In today’s data age, businesses are continuously searching for competent professionals who can analyze, interpret, and visualize data in an effort to make effective business decisions. Pursuing a comprehensive data analytics course is an intelligent decision for an individual who wishes to become a part of this vibrant field. If you are a college graduate, or a working professional who is interested in switching careers to a data career, the right course will provide you with the training and hands-on experience that you need to get hired. In this blog, we talk about the advantages, skill set one needs, and career prospects for pursuing a data analytics course and how it leads to a successful career in analytics.
Why Choose a Data Analytics Program?
A data analytics course program provides much more than classroom instruction. It provides experiential learning with hands-on training, live projects, mentoring, and career counseling. These programs aim at meeting the increasing need for data professionals in terms of job-readiness.
- Data Analytics courses provide value in the form of learning the latest tools such as Python, SQL, Power BI, and Tableau.
- Provides access to in-class or online real-time instruction.
- Is implemented in real-world situations through over 25 projects.
- 100% job guarantee with interview guarantee.
- Good resume development and interviewing skill help.
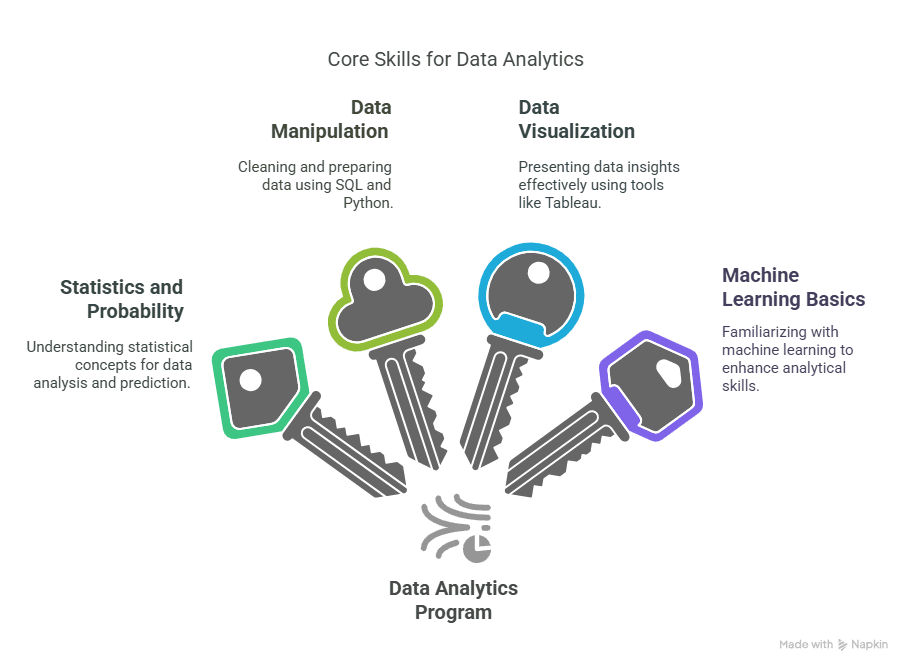
What Skills Do You Gain from a Data Analytics Program?
One of the major features of any data analytics course is its focus on work-based, functional skills. They are the skills that one needs to succeed in the current competitive employment market.
Technical Skills
- Python & R: Learn programming in Python and R in order to clean, process, and visualize data.
- SQL: For querying databases and processing structured data.
- Excel: Starting point for basic data analysis and reporting.
- Power BI & Tableau: Develop dashboards and visualizations to guide business decisions.
Analytical Thinking
Critical thinking and evidence-based problem-solving form the foundation of any data analytics profession. Such courses would normally encompass understanding the interpretation of big data sets, identifying patterns, and providing strategic recommendations.
Communication Skills
Transforming complex data results into simple-to-understand visualizations and actionable recommendations takes tremendous communication skills. Data storytelling well is the soul of a data analytics course.
Business Acumen
Having knowledge about the business environment is necessary. Most of the courses enable making sure that the students understand how data affects different parts of a business like marketing, operations, finance, and human resources.
The Structure of a Quality Data Analytics Program
An excellent data analytics course is not just course work and assignments. That is why it is comprehensive:
Live Learning Sessions
Live classes enable students to interact with instructors in real time. Imarticus’ Postgraduate Diploma in Data Science and Analytics also has online and offline facilities, which are ideal for every type of learning.
Real-World Projects
There are more than 25 industry-focused projects that replicate real-world scenarios that provide hands-on exposure to solve business issues of a data nature.
Tools Mastery
Master 10+ industry data tools. Hands-on experience using tools such as Python, SQL, Tableau, and Power BI makes you job-ready from day one.
Hackathons and Competitions
Coding hackathons enhance your problem-solving ability and give that extra oomph to your resume.
Dedicated Career Services
Resume building, mentorship, mock interviews, and job guarantee sessions train students to transition from the classroom to the boardroom.
Data Analytics Career Path in India
Data Analytics career is spreading at lightning speed as far as India is concerned because of the booming Digital data in business. Organizations from all industries like finance, health care, retailing, and technology require people to analyze amounts of data.
Some of the most in-demand skills for data analysts are:
- Data visualization (ability)
- Data cleaning and data transformation
- Understanding statistical concepts
- Machine learning background (senior positions)
Entry-Level Roles:
- Basic Data Analyst
- Basic Business Intelligence Analyst
- Reporting Analyst
Mid-Level Roles:
- Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Analytics Consultant
Senior Roles:
- Data Architect
- Director of Analytics
- Chief Data Officer
Job-Ready Data Analytics Skills for 2025 and Beyond
As AI and Gen AI kick in, data analytics will more and more get entangled with newer automation. Therefore, the new course in data analytics must include:
- Gen AI Integration: Learning about how AI tools assist in pattern detection and predictive analytics.
- Cloud Platforms: Familiarity with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud is the new norm.
- APIs and Data Engineering Fundamentals: Ideal for processing data pipelines and integrations.
Data Analyst Training Program at Imarticus
Imarticus’ Postgraduate Program in Data Science and Analytics is India’s highest-rated job-guaranteed program:
- Duration: 6 Months
- Mode: Live Online + Classroom
- Eligibility: Freshers and professionals in technical domains
- Placement: 10 guaranteed interviews, 100% job guarantee
- Projects: 25+ case studies
- Tools Included: 10+ such as Python, SQL, Tableau, Power BI
Learn Data Analytics Online with Confidence
Online learning data analytics has ensured entry into this profession is now simpler than ever. Interactive websites and guide mentor experts make it possible for students to reach the same level as traditional classes with the comfort of convenience.
Benefits of Learning Online:
- Learn at your own pace
- Watch video lectures
- Live interactions with experts
- Interactions with classmates worldwide
CFA vs Data Analytics: Which is Better?
Data analytics and CFA are both in high demand, and most of the professionals get confused about whether to pursue CFA or data analytics. CFA is perfect for investment and finance careers, but data analytics gives exposure to a variety of industries such as retail, health, IT, etc.
Everything depends on:
- Your career option: Investment or Analytics
- Your background: Finance or Tech
- Employment market demand in your field of interest
Top Recruiters Hiring Data Analytics Talent
Job-ready data analytics demand has attracted Indian and global top players. Imarticus has collaborated with 2000+ recruiters such as:
- Deloitte
- PwC
- KPMG
- Accenture
- Capgemini
- HDFC Bank
- Cognizant
- Infosys
- EY
Average Salary and Career Growth in Data Analytics
- Entry-Level: ₹6 LPA to ₹8 LPA
- Mid-Level: ₹10 LPA to ₹15 LPA
- Senior-Level: ₹20 LPA+
- Highest Salary Achieved by Imarticus Graduate: ₹22.5 LPA
- Average Hike: 52%
ROI on a well-planned data analytics program is high. The more digital disruption occurs in industries, the more skills-based data professionals are the need of the hour.
Is a Career in Data Analytics Right for You?
You would like to have a data analytics career if you:
- Like playing with numbers and patterns
- Possess a logical and analytical mind
- Are ready to learn new tools and techniques on a daily basis
- Like to be in a high-growth, high-demand profession
Conclusion
A course in data analytics is the door to a prosperous profession in the modern digital economy. It not only provides you with training for the most attractive jobs, but it also renders you hireable with experiential skill sets, live project tools, and industrial exposure. If you are looking to switch to a career in data analytics or wish to begin one, a well-designed training program like the Postgraduate Program in Data Science and Analytics by Imarticus Learning is the perfect starting point.
With the choice between 100% job guarantee, exposure to leading recruiters, one-to-one career counselling, and experiential training, this course has everything to get you going.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of a data analytics program?
It gives you practical experience in data tools, project experience, mentorship, and job guarantee. All together, they make you industry-ready for high-growth careers.
2. What is the average salary after completing a data analytics course?
Salary in the first year is around ₹6-8 LPA, and experienced people earn over ₹20 LPA based on skills and designations.
3. Can I learn data analytics online?
Yes, online education provides adaptable, interactive environments with real-time classes, doubt clarification, and peer networking.
4. Is data analytics a good career in 2025?
Yes, demand for data professionals will increase manifold with growing digital transformation and AI.
5. What industries hire data analysts?
Finance, retail, health care, IT, manufacturing, and consultancy firms recruit skilled data analytics professionals on a regular basis.
6. What tools will I learn in a data analytics program?
Python, SQL, Tableau, Power BI, and Excel are typically full-course offerings.
7. What kind of projects are included in the course?
Real-world case studies of e-commerce, banking, health care, and logistics to allow you to apply what you learned.
8. Do I need a tech background to enrol?
Though preferred, the majority of courses also accept non-tech candidates who are willing to learn and put in the effort from scratch.
9. How long is the data analytics program by Imarticus?
The Postgraduate Program in Data Science and Analytics is a 6-month program that is fast-track and highly effective in terms of job readiness.
10. Will I get placement support after completing the program?
Yes, Imarticus offers 100% job guarantee with 10 guaranteed interviews, resume preparation, and mock interviews.