Introduction
If you’ve been hearing a lot about blockchain but aren’t sure what it really is, you’re not on your own. This game-changing tech started by making things like Bitcoin work and has now gone on to change many areas, like supply control, health care, money matters, and more. But here’s the key question: what exactly is blockchain tech, and why are big tech firms and new small firms all rushing to use its power?
In this blog, we will explore the nuts and bolts of blockchain technology to see how it works, game-changing use cases, and its future. As a curious learner or business manager, this guide will assist you in grasping the game-changing influence of blockchain in the contemporary world.
What is Blockchain Technology?
By its very nature, blockchain is a decentralised digital ledger that makes transactions on many computers so the information cannot be tampered with in the past. This provides transparency, security, and trust–without intermediaries. It is such as a shared Google spreadsheet, yet one no one person has access to and where every transaction is irreversibly logged.
When you hear the term blockchain tech, it means a system for keeping data in “blocks” linked in time order and with strong code. This setup makes it hard to mess with, giving it big use for safe data use in many areas.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralisation: No one owns the data.
- Immutability: Data cannot be altered once it has been recorded.
- Transparency: Everyone involved can see the ledger.
- Consensus: Data is confirmed by consensus among nodes.
| Feature | Description |
| Decentralised | Eliminates the need for a central authority |
| Transparent | Participants can view and verify the entire transaction history |
| Immutable | Once data is recorded, it cannot be modified |
| Secure | Cryptographic principles secure every block |
| Consensus-driven | Transactions validated via consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) |
Blockchain Applications Across Industries
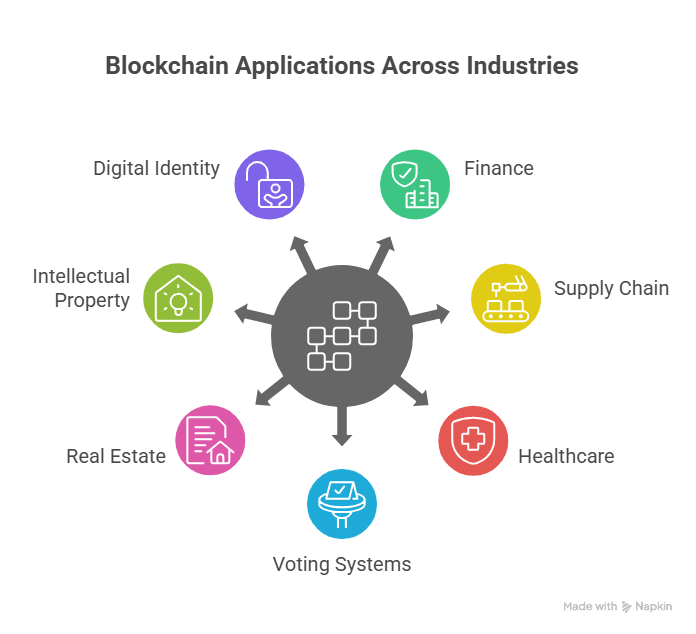
Practical applications of blockchain extend far beyond cryptocurrency. Organizations across industries are today researching the potential of blockchain applications to address actual problems and spur innovation.
In finance, blockchain provides secure and faster transactions. In health, it allows for tamper-proof medical records. In supply chain, it offers end-to-end product traceability. Even governments are leveraging blockchain for land registration and digital identity.
Main Uses of Blockchain
- Supply Chain Checks: Live checks and where goods are.
- Health Care: Safe info share and patient files.
- Banks & Money: Safe money moves across borders quick and clever deals.
- Digital ID: Checked IDs to stop cheats.
- Voting Systems: Tamper-proof and transparent electronic voting.
- Intellectual Property: Royalty distribution and copyright protection.
External Resource: World Economic Forum on Blockchain Applications
Blockchain in Business: Revolutionising Operations
Blockchain in business is not a buzzword—it’s an engine of efficiency and trust. From automating back-end operations to greater transparency of transactions, blockchain is rewriting the rules of how companies work.
Companies are employing smart contracts to automatically enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries and legal documentation. Blockchain also facilitates the simplification of audit, logistics, and customer validation processes.
Advantages of Blockchain in Business:
- Enhanced Traceability: Every transaction is timestamped and verifiable.
- Fraud Prevention: Hard to falsify or modify records.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates middlemen and third-party authenticators costs.
- Faster Settlements: Instantaneous processing of transactions.
| Business Function | Blockchain Use Case |
| Finance | Cross-border payments, smart contracts |
| HR & Recruitment | Credential verification |
| Supply Chain | Inventory management, provenance tracking |
| Legal | Smart contracts, digital notary |
External Resource: Harvard Business Review on Blockchain in Business
Distributed Ledger Technology: The Backbone of Blockchain
To get a proper idea of what is blockchain technology, we have to discuss Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). Blockchain is a form of DLT—a network of computers (or nodes) that maintain synchronously a common, secure database.
DLT does away with a central record-keeper. All the nodes have visibility to the same data, and any modification is propagated throughout the system in real-time. This arrangement increases trust and transparency, particularly in multi-party settings.
Differences Between Blockchain and DLT:
| Feature | Blockchain | Distributed Ledger Technology |
| Data Structure | Blocks linked in a chain | No specific structure required |
| Use of Tokens | Often includes cryptocurrencies | May not include tokens |
| Public Access | Can be public or private | Usually permissioned |
| Example Technologies | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Corda, Hyperledger Fabric |
External Resource: IBM Explains DLT vs Blockchain
Blockchain Industry Impact: Key Sectors Transformed
The blockchain industry impact has been massive across several sectors. It’s not only seen in fintech. We see its mark in logistics, fun, learning, and even farming.
Blockchain brings safe, clear, and good work ways, building trust in fields where keeping data true is key. Let’s see how many areas gain from it.
Industries Revolutionized by Blockchain:
- Finance: Real-time settlements, fraud prevention mechanisms, smart loans.
- Healthcare: Tamper-evident health records, accelerated insurance processing.
- Retail: Sourcing transparency, loyalty schemes.
- Agriculture: Farm-to-fork traceability, proof of fair trade.
- Media: Digital rights management, ownership through NFTs.
- Education: Verified credentials, decentralised learning platforms.
Future of Blockchain: What’s Coming Next?
The road ahead for blockchain looks bright. It will mix with AI and IoT, and more folks will use DeFi. As more work goes digital, blockchain is set to be key.
Governments are also welcoming it for intelligent governance and regulatory alignment. Startups are creating end-to-end ecosystems based on blockchain, while incumbent companies are integrating it into existing infrastructure.
Future Trends in Blockchain:
- Decentralised Finance (DeFi): Banking-free open financial services.
- Interoperability: Blockchains that can talk to one another.
- Green Blockchain: Efficient energy use in consensus models.
- NFT 2.0: Tokens driven by utility beyond art and collectibles.
- AI + Blockchain: Improved decision-making with secure data.
If you want to build a job in the world of money and blockchain later on, the Post Graduate Diploma in Fintech at Imarticus Learning has a good course list that fits what the job world needs.
Key Takeaways
- What is blockchain tech: A Decentralised digital ledger no one can change.
- Blockchain uses reach into money, health, school, and the flow of goods.
- Blockchain in work makes things easy and builds trust.
- Distributed ledger technology supports blockchain’s secure design.
- Blockchain industry influence is evident in retail, media, and governance.
- The future of blockchain is about AI, DeFi, and green innovation.
FAQs
1. What is blockchain tech in easy words?
Blockchain is a setup that keeps data in parts linked in a sure, firm line, making it clear and trusted.
2. How do folks use blockchain out there?
It’s used in banks, health, supply lines, vote systems, and more, for safe and clear record-keeping.
3. What work areas use blockchain now?
Areas like money, health, news, farming, and learning are using blockchain for different uses.
4. Is blockchain just for digital money?
No. While it first came for digital money, blockchain now runs things from online ID to moving goods tracking.
5. How does distributed ledger work?
It keeps all of the copies of the database in sync across many locations, so it’s essentially impossible to modify the data.
6. What are the types of blockchain?
There are public, private, consortium & hybrid blockchains -each used for different use cases & privacy requirements.
7. What is a smart contract?
Smart contracts are executing contracts with terms embedded directly into code, making it automatic and trusted execution.
8. Is blockchain secure?
Yes. Its decentralised and encrypted nature makes it virtually impossible for any one party to tamper with data.
9. What are some blockchain platforms?
Popular platforms are -Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Corda & Tezos.. each with its own features.
10. Is it possible for me to have a blockchain career?
Yes. With careers such as blockchain developer, architect, and analyst, it’s an emerging field with high demand.
Conclusion
Now that we know what blockchain tech is, it’s clear it’s more than a cool word. It’s spread-out, safe, and open in ways that make it a strong help for companies and fields that aim for trust and speed. As blockchain grows, being up to date and learning more is very key.
If you are a fintech fanatic or even a business leader, now is the best time to jump into the blockhain world. Ready to take the leap? Discover the PGDM in Fintech by Imarticus Learning and arm yourself with hot skills that will craft tomorrow’s digital economy.