Introduction
Data Science course fees are a key issue for a great number of professionals and graduates seeking to enter one of the most buzzed-about professions today. In a world where data is oil, the expense of obtaining a formal qualification in data science can look prohibitive.
But just as important is understanding how the fees relate to the potential salary and increase in this field of endeavor. By putting the cost of data science courses against the potential for data science salary, you know whether or not this is a career that you desire.
In this post, we get into the nuances of profit-making investment in education in data science, returns, and real-life things that can help you make a decision whether this is an ideal career choice.
If you’re evaluating Data Science course fees versus the potential earnings, remember that while tuition costs can be substantial, the career trajectory in data science often leads to lucrative roles with high demand and competitive salaries. Many find that the ROI of data science education quickly surpasses initial expenses.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Data Science Education
In the last few years, data science has evolved from a mystical topic into a cornerstone of strategic decision-making throughout industries. From healthcare to finance and beyond, organisations are applying giant datasets to gain valuable insights.
So, formal education—either in college, in a bootcamp, or an online course—is now a necessity for aspiring data scientists to learn statistics, machine learning, and data visualisation.
But as data science becomes more popular, so does the range of course types and prices. On the one hand, there are low-cost self-study online courses. On the other, high-profile institutions can charge a premium for their course, with prices often in the thousands of pounds.
In order to understand if this trip is indeed worthwhile, it’s essential to explore how prices are set, what they really include, and the interplay between Data Science course prices and the need for a satisfying career.
Factors that Influence the Price of Data Science Courses
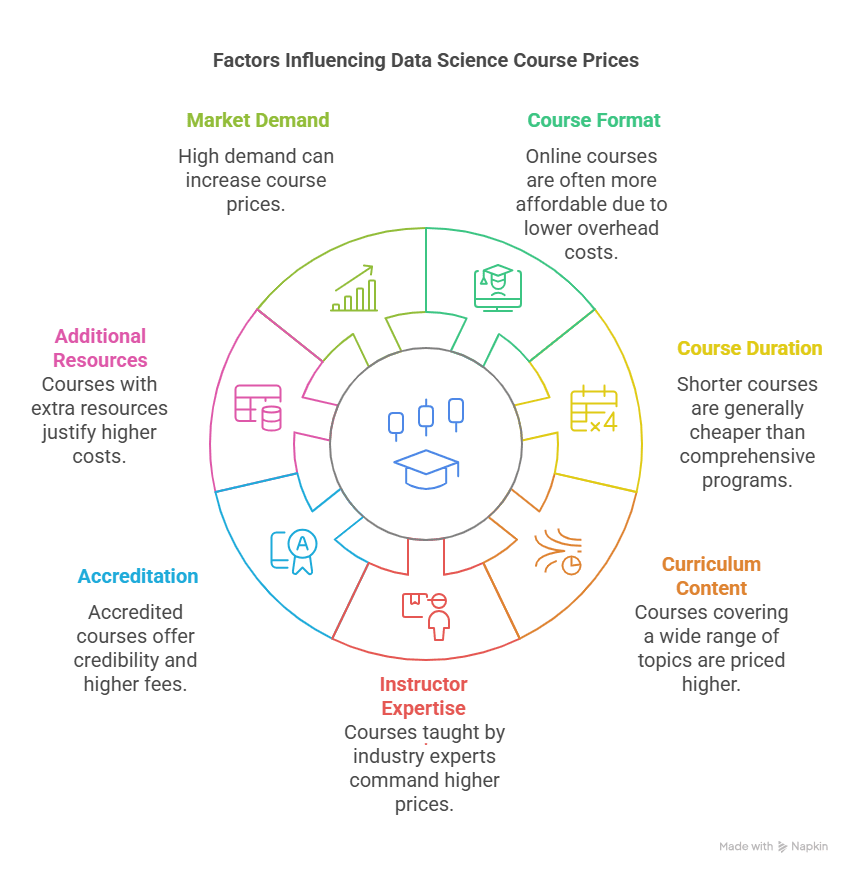
Data science course price is not just the amount paid for tuition. Each program is different and can be worth paying a little extra. Look at the following factors:
Reputation and Brand Value
Colleges/Institutions with rich history in offering quality education and securing the graduates in lucrative jobs are usually costlier. Their programs carry prestige, leading to better networking and greater recognition in the marketplace.
Depth of Curriculum
Some programs provide a broad, introductory treatment of data science, while others focus on particular topics like deep learning, natural language processing, or big data engineering. Specialized programs tend to be more expensive.
Mode of Delivery
Traditional, full-time campus programs usually are more costly due to the infrastructure and facilities provided. Distance or combined modes cost less, but certain online institutions have a high cost since they are providing additional services, live mentoring, and access to networking facilities.
Fees levied by institutions in major cities or capitals of international education can be higher since there’s a business cost of doing things higher here and the consideration of the better location.
It’s possible that most programs provide add-ons like career counseling, internship experience, interview sessions, and alumni connections. These add-ons drive the cost up but contribute to the worth of the education.
When you look at the cost of data science courses, watch out for the extras besides lectures and books. You want a course that provides hands-on applications and actual projects, which will prepare you for the job market competition.
Is a Data Science Course Worth It? Measuring Your Return on Investment
One of the most common inquiries from prospective learners is: “Is a course in data science worth it?”
The response lies in understanding Return on Investment (ROI). ROI is the formula that weighs against each other the worth of a course—e.g., potential salary increases, career development, and the immaterial benefit of learning cutting-edge technologies—and its cost.
Here are significant fields to remember:
Immediate Employability
A recognised qualification can improve your interview chances, as organisations tend to look for formal qualifications as proof of competency.
Salary Increase
Jobs in data science generally carry good salaries. Even a small salary hike post-course completion can pay back fees in a couple of years.
Career Prospects in the Long Run
Growing demand for data professionals means continuous career progression. Data scientists get promoted to senior roles such as data science managers, directors, or chief data officers.
Industry Versatility
Data science talent is versatile across many industries, which provides it with confidence and ample scope for expansion.
Networking and Mentoring
Access to alumni networks, faculty specialists, and industry experts can be a boon for potential career progression.
Deciphering the ROI of Data Science Education in Numbers
Let us consider some numbers from a series of global surveys into perspective. To put it simply, Forbes mentions that companies which completely adopted data-driven strategies had revenues increase by 20% over two years. McKinsey highlights that demand for data scientists continues to be greater than their supply and hence drives their market value upwards.
If you invest, say, ₹2,00,000 in a thorough data science course and your starting salary jumps from ₹4,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 per year, the salary hike could help you recover the course fee within the first year itself. This back-of-the-envelope estimate shows how the ROI of a data science education can be extremely appealing.
The Unique Element: More Than Just Technical Expertise
True, raw technical information is found on the web for free. Structured programmes, though, provide something distinct: opportunities for collaboration. Peer reviews, group projects, and exposure to up-to-date data sets offered by the programme provide insight into how data equates to strategic thinking. This experience differentiates high-calibre data scientists from solo study without similar hands-on experience.
Data Science Salary Potential: An Ever-Evolving Landscape
The earning capacity of a data science professional in India depends on various factors like your education level, the industry you work in, and your willingness to embrace new technologies. Entry-level data scientists typically earn between ₹6,00,000 and ₹12,00,000 per annum, according to Glassdoor India. With the right experience and specialised skills, this figure can rise significantly—often crossing ₹20,00,000 or more in senior roles.
Additional motivators such as yearly bonuses, stock options, and shareholder dividend plans enhance overall compensation even more. Data science’s great ability to earn is still an essential factor in the minds of most future professionals.
Fees vs. Earning Capacity in Data Science
One useful method for comparing the prices of Data Science courses is to compare educational expenditure, job roles, and entry-level salaries side-by-side. Look at the condensed table below, remembering that true costs vary by school and market conditions:
| Programme Type | Approx. Fees (₹) | Typical Entry-Level Salary (₹) | Potential Senior Role Salary (₹) |
| Online Bootcamp | ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,50,000 | ₹5,00,000 – ₹8,00,000 | ₹15,00,000 – ₹25,00,000 |
| University Master’s | ₹6,00,000 – ₹12,00,000 | ₹7,00,000 – ₹10,00,000 | ₹18,00,000 – ₹30,00,000 |
| Executive Programme | ₹5,00,000 – ₹10,00,000 | ₹8,00,000 – ₹12,00,000 | ₹25,00,000 – ₹40,00,000 |
Even at the higher rates of tuition, the pay in data science can often return the investment in a few years.
Highlight on Best Value Data Science Programs
While choosing a program, not only the course fee for Data Science must be taken into account, but also the course, reputation, and career guidance mechanism. For example, the Imarticus Learning Postgraduate Programme in Data Science and Analytics has a proper mix of theory, live projects, and strong career guidance. Further details about the course can be found on their website: Imarticus Learning’s Postgraduate Programme.
Such courses seek to offer the best value data science courses by finding a balance between costs and quality course provision so that you are well equipped for the data-driven career market.
All About Data Science and Analytics Course by Imarticus Leaning | Data Science For Beginners
How Data Science Career Investment Pays Off in the Long Run
While the short-term financial reward is tempting, the payback on a data science career investment tends to grow in the long term. Take a look at these points:
Continuous Skill Development
The ever-changing nature of data science requires constant upskilling, updating your skills from time to time.
Leadership Shift
Experienced data scientists can transition into leadership roles, influencing key business decisions and increasing their salaries as they ascend the corporate ladder.
Flexibility and Employability
Data science skills are in high demand and are highly transferable across many industries, forming a solid foundation for long-term career growth.
FAQs: Answers to Your Questions
- What do typical Data Science course fees look like?
Fees can range from a few thousand pounds for bootcamps up to over £15,000 for university programs that cover everything.
- Are data science course scholarships an option?
Yes. Many institutions offer scholarships or early-bird discounts. Always check the program’s website or contact admissions for the most recent options.
- How quickly can I recover my investment after completing a course?
Recovery time will depend on how much your salary increases after completing the course. Many professionals find the investment worthwhile within one to three years.
- Do I need a good maths background to pursue data science?
A familiarity with statistics, algebra, and calculus is an assistance, though much coursework includes foundation refresher instruction.
- Is it worth taking a data science course if I’m career-changing?
Yes. Official programs can assist in making the transition easier and more attractive to the market, especially if you build on what you already know.
- Can I specialise in one industry after completing a data science course?
Yes. The majority of programmes have elective modules or projects focused on specific industries like healthcare, finance, or marketing.
- What kind of job positions will I be searching for upon graduation?
Typical positions are Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Business Intelligence Analyst, Machine Learning Engineer, and Data Engineer. Advanced positions tend to develop with experience.
- Do hiring managers prefer accredited programmes?
Though accreditation is appreciated, employers also highly appreciate demonstrated skills and experience.
- How important are internships and projects during the course?
Very important. Internships and project-based work enhance your skills and curriculum vitae greatly.
- What are the key differentiators of best value data science programs?
The proportion of tuition fees to quality of curriculum, coupled with effective career guidance and mentorship, typically distinguishes the best value programmes.
Conclusion
Balancing Data Science course costs with potential returns is a determining factor for anyone willing to take up this fascinating career. The charges are significant, from online bootcamps to university master’s programs, but data science is one of the most fulfilling careers in today’s times. Data science earning potential and flexibility in positions guarantee the investment is typically paid back in the near and distant future.
Key Takeaways:
- High ROI: Data science proficiency is in demand, and pay raises can easily fund tuition.
- Quality of Curriculum Matters: Choose programs with real-world projects and strong mentorship to get the best outcomes.
- Long-Term Growth: Data science careers offer long-term relevance, leadership opportunities, and ongoing skill enhancement.
Ready to embark on your data science journey? Learn about established programmes and career materials. Cross-validate course formats, do your own research, and engage in lifelong learning and networking. Investing in education can open doors to an entire universe of professional opportunities.
Do research on multiple programs and benchmark them against your career objectives.
Explore established programs such as Imarticus Learning’s Postgraduate Programme in Data Science and Analytics.
- Stay updated with industry trends through websites like Data Flair.
- Join data science communities or forums to network.
- Continuously keep yourself updated to remain ahead in this fast-evolving career.
A wise evaluation of potential earnings, course fees, and the whole data science career investment schedule can take you to a successful and lucrative future. Use these results to decide if Data Science course fees are an apt investment for your professional life.