Finance still occurs at breakneck paces in 2025, and so does the training program that is producing next-generation bankers. There is one word that still reigns supreme over such a rapid shift and that is the Investment Banking program. With fintech and AI revolution ruling the financial services space, such programs are not the same programs they were five years back. They are hi-tech, technology-oriented, and future-engineered programs.
The Evolution of the Investment Banking Course in 2025
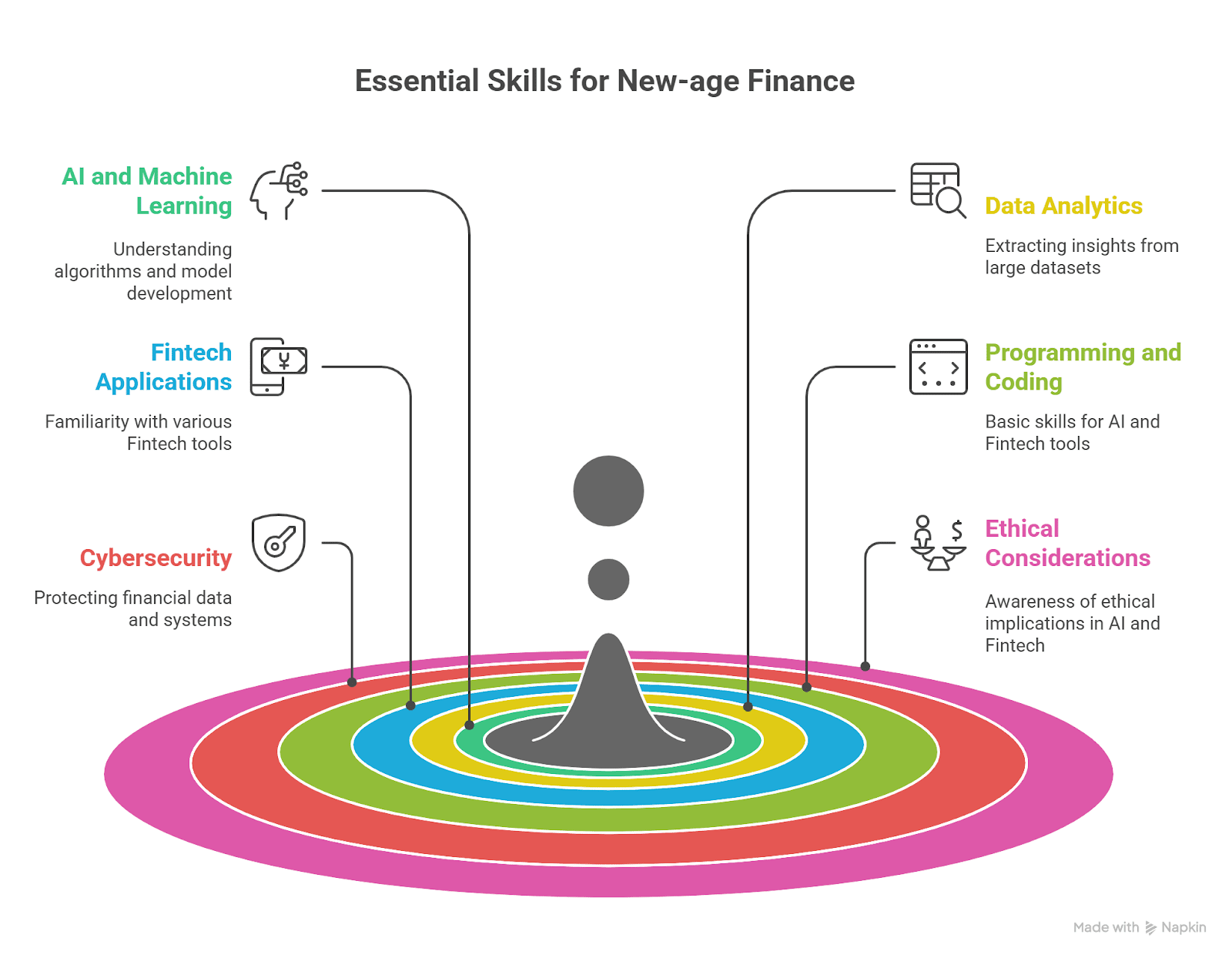
As fintech and AI tech merge, the investment banking syllabus for 2025 is evolving. The traditional corporate finance, mergers and acquisitions, and financial modeling syllabus is now interspersed with new tech, data analytics, and machine learning methods. The reason is simple: make students financially literate but also technology-literate to thrive in digitally reconstituted markets.
New courses utilize AI modules for real-world-esque financings, investment governance and strategy enactment, and risk estimation on ginormous data sets. Fintech case studies, however, enable learners to research new subjects such as blockchain banking, decentralized finance (DeFi), and robo-advisory models.
Why AI and Fintech Are Transforming Finance Education?
AI learning finance is pedagogical irreversibility, not a passing trend. It is the interactive simulations using AI that are replacing the lectures. Predictive modeling and machine-based trading are available at students’ fingertips to study in virtual labs of simulation where they are being taught by real-time feeds.
Likewise, fintech banking certifications are closing the gap between practice and theory. Most prominent certifications guarantee blockchain competence, API-based design, regtech, and cloud banking. Training institutes’ investment banking courses have understood that the best method to stay current is by continuously innovating with the fintech innovations and trends.
Key Features of Investment Banking Course Trends
Certain trends are dominating the investment banking course trends of 2025:
- Blended Learning Models: Transitioning towards hybrid lecture classroom and fully immersive virtual lab models.
- Micro-Certifications: Fintech short-term certification including core curriculum.
- Project-Based Curriculum: Emphasis on learning with AI tools and fintech solutions to solve real-world financial challenges.
- Personalised Learning: AI-based platforms providing content customized according to the individual learner’s speed and ability to learn.
- Global Finance Integration: Courses now integrating compulsory modules on potential bank career streams worldwide.
These alterations not just make the courses flexible but also have a tendency to increase overall access for working professionals, internet-based students, and international students.
How AI and Fintech Improve Employability in Finance?
One of the largest value additions of such enhanced courses is that they are employee-centric. AI-based courses on training websites monitor the talent of a learner, measure employability preparedness, and recommend specialization in streams to continue.
Apart from that, fintech-driven modules make the students career-ready in jobs like digital payment, compliance automation, risk detection, and AI-driven customer onboarding processes. The investment banking course is therefore a career driver for technology-enabled finance professionals.
Redefining the Investment Banking Course for 2025 and Beyond
What actually sets the day’s investment banking course apart is its future-oriented structure. Universities are joining forces with fintech companies in courses that map the sector’s future.
Collaborations with AI constructor and fintech start-ups provide students with real-world experience through internships, mentorship projects, and capstone projects. Collaborations make students become prepared for new positions such as:
- Digital Investment Banking Analyst
- Fintech Product Consultant
- Quantitative Risk Modeller
- Data-Driven Compliance Officer
In addition to this, soft skills like teleworking, flexibility, and ethical decision-making are increasingly being infused into learning platforms, and students are more concentrated.
The Global Influence of Finance Industry Technology
Use of technology within the money world to investment banking education is basic to international harmonization between money cultures. International students are now in a position to utilize globalized platforms and study the case studies of the leading markets such as London, Singapore, and New York.
With technology taking the shape of generative AI, deep learning models, and blockchain simulations, geography is no longer present, and the path of investment banking is set anywhere. These, web-based bootcamps with international networking opportunities and peer-to-peer interactions facilitated by AI, contribute to the richness of learning.
Making a Career in Global Finance Through Tech-Driven Learning
The future investment banking is swiftly becoming a passport for a well-paying professional career in global finance. The finance industry of 2025 requires hybrid competencies fusing financial and technical competencies.
The best of fintech-hiring courses places their top talent in asset managers, international banks, hedge funds, and regtech start-ups. The addition of research on the job market into course materials allows their students to possess the same skills employers are requesting.
Second, the practice of cross-border internships through virtual reality platforms and blockchain-verifiable certificates has encouraged mobility as well as openness.
Role of Investment Bankers in a Fintech World
As fintech is now a part of every single financial transaction, the population of investment bankers has grown. They not only help negotiate transactions, but also advise on tech interfaces, risk assessment, and AI-enabled regulatory compliance.
Courses are imparting investment bankers the skill to filter out massive data volumes, identify predictive insight through AI tools, and work with cross-functional tech teams. All these skills are revolutionizing leadership finance and giving rise to a new breed of banker: tech-enabled and insight-driven.
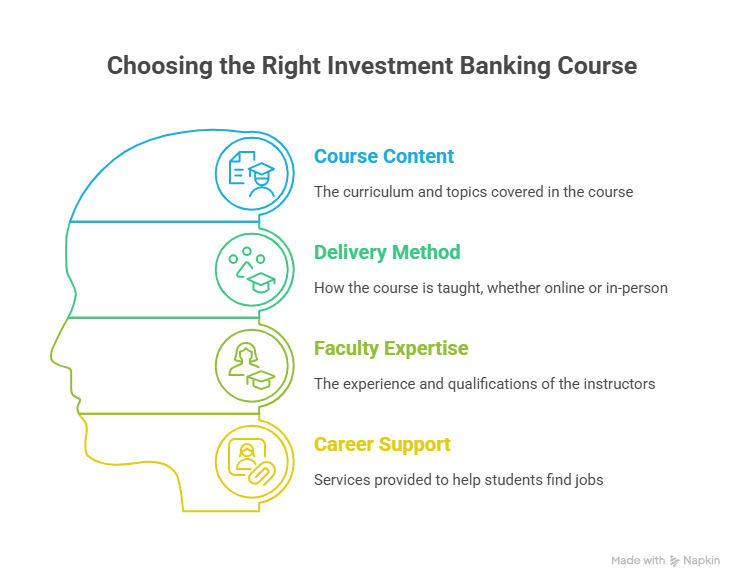
Choosing the Right Investment Banking Course in 2025
With all the shifting trends, selecting the proper course in investment banking in 2025 can be puzzling. The most significant factors to pay attention to are:
- Interconnectedness of fintech and AI modules
- Internships and industry collaborations
- Hybrid or online mode of study
- compatibility of the global curriculum
- Live case studies and simulations
Select online courses that are not theoretical but offer hands-on tools, project work, and experience on digital platforms.
Why Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional (CIBOP) Is the Ideal Choice?
During this period of educational turmoil are training programs that blend the Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional (CIBOP™) by Imarticus Learning. It is a career-launching course in investment banking for 0-3 years of experience finance graduates.
With a high 85% placement rate and highest salary packages of ₹9 LPA, the course is set to provide students with hands-on banking operations like securities processing, wealth management, AML processes, and risk assessment. The 3-month and 6-month tenures are well-suited for working professionals and fresh student hires.
What Makes CIBOP Stand Out
- Industry-focused Syllabus: With support from investment banks and fintech companies.
- Project-first Orientation: Compliance, ethical banking, and trade-based money laundering applied modules
- Guaranteed Career Support: 7 interview guarantees, 60% average salary increase, and access to 1000+ recruitment partners
- Recognised Excellence: Best Education Provider in Finance at 30th Elets World Education Summit 2024
The training also encompasses aptitude, resume preparation, and mock interviews for placement readiness improvement.
CIBOP graduates can apply for the following positions:
- Investment Banking Associate
- Hedge Fund Analyst
- Regulatory Reporting Officer
- Trade Surveillance Analyst
- Risk Management Consultant
With more than 50,000 students and 1200+ batches successfully trained, Imarticus Learning remains to shake up the investment banking courses industry in India and worldwide.
Conclusion
With the evolution towards a more technified global finance, investment banking education in 2025 will be a smart, versatile, and internationally oriented learning experience. Fintech and AI will drive it so that it equips its graduates to confidently encounter through the intricate mechanism of global finance.
To set a strong foundation in the subject of interest for the earnest, the Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional program offers the ideal combination of theory, technology, and career guarantee.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the relevance of an investment banking course in 2025?
The investment banking course of 2025 is more technologically driven, where students are taught the type of job that incorporates finance, along with AI, data analysis, and fintech platforms.
2. How is AI used in finance education today?
AI is applied in finance education for personalized learning facilitation, simulation of trading scenarios, risk calculation automation, and career mapping.
3. Are fintech certifications important for investment banking careers?
Yes, fintech bank certification is supportive of conventional technological competencies such as blockchain, digital payments, and regtech, enriching the investment banking profession opportunities.
4. What are some top trends in investment banking courses?
Blended learning, AI programs, project modules, and global connectivity of finance are few of the most recent investment banking course trends.
5. How do investment banking courses support global finance careers?
Investment banking courses use global case studies, virtual internship, and globally recognized certifications to ease cross-border mobility.
6. What roles can I pursue after completing an investment banking course?
Professional qualifications such as Investment Banking Analyst, Hedge Fund Associate, Regulatory Reporting Analyst, and Risk Consultant can be selected.
7. Why should I choose the Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional course?
CIBOP delivers career guarantee, in-work training, technology-based study materials, and access to top employers globally, which is an ideal career start.