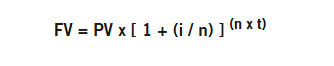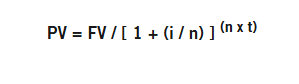Currency movement plays a vital role in influencing investment outcomes in today’s globalised financial markets. You could be investing in international stocks, bonds or real estate, but your returns are not immune to fluctuations in exchange rates. That’s where currency management comes into the picture.
So what exactly does currency management for investors look like?
For investors, currency management is about analysing, monitoring and managing currency exposure in their portfolio. You may ask why. Of course, to optimise returns on their investment and minimise risks.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the basics of currency management, its importance for investors and practical strategies for risk management. You can also take the CFA course by Imarticus Learning to learn more about investments and finance.
Watch: Chartered Financial Analyst: Introduction Video
Why Currency Management Matters
There are two things investors must keep in mind when investing internationally: the performance of the underlying asset and the denomination currency.
Let’s say you invest in European stocks from India. A strong euro relative to the Indian rupee could increase your returns when you convert your profits into INR, even if the investment brings modest gains in euros. On the other hand, your returns could decrease if the euro weakens, even if the stocks did well in Europe.
Whether you’re a finance professional or a retail investor, currency management is necessary.
Active management of exchange rate exposure lets investors:
- Minimise the risks of currency fluctuations
- Protect international investments
- Get more predictable and stable returns
Understanding Currency Risk
When you are engaged with investing in international stock markets, there can be an exchange rate risk or currency risk. This risk is actually the potential loss that a company or investor may suffer because of sudden changes that take place in the currency exchange rates. For example, let’s say, you invest in US stock, and then, due to some circumstances, the dollar value drops. If that happens, despite the stock’s performance, your returns in the home currency will be affected and go down.
Currency risk can be of several types:
- Economic risk: This long-term risk results from currency fluctuations and impacts market value.
- Transaction risk: This risk is associated with financial transitions involving foreign currency.
- Translation risk: Also known as accounting risk, this type of risk occurs when financial statements from foreign assets are converted into the parent company’s home currency.
Key Currency Risk Management Techniques
With so much risk threatening your international investments, the question arises: How do I protect my foreign investments in a volatile environment?
Needless to say, this is where currency risk management strategies come into play.
Managing currency risk means identifying exchange rate exposure and employing strategies to reduce possible losses. Here’s an overview of some common currency risk management techniques for investors with a global portfolio:
- Options and futures
Currency options and futures help manage exposure. Currency options give investors the right to buy or sell at a specific rate on or before a particular expiration date. However, this is not an obligation. On the other hand, futures are standardised contracts traded on exchanges. They obligate investors to exchange currencies at a predetermined price at a future date.
- Hedging with forward contracts
Currency forward contracts are another option to minimise currency risk. Forward contracts help in setting a predetermined exchange rate between two parties and even if there is a exchange rate change in the future. Institutional investors and companies can use forward contracts for hedging.
- Natural hedging
Another popular currency risk management technique is natural hedging, where revenue and costs are matched in the same currency to balance currency exposure. For example, a business operating in a foreign country can open production facilities in the foreign country. This allows the business to generate revenue and expenses in the foreign currency. Thus, currency fluctuations have minimal impact on the bottom line.
- Operational diversification
A company can reduce its overall portfolio risk by spreading business operations across multiple currencies and countries. However, diversifying operations only lowers but does not mitigate currency risk.
Watch: CFA Certification: 5 Surprising Benefits for Your Finance Career
Currency Trading Strategies for Investors
The high liquidity of the currency market causes value fluctuations, which, if capitalised, can create profit opportunities for investors.
So, as an investor, if you are actively trading in the foreign market, you should have a strong understanding of currency trading strategies. You might think that this knowledge is more suited for experienced professionals and investors, but now, with trading made easy via mobile apps, managing a diverse portfolio can benefit from this knowledge.
Let’s give you some idea about some standard currency trading strategies:
- Carry trade strategy
A carry trade strategy is where an investor borrows in a low-interest-rate currency and reinvests in one with a higher rate. The interest rate differential accounts for the profit.
- Trend following strategy
The trend following strategy relies on momentum and market patterns. Investors use technical indicators to identify and follow currency trends.
- Range trading
Currencies usually move within certain price limits. Investors gain from short-term price changes by buying when the price is low and selling when the price is high.
Currency Management for Different Types of Investors
A one-size-fits-all approach does not work in currency management because it depends on the investor’s profile. Let’s look at some examples:
- Businesses
Businesses can use both financial and operations hedges to manage foreign currency exposure.
- Individual investors
These investors can use ETFs or mutual funds that have built-in currency hedging.
- Institutional investors
Institutional investors often apply advanced hedging techniques using derivatives.
Common Mistakes in Currency Management
As essential currency management is for investors, they must also know where to draw the line to avoid losses. Avoiding these mistakes is key to successful currency management:
- Ignoring currency risk
Many new investors completely overlook currency risks and assume exchange rates will remain stable.
- Over-hedging
Investors must be cautious of over-hedging since too much hedging can eat into potential gains.
- Not reviewing strategies
Currency markets are dynamic, so should be strategies. Strategies must be reviewed and adjusted regularly as the market changes.
Conclusion
When investors deal with foreign market exchanges, sometimes, they do not get into the nitty-gritty of how currency management for investors can actually affect returns. As an investor, you should know the risks associated with currency exposure and then, use the right techniques to protect your portfolios to maximise returns in the home currency.
Moreover, knowing currency management gives you more direction into risk-management. However, if you’re a student learning the ropes or a working professional diversifying your portfolio, you can sign up for the CFA course by Imarticus Learning to gain deep expertise in investments and finance.
FAQs
How does currency affect investment?
Currency affects investment since changes of currency value can determine what value of returns you are getting when you sell a good-performing foreign stock. Exchange rates can often be sudden and may not even favour your returns, making an investment not as fruitful as planned.
Why is currency risk management important?
It protects investors from losses resulting from changes in currency exchange rates.
Are currency trading strategies suitable for beginners?
Most strategies, like carry trade or trend following, are recommended for experienced investors due to their higher risks.
Is currency management necessary for domestic investors?
While currency management is primarily for international investments, domestic investors may still be exposed if the companies they invest in have global operations.
What are the three types of FX risks?
Economic, transaction and translation are the three types of foreign exchange (FX) risks.
How to calculate currency risk?
Currency risk is often calculated by measuring the difference between the current exchange rate and probable future rates. Then, it is estimated how these changes can affect returns.