The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) credential is the highest in the accountancy and finance sector with extremely rewarding career prospects worldwide. From setting up your professional life as an expert to moving up as an already proficient accountant requiring more compensation, there is a requirement to learn how CPA income progress with time.
With public accountant certification, your salaries vary based on experience, specialty, location, and industry. From starting accountants earning a decent starting wage to senior experts gaining lucrative CPA roles, the scope for professional growth and income increase is outstanding in this discipline.
Here in this article, we are discussing CPA salary trends, average CPA salary at different points of length of their career, CPA earnings potential, and CPA compensation analysis by types of employment and industries. If you are looking to get a CPA certification, this article will provide you with an idea of how your salary rises with years elapsed.
1. CPA Salary Trends: How Income Grows Over Time
CPAs are entitled to increased remuneration as they gain experience and familiarity with the world of business. Salary increases at a reasonable level, from inductees to top managers.
Entry-Level CPA Salary (0-2 Years Experience)
- The typical salary of a CPA freshers would be anything between ₹5 LPA to ₹9 LPA in India
- Newly passed-out CPAs are hired as financial analysts by Big 4 firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG) and multinational companies’ staff accountants and auditors
- Ranking at the university level, internship, and other finance certification may have an impact on the initial salary
Mid-Level CPA Salary (3-7 Years Experience)
- CPAs with 3 to 7 years of experience can expect their salary to rise from ₹10 LPA to ₹20 LPA
- Then, the experts move to designations such as Senior Accountant, Financial Controller, or Tax Consultant
- Risk management, financial planning, or forensic accounting professionals can even command more
Senior-Level CPA Salary (8+ Years Experience)
- CPAs who have more than 8 years of experience can expect to be paid well in the form of CPA jobs ranging from ₹20 LPA to ₹40 LPA.
- These roles such as Finance Director, Chief Financial Officer (CFO), or Audit Partner come with huge salary packages, bonuses, and stock options.
- Those who work for multinational organisations, private equity firms, or investment banks are better paid.
2. CPA Earnings Potential Across Industries
The company you work for is contributing the biggest share to your increase in CPA salary. We will be examining other industries offering good pay packages to CPAs.
Accounting & Auditing
- Big 4 CPA Salary: ₹7 LPA – ₹25 LPA (junior and middle); ₹35 LPA+
- CPAs working with audit firms have secure career opportunities in a potential to become audit manager, partner, or CFOs
Banking & Financial Services
- Investment Banks & Asset Management Companies: ₹8 LPA – ₹30 LPA
- CPAs working in corporate finance, risk management, and wealth management receive compensations relatively
Technology & IT
- Technology companies that hire: Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Infosys
- Salary range: ₹10 LPA – ₹35 LPA
- CPAs working with the finance arm of tech firms participate in planning for finances, handling risks, and taxation.
Consulting & Advisory
- CPAs working with firms in consulting fields in finance areas have a pay package between ₹8 LPA and ₹40 LPA.
- Top recruiters: McKinsey, Accenture, Bain & Co., and Deloitte Advisory.
Government & Public Sector
- Government CPAs receive between ₹6 LPA and ₹15 LPA as salary based on the rank.
- Government regulatory agency careers such as those in SEBI, RBI, and Ministry of Finance can offer long-term employment security.
3. High-Paying CPA Roles & Compensation Analysis
Following is a list of some of the most remunerative CPA job positions and their average compensation range:
| CPA Job Role | Experience Level | Average Salary Range (INR LPA) |
| Staff Accountant | 0-2 years | ₹5-9 LPA |
| Senior Accountant | 3-5 years | ₹10-15 LPA |
| Finance Controller | 5-8 years | ₹15-25 LPA |
| Audit Manager | 6-10 years | ₹18-30 LPA |
| Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | 10+ years | ₹30-50 LPA+ |
| Partner (Big 4 Firms) | 12+ years | ₹50 LPA+ |
Senior-most managers as CFOs, Finance Directors, and Audit Partners can exceed ₹50 LPA with performance-based bonuses and profit-sharing programs.
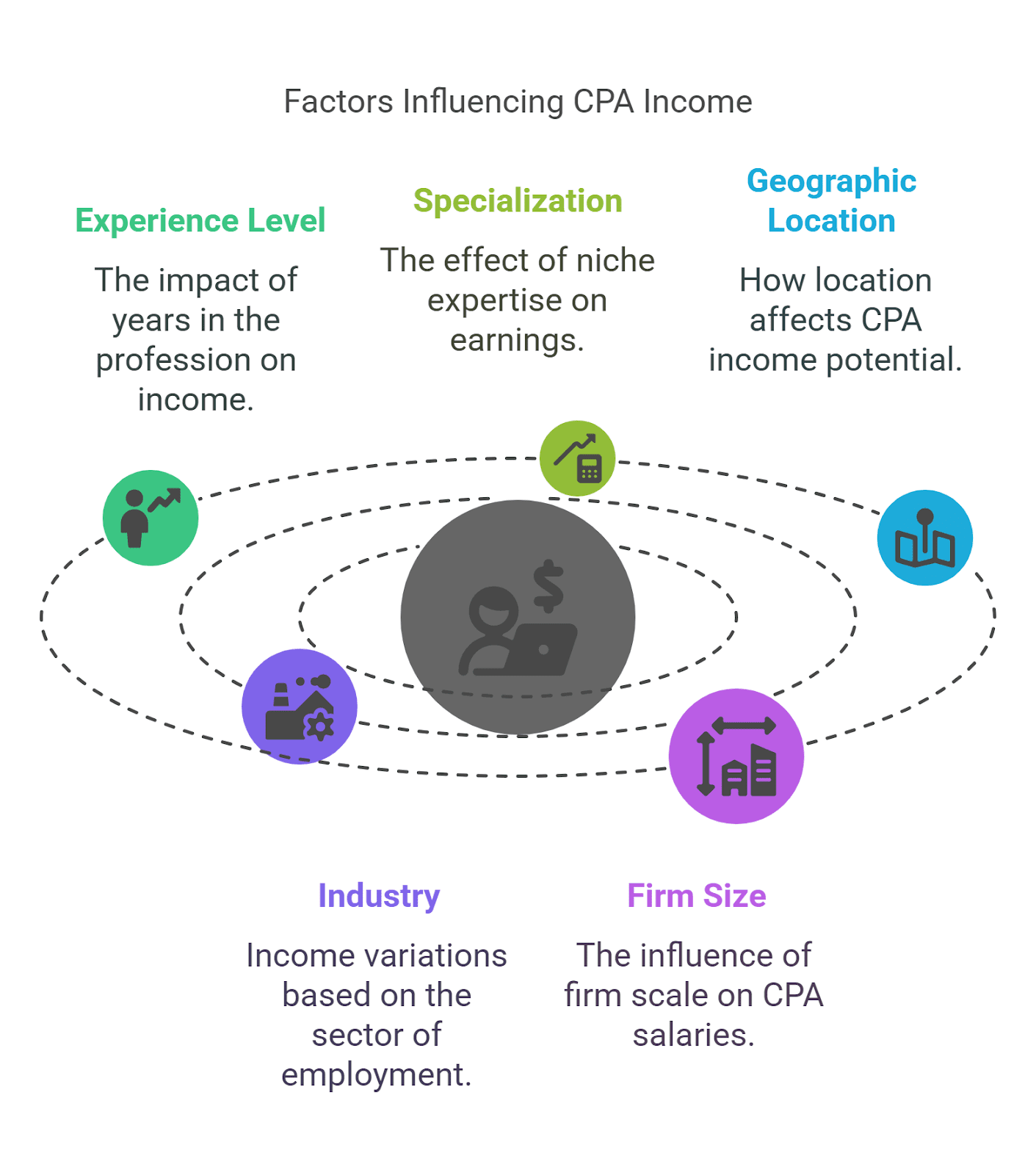
4. Factors Influencing CPA Income Growth
1. Experience & Expertise
- Experience brings higher salary, bonuses, and management positions
- CPAs with tax, forensic accounting, and financial planning skills command higher remuneration
2. Location of Employment
- Packages in cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore are higher based on demand
- US, Australia, or Canada international CPA jobs get greater salary increases
3. CPA Certification & Additional Qualifications
- CPA certification from a well-known agency like Imarticus Learning gets more salary increases
- Pursuing CFA, CMA, or MBA (Finance) can also yield earnings
4. Employer Type
- Big 4, investment banks, or MNC job gets more salary increases
- Private companies and start-ups can afford to include equity in the compensation package
FAQs
1. What is the salary of an Indian CPA on average?
A standard CPA can get anything from ₹7 LPA to ₹20 LPA, depending upon the firm, location, and experience. An executive CPA could get anything up to ₹50 LPA or more.
2. Is a CPA’s salary different from other accountancy certifications?
In comparison to CA, CMA, and ACCA, CPAs are found to earn higher salary on the basis of international recognition they have and greater professional stature with multinationals.
3. What are the best-paying CPA jobs?
CFO, Finance Director, Audit Partner, and Investment Banking Analyst positions come with ₹30 LPA to ₹50 LPA+ salaries.
4. Is working abroad a reason for a higher CPA salary?
Yes. CPAs working in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia get much higher salaries, between $80,000 and $150,000 annually.
5. Where do CPAs get the highest salary?
Multinationals, investment banks, IT firms, and Big 4 accounting firms offer the highest CPA salary packages, with a maximum of ₹50 LPA for senior-level jobs.
Conclusion
CPA certification is an absolute investment in one’s career that is exponentially income-boosting. From staff accountant to a potential CFO, the potential earnings for this career are rather high.
The demand for CPAs with high-level competence increases year by year, and there could hardly be a more timely moment than the present to register for a CPA course and speed up your career growth in a fast track. Proper exposure, training, and certifications enable CPAs to be the ideal choice for demanding fat compensation packages from world-class organisations.
You can take your accounting career to scale and ease life if you sign up for a CPA certification program today and enjoy unparalleled revenues!