Choosing between CA vs ACCA is rarely a simple academic decision. It’s the moment you decide the kind of finance professional you want to become, the countries you might one day work in, the boardrooms you hope to step into, and the expertise you want to be known for. The two qualifications don’t just differ in syllabus or exam structure; they shape entirely different professional identities.
Across India today, this decision has become even more important. Global capability centres are expanding their teams at a record pace, Indian corporates are strengthening their finance and compliance functions, IFRS is becoming central to multinational reporting, and AI-driven analytics is reshaping what finance jobs look like.
In the middle of this shift, students are trying to decode one essential choice: “Should I take the deep statutory path of CA or the globally mobile, analytically rich route of ACCA?”
The truth is that both qualifications open powerful doors, but the doors open in very different directions. One prepares you to master India’s financial backbone; the other positions you for a world where finance teams collaborate across borders and make decisions from real-time data.
This guide breaks down CA vs ACCA in a way that goes beyond surface-level comparisons. You’ll understand how each qualification impacts your daily professional life, what industries value each one, how salaries progress over time, and where long-term growth truly lies, in India and across global markets.
What is CA?
The CA (Chartered Accountant) qualification in India is administered by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI). It covers several levels:
Foundation → Intermediate → Final, with mandatory articleship (typically 3 years) for practical training.
The exam syllabus spans accounting, auditing, corporate law, taxation, strategic financial management and more. Given its Indian regulatory framework, the CA route is especially suited if you plan to practise audit, tax or consultancy focused on Indian statutes.
What is ACCA?
Before choosing between CA vs ACCA, it helps to understand what is ACCA in the first place. The ACCA qualification, officially known as the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants, was designed to meet the demands of a world where finance doesn’t pause at national boundaries.
Its structure across Applied Knowledge, Applied Skills, and Strategic Professional stages isn’t just academic layering; it mirrors how real organisations expect finance talent to evolve: from understanding fundamental accounting logic to managing global reporting frameworks to eventually guiding business decisions.
In the broader CA vs ACCA conversation, the ACCA course stands out as the route for those who see their career stretching beyond Indian statutory roles, or for those who want to work in global capability centres, Big Four international teams, FP&A functions, or finance transformation projects. It’s the qualification built for a world where the finance office is no longer a single room in one city: it’s a digital, interconnected ecosystem spread across continents.
Learning Structure: Overview of CA vs ACCA
| Feature | CA | ACCA |
| Global Orientation | India-centric | International; recognised in 180+ countries |
| Exam Levels | Foundation → Intermediate → Final | Applied Knowledge → Applied Skills → Strategic Professional |
| Exemptions | Limited | Extensive, based on academic background |
| Primary Reporting Focus | Indian GAAP, Ind AS, Indian Tax | IFRS, global audit & reporting |
| Flexibility | Fixed exam cycles | Modular exams, quarterly sittings |
Watch this video to delve deeper into ACCA and understand the full scope of this global qualification:
Syllabus, Exam Structure and Completion Time
One of the first factors in comparing CA vs ACCA is how long it takes, how many exams you face, and how structured the journey is.
CA Structure
- Foundation (for those without a prior commerce degree/12th Commerce stream) → Intermediate → Final.
- Practical training (articleship) for 3 years is mandatory during or after the Intermediate level under a practising CA.
- The pass rates are quite challenging: for example, the May 2025 attempt of ICAI’s CA Foundation Group 1 recorded only ~14.17% pass rate. (CAclubindia)
- Because of its depth and Indian statutory focus, the time to clear all levels commonly ranges from 4 to 5 years (or longer), depending on how quickly each exam is cleared and how articleship aligns.
ACCA Structure
- Adaptive path: if you already hold a relevant degree, you may be eligible for exemptions.
- Modules are divided into: Applied Knowledge → Applied Skills → Strategic Professional.
- Flexible scheduling: ACCA exams are held quarterly in many regions, offering faster progression.
- Example: In the March 2025 sitting, 90,707 candidates entered, and 3,877 completed their final exams to become ACCA affiliates.
- Many students complete ACCA in 2-3 years, depending on exemptions, pace and employer support.
CA vs ACCA (Course Duration & Structure)
A quick look at how CA and ACCA differ in exam levels, timelines, and learning structure to help you understand what each journey demands.
| Metric | CA | ACCA |
| Typical minimum duration | ≈ 4–5 years (including articleship) | ≈ 2–3 years (with exemptions) |
| Mandatory practical training | 3 years articleship (India) | Practical experience requirement (36 months) + exams |
| Number of major exam levels | 3 (Foundation → Intermediate → Final) | 3 major levels + optional modules |
| Pass rate example (recent) | Foundation Group I ~14% pass rate (May 2025) | Final affiliate conversion ~3,877 of 90,707 entrants (March 2025) |
| Global recognition orientation | Primarily India (with some reciprocity) | Globally recognised (180+ countries) |
Global Recognition & Geographic Mobility
When evaluating CA vs ACCA, a key dimension is global mobility: Will your qualification open doors abroad? Will multinational companies recognise it?
CA Recognition
- In India, the CA is a highly respected credential. For example, ICAI reports that in its campus placement season, the highest domestic CA salary offered reached INR 23.70 lakhs per annum; international postings reached up to INR 49.20 lakhs.
- Outside India, while the CA qualification has value, recognition for signing audit reports or practising may become complex without additional local certification or membership reciprocity.
ACCA Recognition
- ACCA is present in over 180 jurisdictions, offering strong global portability. For example, recent commentary states that ACCA offers “global recognition, high salaries … and flexible exams” in 2025.
- Survey data from ACCA’s “Global Talent Trends 2025” shows increasing demand for ACCA professionals in shared services, global business services and multinational finance centres.
- For someone targeting finance roles in the UK, UAE, Singapore or other global hubs, ACCA provides a clear edge in recognition and mobility.
Implication for you → If you plan to stay and practise in India (audit/tax/consultancy), the CA route offers strong relevance. If your dream is working in a global business services centre, a multinational corporation, or relocating abroad, ACCA may give you better mobility.
Cost of Certification & Time Investment
The investment you make in time, money and effort is significant for both CA vs ACCA.
CA Cost Elements
- Registration, study materials, exam fees, plus practical training period (often paid modest stipend).
- Articleship period typically earns you a stipend; typical amounts quoted in older data were Rs 5,000-8,000 per month, rising if in a Big 4 environment.
- Since CA takes longer to complete, you spend more time studying instead of working full-time, which increases your overall opportunity cost.
ACCA Cost Elements
- Fees include registration, annual subscription, exam fees, study materials and revision courses.
- No fixed paid articleship for all countries; practical experience requirement (PER) has flexibility with employer reports.
- Example figures: In India, fresh ACCA affiliates may start at ₹3–7 lakh per annum, but the cost of studies varies by institute, region and exemptions.
- Because the route can be shorter, the time-investment cost may be less.
Considerations
- When calculating cost, include: course fees + exam fees + study material + exam attempts + opportunity cost of working full-time vs studies.
- Also consider: employer sponsorship, exemptions (for ACCA), ability to study while working (important for CA articleship, which is full-time). You can budget your ACCA journey with a few strategic considerations too.
In practical terms, if you’re a fresh graduate aiming to choose between CA vs ACCA, you may estimate the total investment (in years + cost) as:
- CA: ~4-5 years + articleship + fixed cost annuities
- ACCA: ~2-3 years (if you qualify for exemptions) + flexible practical experience + variable cost (ACCA Course Duration)
Entry Requirements and Strategic Fit for India-Based Students
Next, let’s think about how CA vs ACCA fit if you are based in India (e.g., Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore) and want to plan strategically.
CA Entry Requirements
- Often commerce background is beneficial, though not strictly mandatory.
- You register for Foundation (if no prior commerce degree or 12th commerce background) → then Intermediate → then Final.
- You must complete articleship (3 years), typically during or after Intermediate, with audit/tax firm exposure.
- If you pass Intermediate and complete articleship, you proceed to CA Final.
- The time commitment and full-time dedication required mean less flexibility for working full-time while studying.
ACCA Entry Requirements
- ACCA eligibility offers exemptions if you hold relevant degrees (e.g., B-Com, BBA, etc) or have completed certain papers.
- You can join as a full-time student or while working; the practical experience requirement is 36 months, but can often be gained while working part-time or full-time.
- Because of the modular structure and global exam windows, you can pace your studies faster or slower depending on your working schedule.
Strategic Fit for India-Based Aspirants
- If you live in an Indian metro and aim to join a “Big Four” audit firm (e.g., Deloitte, PwC, Ernst & Young, KPMG) in India and aim for the audit/tax track, CA gives deep local relevance.
- If you’re already working (say in finance, shared services or multinational with global exposure) and want flexibility, ACCA allows you to study while you work, and sets you up for global mobility.
- Consider your career horizon: Do you foresee staying in India and practising domestically? Or do you want to move abroad, join a multinational FP&A, or work on IFRS? Your answer will guide which is better for you in the CA vs ACCA decision.
This video discusses both CA and ACCA in detail and tells you which one to pursue as per your career goals:
Early Career Salary Snapshots: India Focus
Early career salaries often influence a student’s decision more than anything else. Understanding ACCA employability and how CA vs ACCA salary is for the initial years helps you set realistic expectations and plan your financial growth.
The salary curve for both qualifications starts differently but evolves in unique ways depending on industry, city, and global exposure. Here’s a simplified comparison to show how freshers typically begin their journey in India.
| Salary Factor | CA (India) | ACCA (India) |
| Average Fresher Salary | ₹7–10 lakhs per annum | ₹4–8 lakhs per annum |
| Big Four Starting Range | ₹8–14 lakhs per annum | ₹5–9 lakhs per annum |
| Mid-Sized Firm Range | ₹5–8 lakhs per annum | ₹4–6 lakhs per annum |
| Industry Hiring Strength | Audit, Tax, Compliance | FP&A, GBS, IFRS Reporting |
| Salary Growth in First 3 Years | Rapid domestic rise (audit/tax-heavy roles) | Accelerated global-role rise (multinational setups) |
| City Influence | Highest in Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru | Highest in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune (GCC hubs) |
| Work-Study Flexibility Impact | Limited (articleship commitment) | Strong (work while studying boosts early earnings) |
Important takeaway: In India, while fresh salary for CA may be slightly higher compared to ACCA, over time, ACCA’s global role potential and CA’s steep growth in Indian practice both offer high ceilings. Your strategic choice should align with your destination and pace.
Realities of Pass Rates & Difficulty: CA vs ACCA Difficulty
A crucial dimension in any CA vs ACCA comparison is how tough the exams are, the pass rates and what that means for your preparation strategy.
CA Pass Rate Realities
- The May 2025 session of ICAI’s CA Foundation Group 1 recorded only ~14.17% pass rate.
- For CA Intermediate and Final levels, the pass percentages can also fall into low double-digits (typically under 20%), reflecting the rigour and high standards.
- Due to its depth of prescribed law, accounting, audit and high importance of articleship experience, many candidates take multiple attempts, which extends duration and cost.
ACCA Pass Rate Realities
- The March 2025 sitting of ACCA had 90,707 entrants, 102,076 exams completed and 3,877 students reached affiliate status (became ACCA members). (ACCA Global Pass Rates)
- While ACCA doesn’t always publish pass rates in the same way as ICAI, the modular structure, frequent exam windows and global infrastructure make progression more flexible.
- Commentators in 2025 note that “ACCA vs CA difficulty” in India is increasingly viewed as more manageable for many working professionals.
Factors influencing difficulty
- CA difficulty arises from: breadth of syllabus, mandatory articleship, strict pass-criteria (40% in each subject & 50% aggregate)
- ACCA difficulty factors: while the global standard is high, modular exams allow pacing; employer support and exemptions reduce load.
- Working while studying: ACCA offers more flexibility; CA often demands full-time commitment.
- Preparation strategy: For CA, multiple attempts are common; for ACCA, strategic planning and employer mentorship help.
Understanding CA vs ACCA Career Evolution
Before committing years of study and financial investment, it helps to visualise what your day-to-day life could look like once you earn either qualification. The CA vs ACCA career paths differ not just in geography but in the type of work you take ownership of, the teams you collaborate with, and the way your expertise grows over time.
A qualification is more than an exam. It’s a professional identity you carry into meeting rooms, boardrooms, client discussions and cross-border projects. Understanding what that identity unlocks is crucial.
CA Career Paths in India
CAs are trained deeply in Indian accounting, auditing and taxation frameworks. That foundation allows them to build a strong presence in the Indian corporate ecosystem.
Typical roles for fresh CAs include:
- Internal auditor in large corporations
- Statutory audit associate in Big Four firms
- Direct tax consultant or indirect tax specialist
- Corporate finance analyst
- Risk and advisory associate
- Articleship-track conversion roles in mid-sized audit firms
Mid-career roles often include:
- Audit manager or senior manager
- Tax practice lead
- Chief Accountant or Controller
- Financial Reporting Manager (Indian GAAP & Ind AS)
- Compliance and governance lead
Senior positions available to experienced CAs:
- Partner in audit/tax practice
- CFO of mid-sized or large enterprises
- Director of Risk, Finance, or Governance
- Practice head in consulting firms
These roles rely heavily on an in-depth understanding of Indian statutes. If your goal is to build a long-term career rooted in India’s regulatory and business environment, these CA ACCA career paths clearly illustrate why CA remains powerful domestically, whereas you can work in 180+ countries with ACCA. The following visualisation shows a few typical CA ACCA job roles:
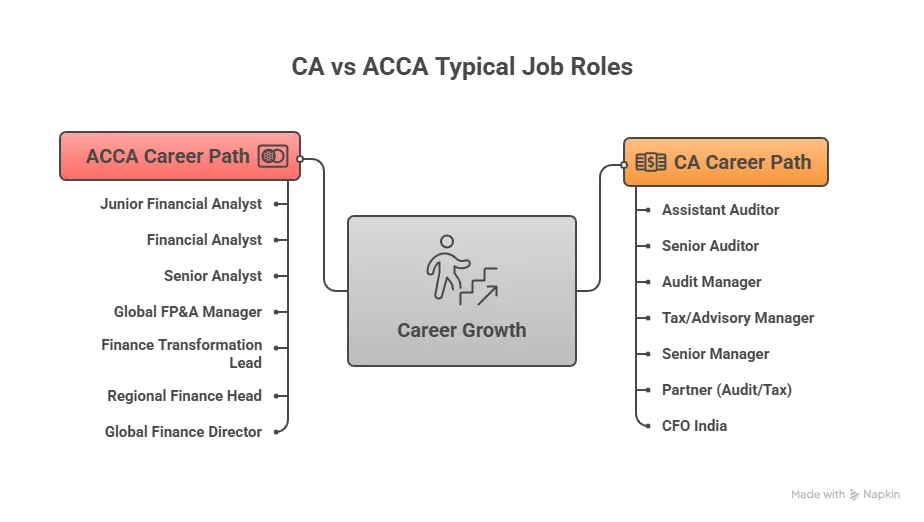
ACCA Career Landscape in India and Abroad
The ACCA network extends across 180+ countries, with strong demand in global business services, multinational finance teams, and shared service centres. Employers value ACCA members for their IFRS knowledge, business analytics capability, and strategic finance exposure. The following represent the ACCA career opportunities globally:
Typical roles for fresh ACCAs include:
- Financial analyst in multinational corporations
- GL, AR, AP roles in global shared service centres
- Associate roles in FP&A teams
- Junior management accountant
- Audit and assurance associate (international standards)
Mid-career roles for ACCA members:
- Financial Reporting Manager (IFRS & consolidation)
- Senior analyst or assistant manager in FP&A
- Treasury and cash flow management roles
- Compliance and internal control specialist
Global senior roles ACCA professionals often grow into:
- Regional finance manager
- Senior FP&A manager (often in the UK, UAE, EU, or SE Asia)
- Global process lead in finance transformation
- Senior auditor in international audit practices
There is noticeable upward mobility for ACCA professionals in markets where IFRS and cross-border accounting are the norm. If your ambitions include working in international offices or specialised areas such as ESG reporting, ACCA builds the foundation for that path.
CA ACCA Career Paths: Sector-wise Mapping
Banking and Financial Services
In banks and NBFCs, CAs often lead audit, credit risk and regulatory functions. ACCA professionals find strong ground in treasury, analytics and IFRS reporting roles.
Big Four and Consulting
Both CA and ACCA professionals work here, but their roles differ. CAs take on statutory audits, GST advisory and tax practice; ACCAs largely enter assurance, process consulting, IFRS reporting, due diligence and global shared services teams.
Corporate Finance
CAs are trusted for Indian regulatory filings, internal controls, and statutory compliance. ACCAs often handle budgeting, financial modelling, consolidation, and global intercompany reporting.
FMCG, Tech, Manufacturing & Startups
CAs strengthen compliance, internal audit and financial control functions. ACCAs lead FP&A roles, MIS reporting, data-oriented finance work, and multi-country consolidation.
This distinction is crucial when making a CA vs ACCA comparison for long-term planning. Your preferred industry and how globalised it is will influence your best choice.
Understanding CA ACCA Benefits Beyond Exams and Pay
When weighing CA ACCA benefits, most students focus on salary or exam difficulty. But the real value comes from the kind of capital: intellectual, global, regulatory, analytical, that the qualification injects into your career.
Here is a deeper look at the benefits that often get overlooked in competitor blogs.
Benefits of pursuing CA
- Deep trust and credibility in India’s corporate ecosystem
- Strong demand in traditional sectors like banking, consulting, real estate and manufacturing
- Authority to sign audit reports in India
- Well-defined progression track for those inclined toward entrepreneurship in audit or tax practice
- Strong government and PSU career pathways
Benefits of pursuing ACCA
- International recognition across 180+ countries
- Strong demand in global business service centres in India (a rapidly expanding sector)
- Familiarity with IFRS, financial planning and analytics
- Flexibility to study while working full-time
- Multi-country employability without needing country-specific recertification in many roles
These CA ACCA benefits influence your journey differently depending on where and how you want to work. A student with aspirations in global finance transformation would lean toward ACCA, while a student who wants to open a tax firm in India would lean toward CA.
Understanding the ROI of Both Qualifications
Instead of simply comparing CA vs ACCA salary, it is helpful to evaluate the return you earn on each year invested in the qualification.
Time Investment
- CA: 4 to 5+ years commonly
- ACCA: 2 to 3 years on average
Early Payback Window
- CA: Students start earning during articleship (stipend) but substantial payback begins post-qualification
- ACCA: Many students work full-time while studying, so payback begins earlier
Relative Early Career Pay
- CA starting salary trend: INR 7 to 10 lakhs per annum
- ACCA starting salary trend: INR 4 to 8 lakhs per annum
Opportunity Cost Difference
Because ACCA completion is quicker for many (with exemptions), the earnings gap over the first 5 years may sometimes narrow more than students realise.
A student who completes ACCA in 2.5 years and works throughout may accumulate more early professional experience than a CA student still in the long exam cycle. Meanwhile, the CA student often overtakes in salary after qualification due to domestic demand. This is why CA vs ACCA salary comparisons depend heavily on the timeline you choose.
Industry Demand Trends for CA vs ACCA
India’s finance ecosystem is evolving. These trends help you understand where each qualification stands.
Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
GCCs such as those built by Deloitte, Standard Chartered, HSBC, Wells Fargo and Amazon have accelerated hiring of ACCA-trained professionals because of IFRS familiarity and global process expertise.
Audit and Tax Practice
CAs remain irreplaceable for statutory audit, GST advisory and specialised Indian compliance services. This is an area where CA retains unmatched authority.
Digital Finance & Analytics
Companies implementing SAP S4/HANA, Oracle Fusion or advanced MIS systems prefer ACCA professionals for FP&A and forecasting roles because they fit more naturally into a data-oriented finance environment.
Regulatory Shifts
With global IFRS convergence and cross-border financial structures, ACCA’s relevance continues to grow. At the same time, increasing Indian regulatory complexity boosts the need for CAs.
Overall industry data shows that hiring trends are not about which qualification is universally superior, but about which one aligns with the sector’s dominant financial framework.
This visual will help you understand the difference between CA and ACCA skills. You can also see what common skills keep both the qualifications aligned:
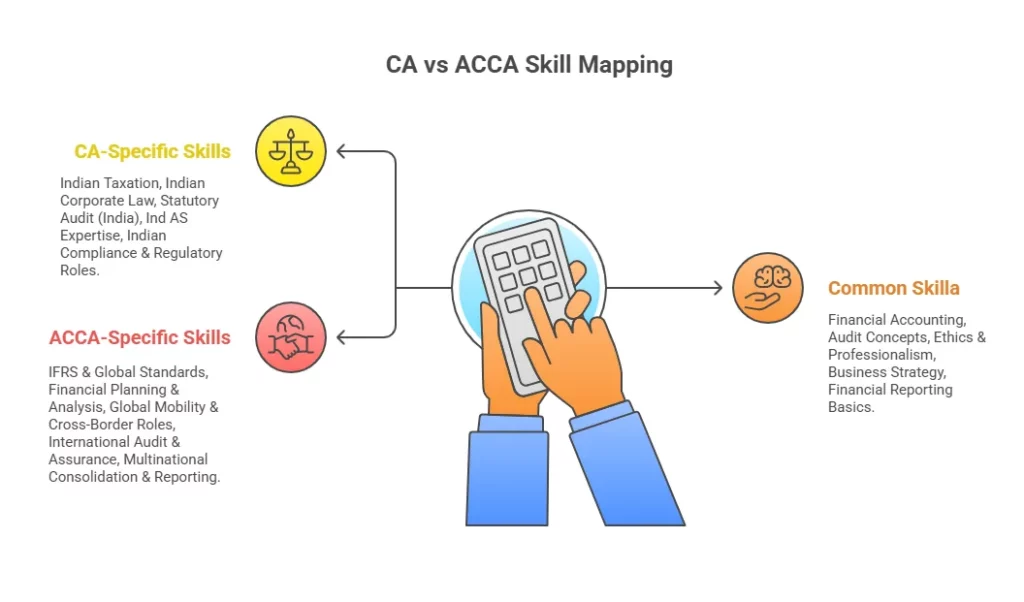
Real-World Scenarios to Choose Between CA vs ACCA
Here are scenarios Indian students commonly face, along with insight on which qualification suits each:
Scenario 1: You want to build a long-term tax, audit or advisory practice in India.
Better suited: CA
Scenario 2: You aim for multinational finance roles or want to work in the UK, UAE, Singapore or EU finance teams.
Better suited: ACCA
Scenario 3: You want to pursue finance transformation, FP&A, MIS or financial modelling roles in global capability centres.
Better suited: ACCA
Scenario 4: You enjoy deep technical accounting, Indian law, and the challenge of multi-layered audits.
Better suited: CA
Scenario 5: You value flexibility and prefer modular global exams rather than a high-pressure, high-stakes Indian exam format.
Better suited: ACCA
Scenario 6: You plan to eventually transition into a CFO role in India.
Both overlap, but CA has a slight domestic advantage.
Scenario 7: You want international audit exposure rather than Indian audit exposure.
Better suited: ACCA
These scenarios help you interpret the CA vs ACCA comparison through everyday decision-making rather than abstract pros and cons. Also, here are some strategic key considerations and questions you can ask yourself if you’re at that juncture of deciding between either of the qualifications.
- Where do you want to work: India-based audit/tax practice or global finance in a multinational?
- How soon do you want to finish? Are you okay spending 4+ years vs aiming for 2–3 years?
- How flexible must your studies be: Can you study while working, or does the route expect full-time study?
- How important is global mobility? Do you want to relocate or stay domestic?
- What’s your starting salary expectation? Do you prioritise early salary or later global ceiling?
- How comfortable are you with difficult pass rates? Are you ready for those odds and investment?
How Recruiters View Each Qualification
A large part of your journey depends on recruiter perception. Understanding employer sentiment provides clarity beyond surface-level comparisons.
What Recruiters Value in CAs
- Mastery of Indian corporate, tax and audit laws
- Reliability in compliance-heavy roles
- Commitment and resilience are reflected in rigorous exam preparation
- Fit for audit firms and PSUs
- Analytical depth in Indian GAAP and Ind AS
What Recruiters Value in ACCAs
- IFRS-driven reporting expertise
- Understanding of global processes and enterprise systems
- Ability to work in multinational and cross-border environments
- Comfort with quarterly exam pacing (signalling continuous learning)
- Fit for FP&A, finance transformation, MIS and global reporting roles
Recruiters often place value not on which qualification is “superior”, but on which one aligns with the financial systems their companies use.
Long-Term Growth and Salary Trajectory (beyond early career)
While early salary data is important, strategic candidates think in decades, not months.
CA Long-Term Growth Patterns
- Rapid upward salary movement after 2 to 3 years of post-qualification experience
- Strong potential for partnership roles in audit/tax
- CFO roles in Indian corporations, manufacturing companies, and newly listed firms
- Opportunity to build your own practice or consultancy
ACCA Long-Term Growth Patterns
- Strong global earning potential
- Rapid movement into FP&A management, finance transformation and consolidation roles
- Easy cross-border movement across IFRS jurisdictions
- Senior roles in global shared service centres and regional headquarters
Your long-term goals matter. For many students deciding between CA vs ACCA salary potential, the ceiling depends heavily on where they want to settle professionally. This video discussed the CA vs ACCA salary prospects at length:
Why Many Students Attempt Both Over Their Career
A rapidly emerging trend in India is dual-qualification professionals: CAs who pursue ACCA for global mobility, and ACCAs who later study Indian taxation or corporate law modules.
Reasons include:
- Expanding their global relevance
- Accessing both Indian and international opportunities
- Building credibility for multi-jurisdictional finance roles
- Increasing employability in multinational companies operating in India
This trend shows that CA vs ACCA isn’t always a strict either-or decision.
Deep-Dive Decision Framework: Choosing Between CA vs ACCA With Clarity
Most students don’t struggle because the syllabus is confusing. They struggle because the decision itself is overwhelming. The qualification you choose influences your pace of career acceleration, the kind of teams you end up working with, and the way employers interpret your career potential. So instead of simply evaluating CA vs ACCA salary or ACCA vs CA difficulty, it helps to break this choice into real decision factors.
Below is a structured framework designed from industry experience and conversations with hiring managers in Big Four firms, multinational finance teams and CFO circles. Treat it like a map.
A. Your Learning Style
- Structured, high-intensity exam cycles:
You may naturally prefer the CA structure, where preparation builds in blocks and each attempt demands deep focus. - Flexible, modular learning with quarterly exam windows:
If your learning rhythm works better with modular exams, ACCA may suit you.
B. Your Work Environment Preference
- Client-facing audit, taxation and compliance-heavy roles:
CA aligns extremely well with this environment. - Team-based global reporting, forecasting, analytics and finance transformation:
ACCA professionals thrive in these structures.
C. Your Geographic Aspirations
- Building a long-term career rooted in Indian regulations:
CA is strongly suited for this track. - Exploring cross-border finance or relocating for global roles:
ACCA gives your profile an international advantage.
D. Your Time Horizon
- You are willing to invest 4–5+ years for a deep India-focused credential:
CA fits this timeline. - You prefer to complete your qualification faster, often within 2–3 years:
ACCA offers that pacing, especially with exemptions.
E. Your Long-Term Ambition
- Indian corporate leadership or practice ownership:
CA builds a powerful foundation for leadership in India. - Senior roles in multinational organisations or global capability centres:
ACCA aligns naturally with this trajectory.
FAQs on CA vs ACCA
This section answers the most frequently asked questions students have when comparing CA vs ACCA, covering career growth, salary potential, global opportunities, exam structure, and long-term prospects, so you can make an informed and confident decision.
Can ACCA earn more than CA?
In the CA vs ACCA landscape, earning potential depends heavily on where the professional works. In India, fresh CA salaries typically begin higher because of domestic statutory demand. However, ACCA members often see strong salary acceleration in MNCs, GCCs and international markets where IFRS-based reporting is essential. Over the long term, ACCA professionals working abroad may earn more than CAs working in India. The deciding factor is location, role type and industry rather than the qualification alone.
Is ACCA closing in 2026?
There is no official indication that ACCA is closing in 2026, and the CA vs ACCA comparison remains fully relevant for future cohorts. ACCA continues to expand its footprint in India and globally through partnerships with employers, universities and finance capability centres. If you are planning to begin ACCA now, you can do so with confidence that the qualification will remain globally recognised beyond 2026.
Is ACCA valued in India?
ACCA has gained substantial traction in India’s multinational finance ecosystem. India’s growth in shared service centres, finance transformation hubs, and IFRS-aligned reporting teams has pushed demand for ACCA members upward. Industries such as IT services, consulting, tech product companies, banking and global capability centres now hire ACCA professionals actively.
With structured guidance, exam-specific mentoring and industry-aligned training, Imarticus Learning helps students prepare effectively for ACCA and build the skills required for these fast-growing global finance roles.
Can ACCA convert to CA?
While you cannot directly convert ACCA to CA, your ACCA background helps significantly if you eventually wish to pursue CA. Many subjects overlap conceptually, particularly in accounting, finance and audit. In the CA vs ACCA comparison, CA requires clearing ICAI-specific exams and meeting statutory articleship criteria.
Is ACCA difficult than CA?
The ACCA vs CA difficulty discussion depends on the kind of academic experience a student prefers. CA is known for lower pass rates and a highly concentrated examination structure, making it one of the most rigorous qualifications in India.
ACCA also requires discipline, but its modular exam structure, quarterly exam windows and globally aligned syllabus make it more manageable for many working professionals. Imarticus Learning provides ACCA-focused training that makes navigating the syllabus and exam strategy more efficient and confidence-driven.
What is the 7-year rule for ACCA?
The 7-year rule applies to ACCA’s Strategic Professional exams. Once a student passes their first Strategic Professional paper, they must complete the remaining Strategic Professional exams within seven years. When discussing CA vs ACCA, this rule often surprises students, but it exists to ensure that professionals qualify with current, relevant knowledge.
Can ACCA earn 1 crore?
Yes, ACCA professionals can earn 1 crore or more depending on their role, geography and industry. ACCA members often reach this level in global finance leadership, regional FP&A roles, finance transformation consulting, and multinational management positions, especially in the UK, UAE, Singapore and Europe.
Senior Indian roles in global capability centres also reach this bracket. Achieving this range depends on experience, leadership and role complexity rather than qualification alone.
Can I finish ACCA in 2 years?
Yes, many students complete ACCA in approximately 2 to 2.5 years, especially if they receive exemptions for Applied Knowledge and Applied Skills levels. In the CA vs ACCA comparison, ACCA’s modular structure and quarterly exam availability allow faster completion than CA.
Students who plan their exam timeline, balance work and study effectively, and maintain consistent financial exposure are the ones who typically finish within this window. Imarticus Learning helps students accelerate their ACCA journey and stay on track for a faster qualification timeline.
How much does ACCA cost in total?
In India, the total ACCA cost ranges widely depending on exemptions, study materials and coaching preferences. When compared within the CA vs ACCA cost equation, ACCA is generally higher in direct fees but often faster to complete.
Students typically spend between INR 2.5 to 3.5 lakhs over the full qualification, excluding optional coaching. The return on investment is often positive for students who enter global roles, FP&A teams or international audit pathways.
Can I get ACCA for free?
ACCA is not available for free, and this is an important factor when evaluating CA vs ACCA. However, students can reduce costs through scholarships, partial fee waivers, university affiliations, or employer sponsorships, especially in multinational companies with strong finance learning budgets.
ACCA occasionally offers discounted registration or exam fee campaigns, but the qualification itself still requires paid components such as exams, books and annual subscriptions.
How many exams are in ACCA?
ACCA consists of up to 13 exams across Applied Knowledge, Applied Skills and Strategic Professional levels, although many Indian students receive exemptions for several papers based on prior qualifications. In the CA vs ACCA comparison, ACCA’s modular exam system is often more flexible, and each paper is attempted individually. With exemptions, a student may end up writing as few as 7 to 9 exams.
Is ACCA expensive in India?
Relative to CA, ACCA is considered more expensive in India due to its exam fees, global subscription charges and optional training modules. Within the CA vs ACCA context, students choosing ACCA often weigh the higher upfront cost against faster completion time and international mobility benefits. Many candidates find the cost worthwhile because ACCA opens doors to multinational finance roles and geographic flexibility.
Conclusion: Bridging Your Future With the Right Qualification
Every student has a unique trajectory, even if the question seems universal: Which is better: CA or ACCA?
CA continues to be a powerful route for those who envision their future in India’s statutory, audit and tax ecosystem.
ACCA, on the other hand, aligns more closely with the way finance roles are evolving today: interconnected teams, IFRS-driven reporting, global capability centres, and cross-border mobility.
Students who want their careers to grow beyond geographical boundaries, participate in multinational finance functions, or build expertise that stays relevant in a global economy often find the ACCA pathway naturally expanding their opportunities.
No matter which route you choose, your decision should come from clarity, not confusion. That clarity is what sets strong careers apart.
And if the latter aligns with your aspirations, the ACCA course prep offered by Imarticus Learning has a structured, industry-aligned preparation ecosystem, complete with expert faculty, mentorship, guided study plans and real-world application support, to help you progress confidently from your first exam to global career readiness.










