACCA is not an explicit requirement for most roles, global corporations value IFRS knowledge, analytical capabilities, and finance leadership traits, all of which strengthen the overall ACCA Salary Insights profile. ACCA professionals who pair their qualification with strong modelling, analytics, and communication skills often find opportunities within tech giants, particularly in financial planning, controllership, and internal audit teams.
Is ACCA worth it in 2025?
Yes, ACCA carries strong value in 2025 based on global hiring data and ACCA Salary Insights. The blend of international recognition, IFRS orientation, and flexible learning continues to make it one of the most relevant qualifications in the finance world. Countries across the GCC, Europe, Australia, and Asia-Pacific actively recruit ACCA talent. Structured learning platforms like Imarticus Learning further enhance the career readiness of ACCA students.
Do the Big 4 hire ACCA?
All Big 4 firms: Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG, hire ACCA professionals extensively, which influences ACCA Salary Insights in nearly every country. These firms recruit ACCA candidates for audit, advisory, taxation, risk, and financial reporting roles. ACCA aligns well with Big 4 work because of its global accounting focus, IFRS integration, and emphasis on applied professional judgment. Entry-level roles begin modestly, but salary escalates rapidly through performance cycles, international projects, and leadership pathways.
Is ACCA demand decreasing?
Current ACCA Salary Insights show stable and rising demand globally. The qualification has expanded into ESG reporting, risk, digital finance, and strategic modelling, areas with high employer demand. In India, the hiring ecosystem has grown because multinational firms are scaling operations, GCCs are expanding, and regulatory alignment is increasing. Internationally, regions like the UAE, UK, Canada, and Australia continue to recruit ACCA professionals consistently. The demand curve is upward, not declining.
Bringing It All Together
As you’ve seen throughout these ACCA Salary Insights, the earning journey of an ACCA professional isn’t defined by a single country, role, or salary number. It’s shaped by how global finance ecosystems evolve, how skills deepen over time, and how opportunities expand when a qualification is recognised across borders.
If this blog helped you understand anything clearly, it’s that the ACCA pathway opens doors in ways that are both structured and flexible: structured in how salaries rise with experience, yet flexible in how easily professionals can move across industries, specialisations, and countries. That blend is what makes ACCA such a strong long-term investment for anyone building a global finance career.
Many professionals choose structured mentoring to strengthen their preparation, and platforms like Imarticus Learning with their ACCA course prep support that journey with the kind of training that builds confidence and competence at the same time.