Investment analysis is the backbone of smart financial decision-making. For finance professionals, it’s essential to be skilled in evaluating investment opportunities and assessing potential returns and risks. In today’s fast-paced economic landscape, investment analysis goes beyond crunching numbers; it involves understanding market trends, assessing a company’s fundamentals, and applying both qualitative and quantitative methods to identify and evaluate potential investments. This guide walks you through the key investment analysis techniques that enable finance professionals to conduct meaningful evaluations, leading to informed and strategic investment decisions. For those looking to advance their expertise, programs like IIM Lucknow courses offer valuable insights and certifications in these critical areas, enhancing one’s analytical skill set.
Understanding Investment Analysis
At its core, investment analysis is about assessing the profitability, risks, and value potential of an asset. This process involves a combination of historical data, industry trends, and forward-looking projections to determine if investing in a particular asset—whether stocks, bonds, real estate, or other financial instruments—aligns with your goals. Armed with this information, finance professionals can decide whether an investment can maximize capital while managing risks.
Types of Investment Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s intrinsic value by examining its financial health, position within the industry, and broader economic influences. Key elements include revenue, earnings, profit margins, and cash flow. This data helps finance professionals determine if a stock is undervalued or overvalued in the market. - Technical Analysis
Technical analysis uses historical price and volume data to predict future market behavior. Professionals in this field study charts to identify patterns or trends, such as moving averages, to inform short-term investment decisions based on repeatable patterns. - Quantitative Analysis
Using mathematical models and statistical techniques, quantitative analysis is data-driven, allowing finance professionals to analyze market trends, assess risks, and optimize portfolios based on statistical insights. - Qualitative Analysis
In contrast to the numbers-based approaches, qualitative analysis evaluates non-quantifiable factors like management quality, brand reputation, and market position. These aspects can offer a broader view of a company’s growth potential and stability, providing context beyond the numbers.
Key Financial Ratios and Metrics in Investment Analysis
Financial ratios and metrics provide critical insights into a company’s operational and financial health. Here are some crucial ratios used in investment analysis techniques:
- Profitability Ratios
-
-
- Return on Equity (ROE): Calculate how effectively a company uses shareholders’ equity to generate profit.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Defines efficiency in generating profits from assets.
- Net Profit Margin: Showcases what percentage of revenue is profit, reflecting financial performance.
-
- Liquidity Ratios
-
-
- Current Ratio: States a company’s ability to pay short-term liabilities.
- Quick Ratio: Prohibits inventory for a stricter assessment of liquidity.
-
- Valuation Ratios
-
-
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Differentiate a stock’s price to its earnings per share.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: Focuses if a stock is undervalued or overvalued in relation to its book value.
-
- Leverage Ratios
-
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Showcases the proportion of debt relative to equity.
- Interest Coverage Ratio: Indicates the ability to meet interest obligations, signaling financial stability.
Steps in Conducting Investment Analysis
Conducting effective investment analysis requires a structured approach to remove biases and ensure consistency. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define Goals and Strategy
Clarify your investment goals, such as growth, income, or capital preservation. Choose a strategy, like growth or value investing, that aligns with these goals. - Gather Data
Collect data from financial statements, industry reports, and economic indicators to form a solid analytical foundation. - Analyse Data and Trends
Use financial ratios and key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess financial health and identify trends that may indicate future performance. - Risk Assessment in Investments
Conduct sensitivity and scenario analyses to understand how different factors affect outcomes. Stress testing can reveal how changes in market conditions impact the investment’s viability. - Valuation
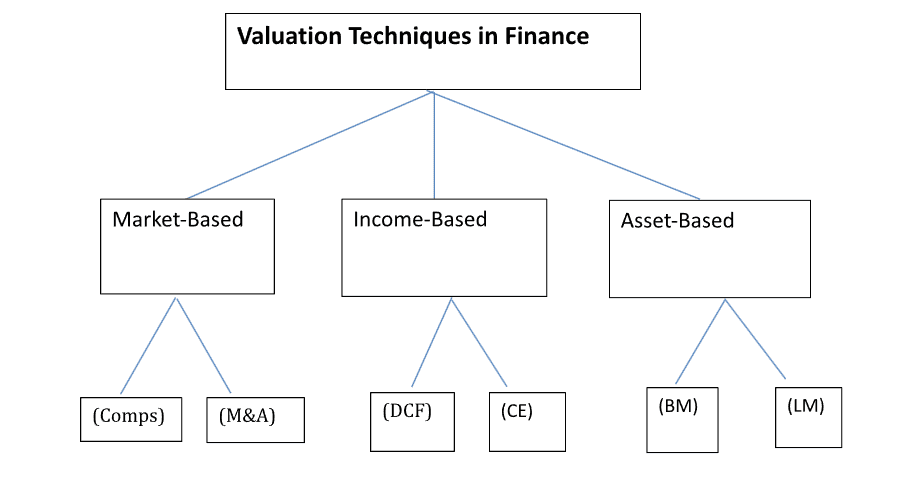
Apply valuation models like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) or comparative analysis. These models estimate an asset’s present value based on future cash flows.
Investment Analysis Tools and Software
Various financial analysis tools make it easier to conduct precise and thorough investment analyses:
- Bloomberg Terminal: Known for its real-time data and in-depth analytics.
- Morningstar: Offers stock and fund analysis, especially beneficial for mutual fund investors.
- Yahoo Finance: Accessible and beginner-friendly, with real-time data and charting options.
These tools streamline access to vast data sets, boosting analysis accuracy and efficiency. They are essential for investment research and portfolio management strategies.
Common Challenges in Investment Analysis
Investment analysis comes with its own set of challenges:
- Market Volatility: External factors, such as political events and economic shifts, can make markets unpredictable, impacting investment outcomes.
- Bias in Analysis: Cognitive biases can influence decisions, making it important to rely on data for objective analysis.
- Keeping Up with Industry Developments: With rapidly evolving markets and analysis methods, staying informed on new techniques is essential.
Practical Tips for Finance Professionals
- Adopt a Systematic Approach: This ensures consistency across analyses.
- Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Keep up with market news and professional networks.
- Network with Experts: Collaborate with other finance professionals to gain fresh perspectives.
- Focus on Continuous Learning: Stay informed on new investment analysis techniques and pursue certifications like those from IIM Lucknow courses to sharpen your expertise.
Investment analysis is a cornerstone skill for finance professionals, guiding them to make data-driven, informed decisions. By mastering both qualitative and quantitative approaches, finance professionals can systematically assess opportunities, manage risks, and contribute to the financial success of their clients or organizations. The right techniques and financial analysis tools are invaluable in making strategic investment choices, helping finance experts excel in portfolio management strategies and thorough risk assessment in investments.
FAQs
- What is the main goal of investment analysis?
To identify profitable and sustainable investment opportunities while assessing associated risks. - What is the difference between fundamental analysis and technical analysis?
Fundamental analysis estimates a company’s financial health, while technical analysis focuses on historical price patterns to forecast trends. - What are the vital financial ratios to consider?
Crucial ratios include ROE, current ratio, P/E ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio. - How do risk assessment and scenario analysis contribute to investment analysis?
They help professionals prepare for different outcomes, improving risk management. - What are some essential tools for investment analysis?
Tools like Bloomberg Terminal, Morningstar, and Yahoo Finance offer critical data and analytics for comprehensive investment evaluations.