The most valued accounting and finance accreditation is to be a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) certified. Universally recognized, US CPA accreditation is an indicator of competence, ethical professionalism, and high performance. Convinced to achieve the most sought-after title, candidates must pass the CPA examination comprising a full course of core subject matter areas financial professionals must obtain.
US CPA topics are designed to examine the competency in the subject matter of core subjects such as auditing, taxation, financial accounting, and business law. Preparing in advance and memorizing CPA exam topics is necessary to pass. The blog is a step-by-step explanation of the US CPA exam syllabus, a clear segregation of CPA topics, and study material for the CPA which will guide the candidates in the right direction for their CPA.
If you want to be a CPA, syllabus, subject, and test pattern will be helpful to become competitive. Let’s proceed to US CPA subjects of requirement and the pattern in which they are offered while providing the CPA examination.
1. Overview of the US CPA Exam
The US CPA exam is administered and organized by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). The exam consists of four sections with a sequence of CPA exam subject matter and testing various accounting, business, and regulation abilities.
CPA Exam Structure
- The exam is split into four:
- Auditing and Attestation (AUD)
- Business Environment and Concepts (BEC)
- Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR)
- Regulation (REG)
- Four of these categories are task-based simulations (TBS), multiple choices questions (MCQs), and written communications tasks.
- It is a test that occurs on a computer annually in one window.
CPA subject matter knowledge under the above four categories must be prepared for. Let us now address each of these categories separately below.
2. Detailed US CPA Subjects and Exam Curriculum
Every section of the CPA exam covers a different topic, and one should be familiar with basic concepts as well as practical applications in depth. Below is the explanation of every section and study material for the CPA.
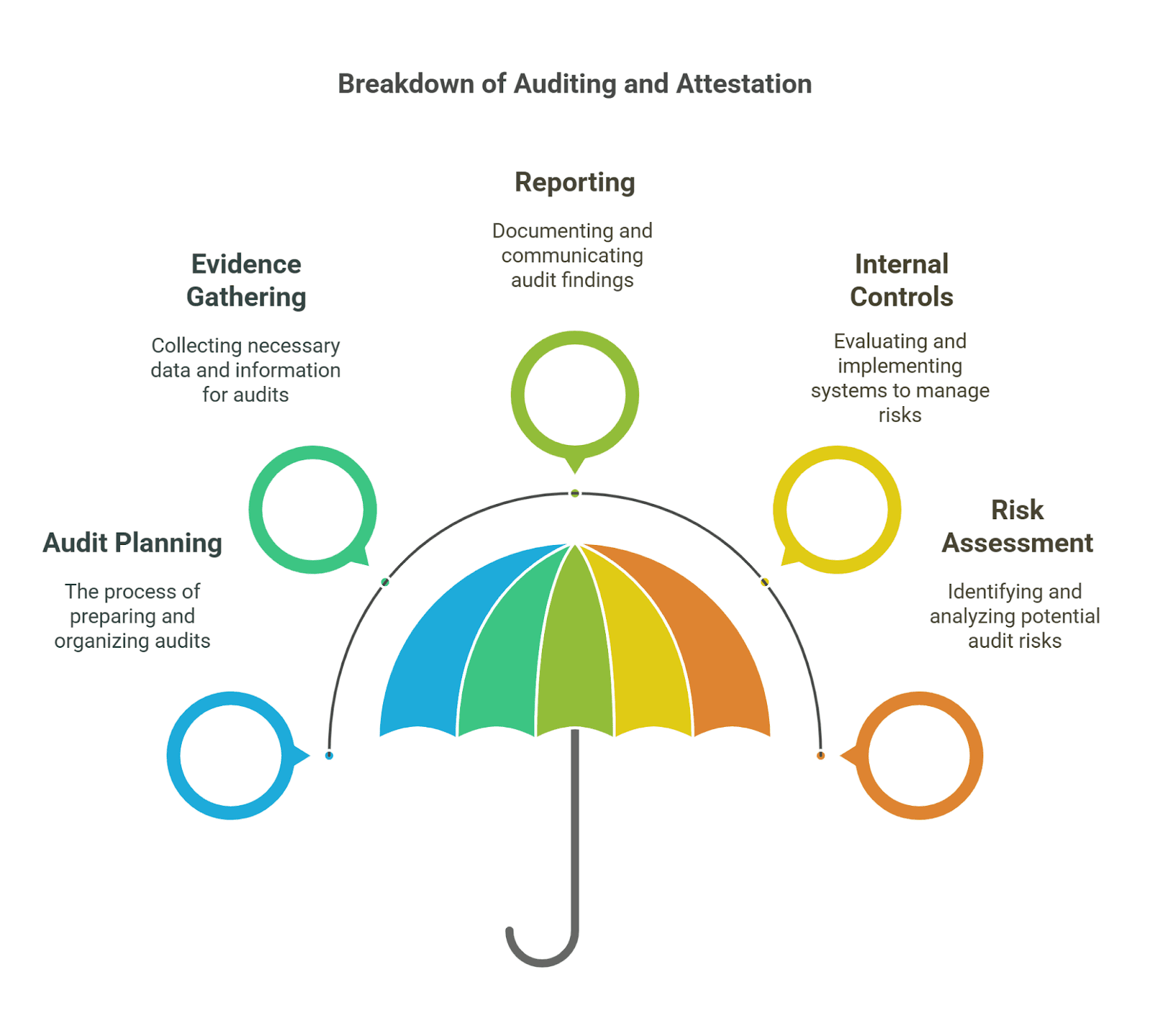
1. Auditing and Attestation (AUD)
AUD section covers audit procedures, attestation, ethics, and risk management. The candidates should be familiar with auditing of financial statements, compliance audit, and fraud detection.
Key Topics Covered in AUD:
- Auditing Principles & Standards – GAAS Application.
- Audit Risk & Internal Control – Audit procedure determination and risk evaluation.
- Engagement Planning & Procedures – Auditing planning, execution, and completion.
- Professional Ethics & Responsibilities – AICPA Code of Professional Conduct.
- IT & Data Analytics in Auditing – Auditing procedures’ impact of technology.
2. Business Environment and Concepts (BEC)
BEC section assesses the candidate’s familiarity with economic theory, company governance, and business concepts. BEC also tests communication skills applied in business.
Key Topics Covered in BEC:
- Corporate Governance & Internal Control – Board roles, compliance, and risk management.
- Economic Concepts & Analysis – Macro and microeconomic features, foreign trade, and demand and supply.
- Financial Management – Planning, risk evaluation, and budgeting.
- Information Technology in Business – IT control, cloud computing, and info security.
- Business Writing & Communication – CPAs must be extra careful about the following.
3. Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR)
Hardest and most technical part is FAR and deals with questions such as financial models of reporting, US GAAP and IFRS, and intricate financial transactions.
Key Topics Covered in FAR:
- Conceptual Framework & Financial Statements – Preparation of balance sheet, preparation of income statement, preparation of cash flow statement.
- Accounting for Transactions – Leasing, revenue recognition, and consolidations.
- Government & Non-Profit Accounting – Applied accounting principles by governmental agencies.
- Fair Value Measurements & Valuations – Intangible, goodwill, and impairment accounting.
- Foreign Currency Transactions & Hedging – Hedging foreign exchange risk of foreign currency.
4. Regulation (REG)
REG course covers the corporation and individual tax and legal law requirements and business ethics information.
Key Topics Covered in FAR:
- Federal Taxation – Business & Individual – Income tax determination, deduction, and credit.
- Corporate & Partnership Taxation – Classification of business forms for tax purposes, determination of tax.
- Estate & Gift Taxation – Estate planning, gift planning, and valuation.
- Ethics & Professional Conduct – Professional ethics of CPAs.
- Business Law & Contracts – Contract formation, negotiable instruments, and securities regulation.
3. Best Strategies for Preparing for CPA Exam Subjects
Because the CPA exam has very wide coverage, the candidates have to study in a structured manner. The following are US CPA’s study processes that they have to follow:
1. Create a Study Plan
- Develop a time table for every subject of the CPA exam based on the difficulty level.
- Enroll in CPA study classes like Becker, Wiley, or Imarticus Learning’s CPA course.
2. Use Mnemonics & Memory Techniques
- Use acronyms for memorizing accounting principles and taxation legislation.
- Flashcards for recalling pesky formulae and phraseology of laws.
3. Practice MCQs and Simulations
- Set 3,000-5,000 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) at least seven days prior to the exam.
- Take simulated exams under timed conditions.
4. Stay Updated on Exam Changes
- AICPA now and then modifies the exam pattern; study guides will need revision.
- Listen to official CPA webinars and discussion forums to be updated.
5. Time Management During the Exam
- Both the sections are 4 hours each in duration; practice in-time answering of questions.
- Start with score questions and subsequently use tougher ones.
FAQs
1. What are the main US CPA subjects?
The four broad CPA exam topics are Auditing and Attestation (AUD), Business Environment and Concepts (BEC), Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR), and Regulation (REG). These are broad subject matter topics for which there are several other accountancy, audit, taxation, and business laws subject matter topics.
2. What is the hardest CPA exam subject?
The hardest part of the CPA exam is FAR since it is the most technology-dependent, and the test-taker must be quite well-acquainted with accounting reports, GAAP, IFRS, and complicated accounting transactions.
3. How many study hours per section of the CPA exam are needed?
All areas of the CPA exam take 120-150 hours of studying. Candidates complete the entire CPA exam in 12-18 months depending on their plan and time table.
4. What is the latest news regarding the US CPA syllabus for 2024?
Yes, the AICPA does make CPA exam syllabus change periodically as per industry progress and regulation mandates. The candidates should take cues from new CPA Blueprints available on the AICPA website to be up to date about exam content changes.
5. Can I sit for CPA exam topics in any order?
Yes, CPA exam can be attempted for exam subject in any sequence. But according to most of the experts, FAR should be attempted first because it unlocks basic knowledge which could be used for other sections.
6. CPA exams are scored?
The CPA exam is marked on a scale of 0-99 and the passing grade is 75. The exam has multiple-choice questions (MCQs), task-based simulations (TBS), and written communications assignments (for BEC only).
7. Do I get a second chance if I fail a subject in the CPA exam?
Yes, the candidates can retake any CPA exam topic after failing the topic. But they can take the failed topic again only in the subsequent test window. Most of the states permit retakes a few times a year.
Conclusion
US CPA study material contains a lot of financial, audit, business, and regulatory content that prepares the candidates to sit for senior-level accounting roles. Familiarization of the content in the CPA exam and learning the fundamental CPA material is what it all comes down to in the passing.
With the proper use of properly designed preparation, better study material, and rigorous practice, upcoming CPAs can become certified by passing the exam and receive a degree accepted internationally. So, are you prepared to start your CPA journey? Join Imarticus Learning’s CPA course and get industry-oriented training, live simulations, and guidance from industry professionals. It is the day that you start your CPA journey—are you ready to start?