When I look closely at the CPA Syllabus, I notice something that most candidates only realise much later in their preparation. The syllabus is not organised around chapters or subjects in the way an academic course is. It is organised around moments of responsibility. Moments where a professional decision has to be made and stood by.
This is why the CPA exam syllabus often feels unfamiliar at first. Knowing the rule is rarely enough. The exam quietly asks
→ Whether you understand when that rule applies
→ Why it exists, and
→ What happens when it is misused.
It rewards clarity over completeness and judgment over recall.
As candidates move deeper into the syllabus, many begin to sense that questions are framed differently. Scenarios include more information than needed. Choices feel closer than expected. Ethical judgment appears in places where it is not explicitly announced. None of this is accidental. The CPA syllabus is built to reflect how real finance decisions are made, where information is incomplete and time is limited.
The blog ahead unpacks these questions. They explain how the CPA course syllabus is structured, why core areas and discipline choices exist, and how the exam pattern is designed to test professional readiness rather than academic memory. Reading the syllabus with this lens changes how it feels, how it is prepared for, and how it is eventually performed under exam conditions.
What Is CPA and Why Is the Syllabus Built This Way
Before going deeper into the CPA Syllabus, it helps to understand what the CPA qualification represents in practice. The Certified Public Accountant (CPA), offered by the AICPA, is a professional license that authorises individuals to take responsibility for financial reporting, audit opinions, regulatory compliance, and advisory decisions.
At its core, what is CPA is not just about passing exams. It is about being trusted with financial information that affects investors, regulators, businesses, and the public. This responsibility is the reason the syllabus of US CPA is structured the way it is.
The CPA designation is governed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and is recognised globally as a benchmark for accounting and finance credibility.
What the CPA Qualification Prepares You to Do
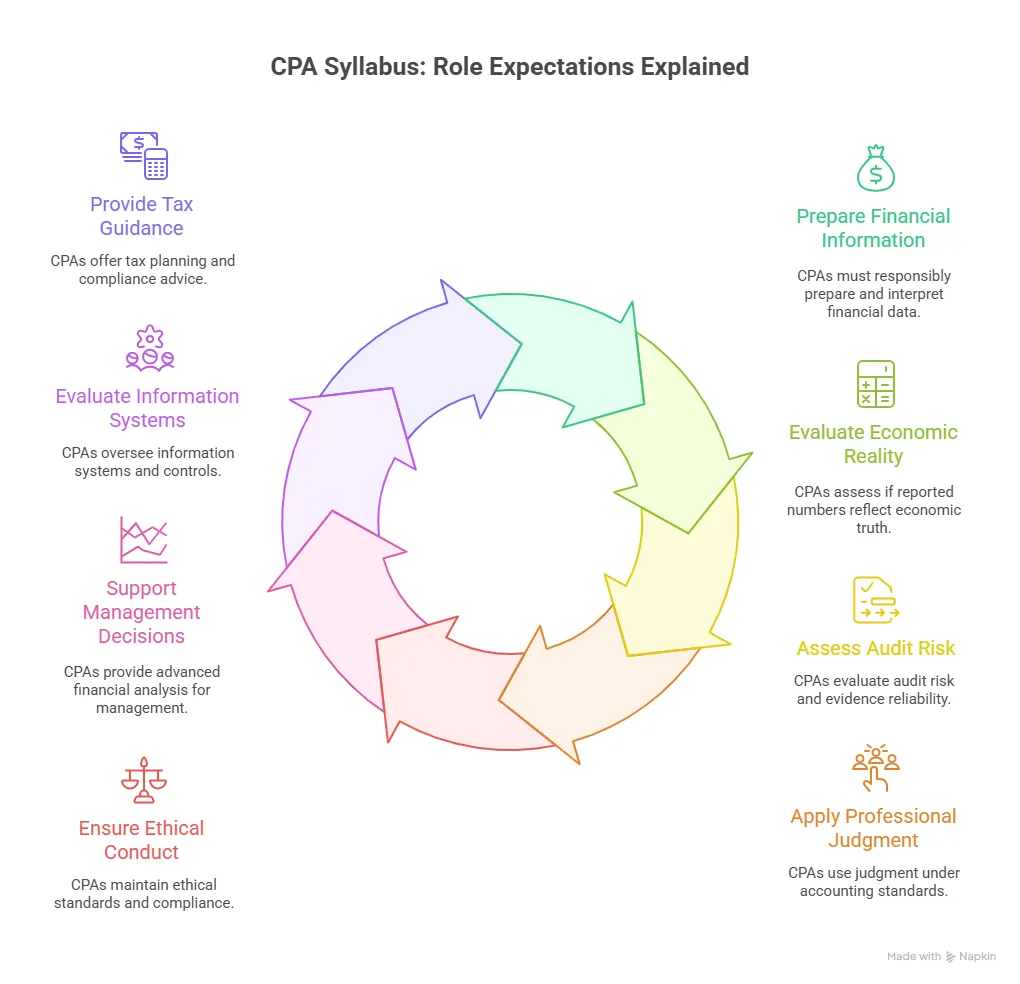
Rather than focusing on job titles, the CPA qualification prepares professionals for specific types of responsibility. These responsibilities directly shape the CPA exam Syllabus.
- Take ownership of financial reporting accuracy
- Evaluate whether financial information reflects economic reality
- Provide assurance on the reliability of financial statements
- Interpret and apply tax and regulatory requirements
- Act ethically while balancing professional judgment and compliance
These expectations explain why the CPA Syllabus focuses heavily on application, analysis, and decision-making rather than memorisation.
How CPA Is Different From Academic Accounting Degrees
To understand the intent of the CPA exam Syllabus, it helps to distinguish the CPA qualification from traditional academic programs.
| Aspect | Academic Accounting | CPA Qualification |
| Primary focus | Knowledge acquisition | Professional responsibility |
| Assessment style | Theory and exams | Application and judgment |
| Outcome | Degree or diploma | Professional license |
| Accountability | Academic performance | Public and regulatory trust |
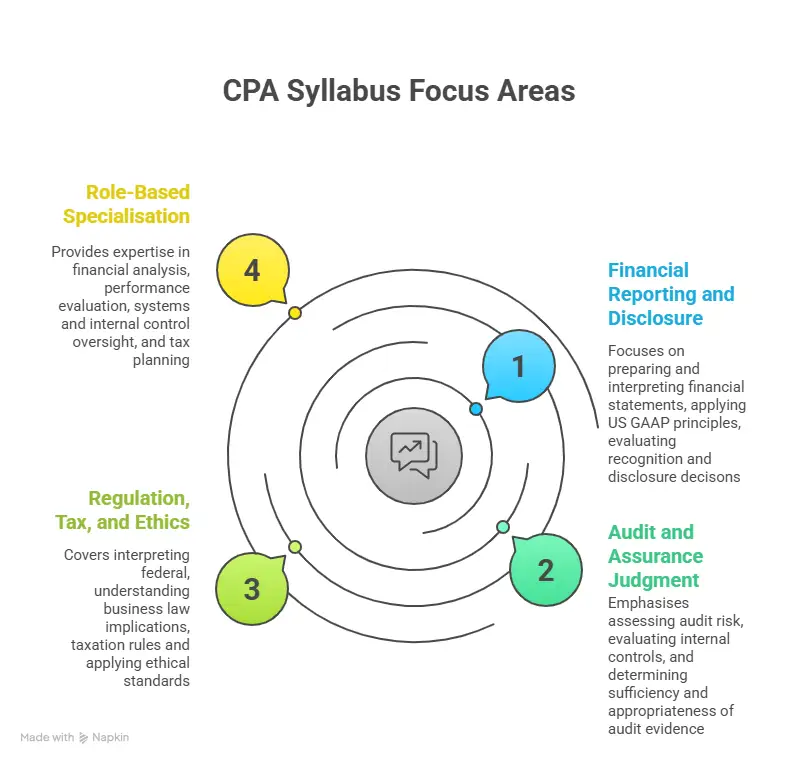
This difference is the reason the CPA Syllabus is structured around real-world scenarios and professional judgment. These focus areas explain why the exam tests financial reporting accuracy, audit reasoning, regulatory awareness, and role-based specialisation as interconnected responsibilities rather than isolated subjects.
Why the CPA Syllabus Is Structured Around Core and Discipline
The current CPA course syllabus follows a Core plus Discipline model. This structure was introduced to ensure that every CPA shares a common foundation while also developing depth in one area of professional relevance.
The Core represents non-negotiable responsibility. Every licensed CPA must be competent in financial reporting, auditing, and regulation. The Discipline component recognises that modern CPAs do not all perform the same role. Some work in financial analysis, some in systems and controls, and some in advanced taxation.
If you have the question, “Is CPA worth it?”, this approach aligns the CPA subjects and syllabus with how finance teams actually function inside organisations.
The Three Core Areas of the CPA Syllabus
Before getting into individual subject detail, it helps to understand what the Core subjects collectively aim to test.
| Core Area | Professional Responsibility |
| Financial Reporting | Accuracy and transparency of financial information |
| Auditing and Assurance | Trust and credibility of reported information |
| Regulation | Legal and ethical compliance |
These responsibilities sit at the heart of the CPA US syllabus. They are also the reason the exam places such a strong emphasis on application rather than recall.
Did you know? According to the official AICPA blueprints, higher-order skills such as analysis and evaluation make up a significant portion of the exam across all Core sections.
Financial Accounting and Reporting as the Foundation
Financial Accounting and Reporting sits at the centre of the CPA exam syllabus. This area forms the technical backbone of the profession.
The CPA FAR syllabus covers how economic events are translated into financial information. It also tests how well a candidate understands the consequences of those translations.
At a practical level, this includes decisions around recognition, measurement, classification, and disclosure. At a professional level, it includes accountability to investors, regulators, and the public.
This breadth explains why FAR often feels tough. It reflects the diversity of environments in which CPAs operate.
Why FAR Shapes the Rest of the CPA US Syllabus
The logic developed while studying FAR carries forward into every other subject. Once a candidate learns how standards are interpreted and applied, the same reasoning patterns appear in audit procedure judgments, tax decisions, and advisory work.
This is also why many preparation strategies treat FAR as an anchor within the CPA course syllabus. The subject builds discipline in reading questions carefully, identifying relevant data, and ignoring distractions.
How the CPA FAR Syllabus Builds the Foundation
| FAR Focus Area | What It Trains in Practice | Why It Matters Professionally |
| Recognition decisions | Identifying when transactions should be recorded | Prevents overstatement or understatement of financial performance |
| Measurement principles | Determining appropriate valuation methods | Ensures financial information reflects economic reality |
| Classification and presentation | Organising financial information correctly | Improves the clarity and usability of financial statements |
| Disclosure requirements | Communicating relevant assumptions and risks | Builds transparency for investors and regulators |
| Government and non-profit accounting | Applying accountability-based reporting | Prepares CPAs for public interest and regulated environments |
Pass rate data published by the AICPA shows that FAR has historically been one of the more challenging sections, with pass rates often hovering around the mid 40% range, depending on the testing window. This statistic often creates anxiety. I view it differently. It highlights how central FAR is to professional readiness.
Auditing as a Measure of Professional Judgment
Auditing within the CPA syllabus is not about ticking boxes. It is about forming and defending an opinion.
The auditing component of the CPA exam syllabus focuses on how assurance is planned, executed, and reported. It tests whether a candidate understands risk, evidence, and ethical responsibility.
This area is deeply connected to trust. When a CPA signs an audit report, that signature carries weight across markets.
The US CPA syllabus integrates auditing standards issued by bodies such as the AICPA and the PCAOB. Candidates are expected to understand not only what procedures are required, but why they are required.
This emphasis reflects real-world practice. Audit failures often occur not because procedures were unknown, but because judgment was weak or independence was compromised.
Auditing and Assurance as a Test of Professional Scepticism
Auditing within the CPA exam syllabus shifts focus away from numbers and toward reasoning. The central skill tested is professional scepticism.
Audit questions rarely ask what should be done in isolation. They ask what should be done given a risk, a control environment, or a prior conclusion.
How Audit Content Is Structured
Audit content flows in the same sequence as a real engagement:
- Understanding the client and environment
- Identifying risks of material misstatement
- Evaluating internal controls
- Designing and performing procedures
- Forming and reporting an opinion
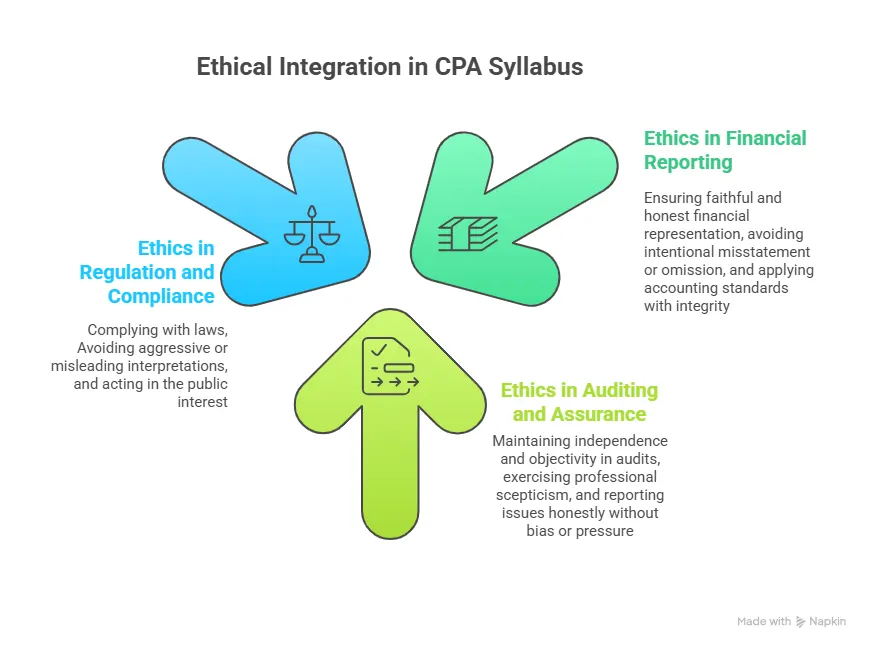
The CPA subjects and syllabus treat ethics as a constant, not a separate topic. Independence and professional responsibility appear throughout audit scenarios.
Ethical judgment is woven throughout the CPA syllabus, appearing within financial reporting decisions, audit responsibilities, and regulatory compliance. This integration reflects how ethics operates in professional practice, guiding choices across multiple contexts rather than existing as a separate topic:
Regulation and the Legal Boundary of the Profession
Regulation within the CPA syllabus introduces a different dimension. It connects financial decisions to legal consequences.
The CPA Regulation syllabus includes federal taxation, business law, and professional ethics. These areas define the boundaries within which CPAs operate.
Taxation is not treated as a mechanical calculation exercise. The syllabus expects candidates to understand intent, compliance, and planning implications.
Did you know? According to data published by the Internal Revenue Service, tax compliance gaps remain a major issue, with billions of dollars in unpaid taxes identified annually.
This context explains why regulation holds such importance within the CPA subjects and syllabus framework.
Regulation and Its Place in the CPA Exam Syllabus
Regulation introduces legal accountability into the CPA syllabus. It ensures that financial competence is paired with compliance awareness.
The CPA Regulation syllabus blends taxation, business law, and ethics into a single responsibility zone. Decisions here have legal consequences.
Taxation Within REG
Federal taxation occupies a large share of the regulation content. It includes:
- Individual taxation
- Entity taxation
- Property transactions
- Tax credits and deductions
- Filing and compliance requirements
The US CPA syllabus treats tax as both a compliance obligation and a planning tool. Candidates are expected to understand how timing, structure, and classification affect tax outcomes. This reinforces why regulation focuses on interpretation and judgment.
CPA professionals can command competitive CPA salary in India packages that reflect their specialised expertise in financial reporting, audit, and regulatory compliance, often higher than general accounting roles due to global recognition and demand.
Here is a quick check on the salary numbers for CPA roles. Understanding how CPA compensation evolves across experience levels, roles, and industries helps place the effort spent on mastering the CPA syllabus and study material into a realistic career context.
Discipline Subjects as Depth, Not Escape Routes
The discipline component of the CPA USA syllabus allows candidates to develop depth without weakening the Core. Each discipline assumes Core competence. The questions extend Core concepts into specialised contexts.
Business Analysis and Reporting in Practice
The discipline focused on business analysis and reporting builds directly on the CPA FAR syllabus.
Topics include:
- Financial statement analysis
- Forecasting and budgeting
- Performance measurement
- Risk assessment
- Advanced reporting models
This discipline reflects how finance teams support decision-making. This shift explains why analysis and reporting have become part of the CPA syllabus.
Information Systems and Controls as a Professional Safeguard
The systems and controls discipline addresses technology-driven risk. As financial processes become automated, the CPA role expands into oversight.
Topics include:
- IT governance
- System controls
- Data integrity
- Cyber risk
- SOC reporting
The CPA exam syllabus includes this discipline because system failures can undermine even the best accounting judgments. This context highlights why system knowledge is now a professional necessity.
Tax Compliance and Planning as Strategic Judgment
The tax-focused discipline extends the CPA Regulation syllabus into advisory territory.
Rather than testing rule application, it tests planning logic. Candidates evaluate structures, timing, and alternatives.
This discipline suits candidates aiming for advisory and consulting roles, where tax decisions influence long-term outcomes.
How the CPA Syllabus in India Fits Into the Global Framework
The CPA syllabus in India is identical to the syllabus tested in the United States. There is no regional variation in content or standards.
What differs is the background candidates bring into the program. Many candidates in India come from commerce, accounting, or professional qualification backgrounds. This often creates strength in fundamentals but requires adjustment in application style. The CPA syllabus PDF published by the AICPA remains the definitive reference regardless of location.
Understanding how to interpret that document becomes critical, especially for candidates transitioning from more theory-driven education systems. Comparing CPA and CA, or CPA vs CMA, often begins with understanding how their syllabi differ in structure, depth, and application focus.
Still wondering which one to choose between CA and CPA? The CPA syllabus places strong emphasis on practical application, regulatory understanding, and decision-making across accounting and finance roles, which influences how candidates plan their preparation and career direction.
How Candidates Should Read the CPA Syllabus PDF at This Stage
The CPA syllabus PDF published by the AICPA outlines content and skill levels. It is not a study plan.
At this stage, the document should be read with one question in mind. What type of decision is this topic preparing me to make? Reading them with intent transforms preparation quality.
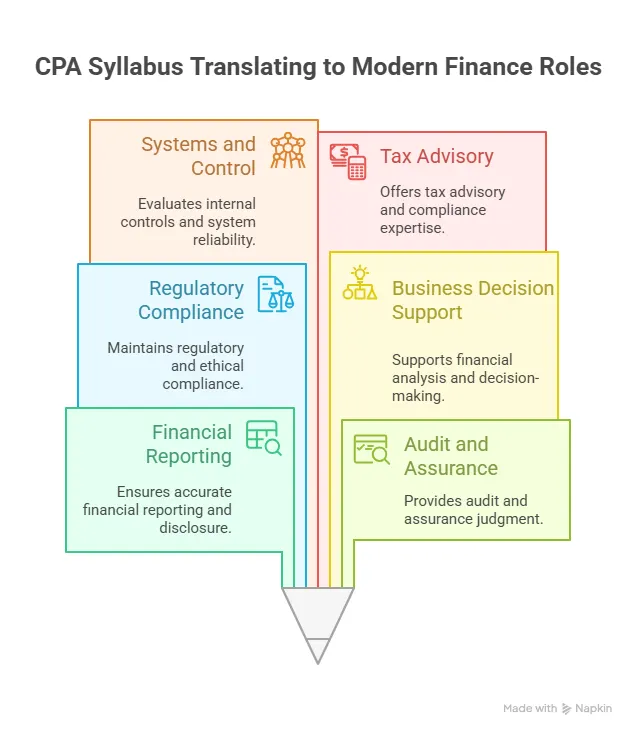
The CPA syllabus is designed to reflect how finance roles function in practice, where reporting, assurance, compliance, and advisory responsibilities often overlap. This connection helps explain how the syllabus prepares candidates to operate across modern finance environments rather than within narrow functional boundaries:
Scoring Logic and the Passing Standard
The CPA exam uses a scaled scoring system, which means the final score reflects both performance and question difficulty. This approach ensures fairness across different exam versions.
CPA Exam Scoring Overview
| Aspect | Details |
| Score range | 0 to 99 |
| Passing score | 75 |
| Score type | Scaled score (not a percentage) |
| Applies to | All sections of the CPA exam syllabus |
| Governing body | American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) |
What a Scaled Score Means
- A score of 75 does not mean 75% correct
- Question difficulty is factored into the final scoring
- More complex questions carry higher weight
- Performance is evaluated across multiple testlets
How Attempts and the 18 Month Window Shape Strategy
Candidates are allowed multiple attempts for each section during their CPA course duration. There is no lifetime cap on attempts. However, once a section is passed, it remains valid for 18 months.
This rolling window defines how candidates should plan the CPA course syllabus timeline. This structure rewards sequencing and consistency rather than speed alone.
How the CPA Exam Pattern Brings the Syllabus to Life
By the time a candidate reaches the exam stage, the CPA syllabus stops being theoretical and becomes experiential. The exam pattern is designed to simulate pressure, ambiguity, and time-bound decision-making.
Each section of the CPA exam syllabus is four hours long and follows the same structural logic. Candidates face a mix of multiple-choice questions and task-based simulations. The simulations are not add-ons. They are central to how the CPA syllabus is evaluated and what makes it a lucrative career path.
The Bigger Picture Behind the CPA Course Syllabus
When viewed as a whole, the CPA syllabus trains one capability above all others. Professional accountability.
Every subject, simulation, and scenario pushes candidates to act in a way that protects public interest. This is why the license carries weight globally.
The CPA USA syllabus and the scope of CPA in India are not designed to be rushed. It is designed to be absorbed.
Why Choose Imarticus Learning for Your CPA Preparation
Preparing for the CPA course requires a learning approach that goes beyond content coverage and focuses on application, judgment, and exam readiness. This is where structured programs offered by Imarticus Learning align well with the way the CPA exam is designed.
Key aspects of the Imarticus Learning CPA program include:
- CPA program in collaboration with KPMG in India, offering industry-aligned exposure and credibility
- Comprehensive study material powered by Surgent, including textbooks, MCQs, simulations, and mock exams aligned with the CPA exam syllabus
- Live instructor-led classes conducted by experienced CPA and CAs who focus on application-based learning
- Dual-teacher model and 24×7 doubt resolution, ensuring consistent academic support across complex CPA syllabus areas
- Structured exam-focused learning plan, designed to help candidates manage the four-paper CPA structure effectively
- Access to internship opportunities with KPMG in India for top performers, adding practical exposure alongside exam preparation
- Career support through interview preparation, resume building, and placement assistance, helping learners transition into relevant finance and accounting roles
This combination of academic structure, practical exposure, and exam alignment makes Imarticus Learning a suitable option for candidates who want their CPA exam prep to reflect real professional expectations rather than just syllabus completion.
FAQs on CPA Syllabus
This section addresses the most frequently asked questions around the CPA Syllabus, covering subject structure, exam difficulty, timelines, attempts, and scoring. These clarifications will help you understand how the CPA USA syllabus works in practice and what to expect while preparing for the US CPA exam.
What is the syllabus of CPA?
The CPA syllabus covers three Core subjects and one Discipline subject. The Core includes financial accounting and reporting, auditing and assurance, and regulation. The Discipline allows specialisation in business analysis, information systems and controls, or tax planning. Many candidates choose to prepare for this structure through guided programs offered by Imarticus Learning, which align the CPA US syllabus with practical application and exam-focused preparation.
Is CPA tougher than ACCA?
The CPA syllabus is focused on US accounting, auditing, and taxation standards, while ACCA follows a broader international framework. Difficulty depends on background and familiarity with US GAAP and US tax concepts. The CPA USA syllabus demands strong application skills and decision-making, which makes preparation style more important than content volume.
Is CPA better than MBA?
The CPA prepares candidates for licensed roles in accounting, audit, taxation, and advisory services. An MBA focuses on management, strategy, and leadership across functions. The CPA exam syllabus suits professionals aiming for technical and regulatory responsibility, while an MBA supports broader managerial roles. The choice depends on long-term career goals.
Can I finish CPA in 1 year?
Yes, it is possible to complete the CPA syllabus within one year with consistent study and structured planning. Candidates who align their preparation with the CPA exam syllabus and maintain steady weekly effort often complete all four sections within 12 months. Guided programs offered by Imarticus Learning help candidates manage timelines effectively.
Is CPA very difficult?
The CPA syllabus is challenging because it tests judgment, not memory. Questions require candidates to analyse situations and apply standards under time pressure. With a clear understanding of the syllabus of US CPA in detail, regular simulation practice, and guided coaching provided by Imarticus Learning, many candidates find the exam manageable.
How many attempts are required to pass the CPA?
There is no fixed limit on the number of attempts for the CPA exam. Candidates can retake any section as needed within the validity window. Understanding the CPA syllabus thoroughly and adjusting the preparation strategy reduces the number of attempts required.
How many papers are in CPA?
The CPA syllabus includes four exam papers. Three Core subjects and one Discipline subject. This structure applies across the entire syllabus of US CPA, regardless of location. Many learners prepare for this format through structured guidance from Imarticus Learning, which helps them plan the sequence and preparation strategy for all four papers effectively.
How many marks are required to pass the CPA?
Each CPA exam section is scored on a scale of 0 to 99. A scaled score of 75 is required to pass. This passing standard is defined by the AICPA and applies uniformly across all sections of the CPA exam syllabus. Candidates often find it easier to meet this benchmark when they follow a structured preparation approach and guided practice provided by Imarticus Learning, which aligns closely with AICPA evaluation standards.
What happens if you fail the CPA three times?
Failing a CPA exam section multiple times does not disqualify a candidate. It usually indicates that the preparation approach needs refinement. Revisiting the CPA syllabus in detail and seeking structured guidance, including support from Imarticus Learning, often improves outcomes significantly.
Where the CPA Syllabus Really Leads
Once the CPA Syllabus is understood in full, it becomes clear that it is not testing how much you can study, but how well you can think. Every section of the syllabus points toward professional judgment, accountability, and the ability to make decisions when the answer is not obvious.
This understanding often changes how candidates approach preparation. Passive learning rarely holds up when the exam demands interpretation and application under pressure. What matters is structured guidance, exposure to real scenarios, and learning environments that train decision-making rather than just content coverage.
For learners building a global finance career, this is where preparation choices start to matter. Imarticus Learning helps develop the same analytical discipline and exam-ready thinking that the CPA Course ultimately requires. With the right foundation, the CPA Syllabus stops feeling overwhelming and starts feeling achievable.