The process of two companies or their major business assets consolidating together is known as M&A (mergers and acquisitions). It is a business strategy involving two or more companies merging to form a single entity or one company acquiring another. The reasons for mergers and acquisitions transactions are entirely on the basis of strategic objectives like market growth, expanding the company’s market share, cost optimisation, and the like.
What are Mergers & Acquisitions
M&As are also an essential component of investment banking capital markets. It helps in revenue generation, shaping market dynamics, and more. This article will provide a profound understanding of mergers and acquisitions including the roles and responsibilities in the M&A process, types, processes, and various other nitty-gritty involved in the investment banking fundamentals relevant to this business strategy.
Types of Mergers and Acquisitions
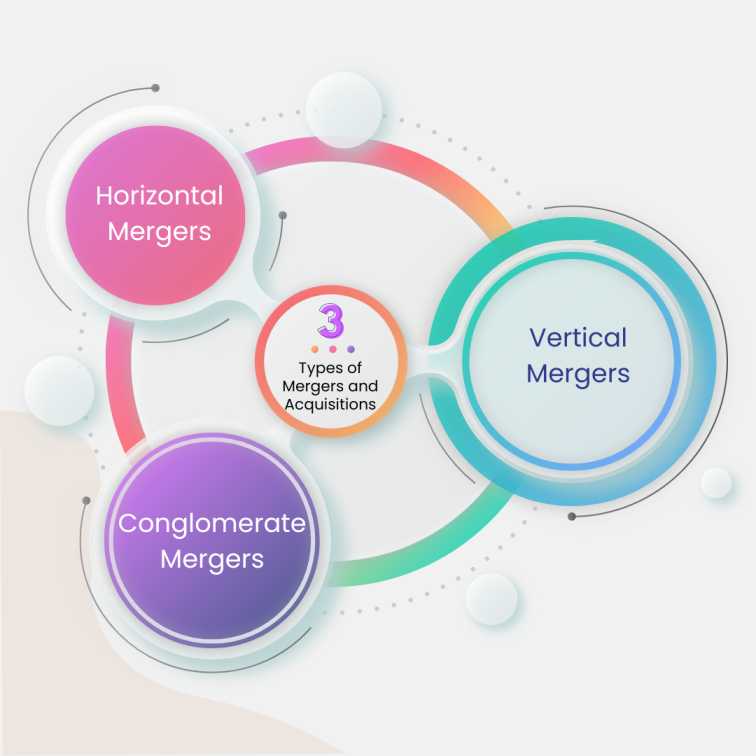
There are many types associated with the mergers and acquisitions strategy. These are:
Horizontal Mergers
The merger or consolidation of businesses between firms from one industry is known as a horizontal merger. This occurs when competition is high among companies operating in the same domain. Horizontal mergers help companies gain a higher ground due to potential gains in market share and synergies. Investment banking firms have a major role to play in identifying potential partners for this type of merger.
Vertical Mergers
A vertical merger occurs between two or more companies offering different supply chain functions for a particular type of goods or service. This form of merger takes place to enhance the production and cost efficiency of companies specialising in different domains of the supply chain industry. Investment banking firms help in the evaluation of said synergies to optimise overall operational efficiency.
Conglomerate Mergers
A conglomerate merger occurs when one corporation merges with another corporation operating in an entirely different industry and market space. The very term ‘conglomerate’ is used to describe a company related to several different businesses.
Friendly vs. Hostile Takeovers
Hostile Takeover
A hostile takeover is a nonconsensual merger that occurs when one corporation attempts to acquire another without the agreement of the board of directors from the target corporation.
Friendly Takeover
A friendly takeover is a consensual merger that occurs because of the agreement between the board of directors of two corporations.
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs)
A leveraged buyout occurs when a company is purchased via two transactional forms, namely, equity and debt. The funds of this purchase are usually supported by the existing or in-hand capital of a company, the buyer’s purchase of the new equity and funds borrowed.
Investment banking services are majorly relied upon throughout the entire process encompassing a leveraged buyout. Investment banking skills are necessary for supporting both sides during a bid in order to raise capital and or decide the appropriate valuation.
Mergers and Acquisitions Process
To succeed in investment banking careers, your foundational knowledge in handling mergers and acquisitions (M&A) should be strong. Guiding clients throughout the processes involved in M&A transactions, including roles and responsibilities in the M&A process, is one of the core investment banking skills.
Preparing for Mergers and Acquisitions
To build a strong acquisition strategy, you need to understand the specific benefits the acquirer aims to gain from the acquisition. It can include expanding product lines or entering new markets.
Target Identification and Screening
The acquirer defines the requirements involved in identifying target companies. They may include criteria like profit margins, location, or target customer base. They use these criteria to search for and evaluate potential targets.
Due Diligence
The due diligence process begins after accepting an offer. A comprehensive examination is conducted wherein all aspects of the target company’s operations are analysed. They may include financial metrics, assets and liabilities, customers, and the like. Confirming or adjusting the acquirer’s assessment of the target company’s valuation is the main goal.
Valuation Methods
Assuming positive initial discussions, the acquirer requests detailed information from the target company, such as current financials, to further evaluate its suitability as an acquisition target and as a standalone business.
Negotiating Deal Terms
After creating several valuation models, the acquirer should have enough information to make a reasonable offer. Once the initial offer is presented, both companies can negotiate the terms of the deal in more detail.
Financing M&A Transactions
Upon completing due diligence without significant issues, the next step is to finalise the sale contract. The parties decide on the type of purchase agreement, whether it involves buying assets or shares. While financing options are usually explored earlier, the specific details of financing are typically sorted out after signing the purchase and sale agreement.
Post-Merger Integration
Once the acquisition deal is closed, the management teams of the acquiring and target companies cooperate together to merge the two firms and further implement their operations.
Taking up professional investment banking courses can help you get easy access to investment banking internships that will give you the required industry-level skills you need to flourish in this field.
Financial Analysis
Financial Statements Analysis
Financial statement analysis of mergers and acquisitions involves evaluating the financial statements of both the acquiring and target companies to assess the financial impact and potential benefits of the transaction. It may include statements like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It is conducted to assess the overall financial health and performance of the company.
In investment banking, financial modelling is a crucial tool used in the financial statement analysis of mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Investment bankers develop a merger model, which is a comprehensive financial model that projects the combined financial statements of the acquiring and target companies post-merger.
Cash Flow Analysis
Examining a company’s cash inflows and outflows to assess its ability to generate and manage cash effectively. In investment banking jobs, one of the primary roles is to assess the transaction structure, including the consideration paid and the timing of cash flows.
Ratio Analysis
Utilising various financial ratios to interpret and analyse a company’s financial performance, efficiency, and risk levels. Investment banking training equips professionals with a deep understanding of various financial ratios and their significance. They learn how to calculate and interpret ratios related to profitability, liquidity, solvency, efficiency, and valuation.
Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable Company Analysis (CCA) plays a crucial role in mergers and acquisitions (M&As) due to its importance in determining the valuation of the target company. In investment banking training, you will learn how to conduct a CCA and identify a group of comparable companies in the same industry as the target company.
By comparing the target company’s financial metrics to its peers, you can identify the company’s strengths, weaknesses, and positioning within the industry and provide appropriate guidance.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is a crucial valuation technique used in Mergers And Acquisitions. It helps determine the intrinsic value of a company. It helps project the potential cash flows of a company in the future. DCF analysis involves factors like revenue growth, operation costs, working capital requirements and the like.
Investment banking training provides the skills in building complex financial models that are required for DCF analysis. They develop comprehensive models that incorporate projected cash flows, discount rates, and terminal values to estimate the present value of a company.
Merger Consequences Analysis
Merger Consequences Analysis helps assess the potential outcomes and impact on financial performance, operations, and value of the entities partaking in the M&A. Investment bankers conduct an extensive evaluation to identify and quantify potential synergies that may result from the merger or acquisition, encompassing cost savings, revenue growth opportunities, operational efficiencies, and strategic advantages.
This analysis aids in estimating the financial implications of these synergies on the combined entity.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
If you are pursuing an investment banking career, knowledge of the various legalities involved in M&As will help you nail any investment banking interview. The regulatory legalities involved in the process of Mergers And Acquisitions that partaking entities and investment banking services need to consider:-
Antitrust Laws and Regulations
Antitrust laws and regulations aim to foster fair competition and prevent anti-competitive practices. In the context of Mergers And Acquisitions, it is vital to assess whether the combination of the acquiring and target companies could potentially harm competition significantly.
Complying with antitrust laws may involve seeking clearance from regulatory bodies or implementing remedies to address any potential anti-competitive concerns.
Securities Laws and Regulations
Securities laws and regulations are of utmost importance in M&A transactions, considering the issuance of securities or transfer of ownership interests. Compliance with these laws governs the disclosure of material information, fair treatment of shareholders, and the filing of requisite documents with regulatory entities.
Regulatory Approvals and Filings
M&A transactions often necessitate obtaining approvals from various regulatory bodies, including government agencies, industry regulators, or competition authorities. These approvals ensure adherence to specific industry regulations and are typically indispensable for proceeding with the transaction.
Additionally, filings and disclosures like Form S-4 or 8-K, may be mandatory for furnishing relevant information about the transaction to legal authorities.
Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure Agreements
Confidentiality is crucial throughout M&A transactions. To safeguard sensitive information and trade secrets, parties involved usually enter into non-disclosure agreements (NDAs). These NDAs outline the terms and conditions governing the sharing and handling of confidential information throughout the entire transaction process.
M&A Documentation
The following M&A documents are instrumental in organising and formalising the holistic M&A process. They give clarity, safeguard the interests of all parties included, and guarantee compliance with pertinent legal and regulatory prerequisites all through the transferring process.
Letter of Intent (LOI)
The Letter of Intent (LOI) is the first and most urgent document that frames the agreements proposed in Mergers And Acquisitions. It fills in as the commencement for exchanges and conversations among the gatherings participating in the business procedure.
Merger Agreement
The Merger Agreement is a legally approved contract that covers every detail of the merger. It may include crucial information like the price of purchase, terms of payment, warranties, post-closure commitments and representations. This arrangement formalises the responsibilities between the partaking parties.
Share Purchase Agreement
The Share Purchase Agreement is a legally binding contract that oversees the assets of the target organisation being acquired. It frames the terms, conditions, and legitimate liabilities connected with the exchange of ownership interests.
Asset Purchase Agreement
An Asset Purchase Agreement is utilised when particular assets of the target organisation are being gained. It is a legal contract that sets out the regulatory commitments attached to the procurement and division of those assets.
Confidentiality Agreements
Confidentiality Agreements, also known as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), play a major role in protecting sensitive data collected during the Mergers And Acquisitions cycle. They lay out rules and commitments to guarantee the safe handling and non-exposure of restrictive proprietary information and secrets.
Due Diligence Checklist
The Due Diligence Checklist is a broad list that helps direct the assessment process by framing the important documents, data, and areas to be evaluated. It works with an exhaustive and deliberate evaluation of the objective organisation’s monetary, legal, functional, and business viewpoints.
M&A Case Studies
M&A case studies serve as a hub of knowledge, enabling companies to make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls. By delving into these real-world examples, organisations can shape their Mergers And Acquisitions strategies, anticipate challenges, and increase the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Some of these case studies may include:-
Successful M&A Transactions
Real-life examples and case studies of M&A transactions that have achieved remarkable success provide meaningful insights into the factors that contributed to their positive outcomes. By analysing these successful deals, companies can uncover valuable lessons and understand the strategic alignment, effective integration processes, synergies realised, and the resulting post-merger performance.
These case studies serve as an inspiration and offer practical knowledge for companies embarking on their own Mergers And Acquisitions journeys.
Failed M&A Transactions
It’s equally important to learn from M&A transactions that did not meet expectations or faced challenges. These case studies shed light on the reasons behind their failure. We can examine the cultural clashes, integration issues, financial setbacks, or insufficient due diligence that led to unfavorable outcomes.
By evaluating failed M&A deals, companies can gain valuable insights so they can further avoid the pitfalls and consider the critical factors to build a successful M&A strategy.
Lessons Learned from M&A Deals
By analysing a wide range of M&A transactions, including both successful and unsuccessful ones, we can distill valuable lessons. These case studies help us identify recurring themes, best practices, and key takeaways.
They provide an in-depth and comprehensive understanding of what are mergers & acquisitions, the various pitfalls and potential opportunities involved in an M&A that can enhance their decision-making processes to develop effective strategies.
Taking up reliable investment banking courses can be instrumental in taking your career to unimaginable heights in this field.
M&A Strategies and Best Practices
By implementing the following M&A strategies, companies can enhance the likelihood of a successful merger or acquisition:
Strategic Fit and Synergies
One of the key aspects of Mergers And Acquisitions is ensuring strategic fit between the acquiring and target companies. This involves evaluating alignment in terms of business goals, market positioning, product portfolios, and customer base.
Integration Planning and Execution
A well-balanced integration plan is crucial for a successful Mergers And Acquisitions. It encompasses creating a roadmap for integrating the acquired company’s operations, systems, processes, and people.
Effective execution of the integration plan requires careful coordination, clear communication, and strong project management to ensure a seamless transition and minimise disruption.
Cultural Integration
Merging organisations often have different cultures, values, and ways of doing business. Cultural integration is essential to aligning employees, fostering collaboration, and maintaining morale. Proactively managing cultural differences, promoting open communication, and creating a shared vision can help mitigate integration challenges and create a cohesive post-merger organisation.
Managing Stakeholders
Mergers And Acquisitions transactions involve multiple stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and regulatory bodies. Managing their expectations, addressing concerns, and communicating the strategic rationale and benefits of the deal are all crucial.
Engaging with stakeholders throughout the process helps build trust and support, ensuring a smoother transition and post-merger success.
Risk Management in Mergers and Acquisitions
M&A transactions involve inherent risks that need to be effectively managed. Conducting comprehensive due diligence, identifying and assessing potential risks, and developing risk mitigation strategies are essential steps.
It’s important to consider legal and regulatory compliance, financial risks, operational challenges, cultural integration issues, and potential resistance from stakeholders.
Post-Merger Performance Evaluation
Evaluating the performance of the merged entity post-transaction is critical to assessing the success of the deal and identifying areas for improvement. This involves tracking financial performance, measuring synergies realised, monitoring customer and employee satisfaction, and conducting periodic assessments.
Continuous evaluation helps refine strategies and ensure the realisation of intended benefits.
Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are intricate processes that require in-depth knowledge and expertise in investment banking operations. The components discussed, such as reasons for mergers and acquisitions, M&A documentation, case studies, and strategies, emphasise the importance of comprehensive analysis, due diligence, and risk management.
Many students tend to pursue investment banking careers because of the comparatively high investment banking salary involved. If you are one of these enthusiasts, pursuing a Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional course from Imarticus can provide you with the investment banking certification you need to get started.
This course helps you develop the specialised skills and knowledge required for a successful career in investment banking. It covers essential topics related to M&A, financial analysis, valuation methods, and regulatory considerations, equipping learners with the necessary tools to navigate the complexities of M&A transactions.