A junior trader at a Mumbai investment firm once entered a derivatives trade without fully grasping the legal terms outlined in their ISDA agreement. When markets moved against them, the firm couldn’t unwind the position smoothly due to a clause they’d overlooked.
The result?
A multi-crore loss, avoidable, had they known what they were signing.
If you’re venturing into derivatives, whether in trading, operations, or legal, you can’t afford to misunderstand the ISDA framework. Your contracts aren’t just paperwork—they’re risk shields. This post gives you the clarity you need to confidently read and interpret the structure and terms of ISDA agreements.
Why ISDA Exists—and Why It Matters to You?
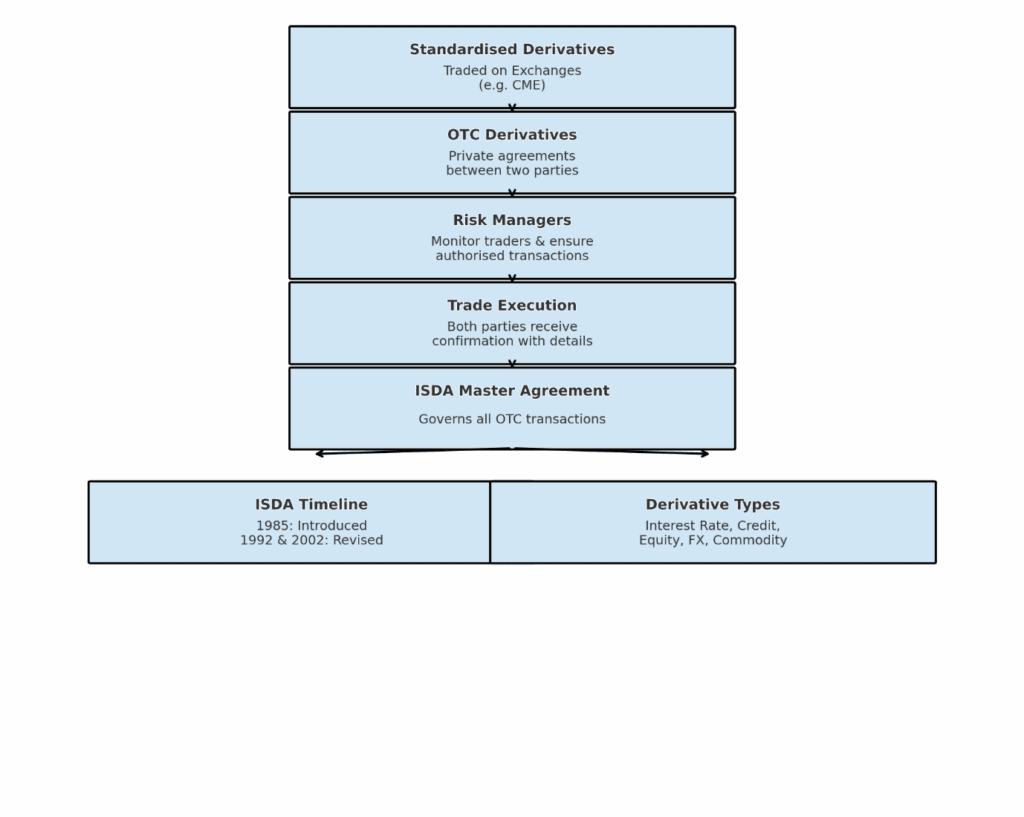
The International Swaps and Derivatives Association introduced the ISDA Master Agreement in the 1980s to standardise over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives trading.
This framework includes the master agreement itself, a schedule, trade confirmations, definition booklets, and credit support documentation.
Today, the ISDA agreement is the go-to framework used by banks, hedge funds, insurance firms, and even sovereign entities. It governs relationships in swaps, forwards, options, and credit derivatives. If you joined investment banking courses, chances are this is one of the first legal documents you’ll study in derivatives training.
The original ISDA Master Agreement was introduced in 1985 to bring consistency to OTC derivatives documentation.
Types of Derivatives Covered Under ISDA Agreements
- Interest rate derivatives
Interest rate swaps, caps, floors, swaptions - Credit derivatives
Credit default swaps - Equity derivatives
Equity swaps, options, forwards - Foreign exchange derivatives
Currency swaps, forwards, options - Commodity derivatives
Commodity swaps, options, forwards
You don’t need to be a lawyer to understand the ISDA agreement—you just need the right roadmap.
Breaking Down the ISDA Agreement: Key Components
Let’s break down the ISDA agreement structure into core components:
1. ISDA Master Agreement (Single Contract Philosophy)
This is the backbone. It standardises terms like netting, termination events, and payment flows. It treats all transactions under one legal umbrella.
2. Schedule to the Master Agreement
This section lets parties customise clauses based on their preferences. Think of it as a ‘personalisation layer’ for risk appetite, tax considerations, or jurisdictional nuances.
3. Credit Support Annex (CSA)
The CSA governs collateral. It decides who posts margin, when, and in what form—vital for reducing counterparty risk.
4. Confirmations
Each trade has a confirmation stating the economic terms. Even if dozens of trades happen, they all fall under the single ISDA Master Agreement.
ISDA Agreement Example:
A bank and a power utility enter into an interest rate swap. The Master Agreement outlines the legal groundwork. The CSA details how collateral is exchanged based on market movements. Confirmations lock in the trade specifics. If the utility defaults, the Master Agreement governs how you can calculate losses.
You’ll come across terms like “cross-default,” “close-out netting,” and “force majeure.” Each has financial consequences if misinterpreted.
How to Interpret an ISDA Agreement in Practice
If you’re just starting out, here’s a practical guide:
Step 1: Identify Parties and Governing Law
This is usually found in the opening paragraph and the Schedule. In India, many agreements fall under English law due to global best practices.
Step 2: Understand Netting Provisions
These help determine how losses and gains across multiple trades are offset during termination.
Step 3: Check Credit Support Terms
Look at threshold amounts, eligible collateral types, and margin frequency.
Step 4: Review Termination Events
Events like bankruptcy, merger, or regulatory changes can trigger early termination. Each clause outlines how parties unwind positions.
Step 5: Study ISDA Agreement Example Templates
Online repositories or regulatory sites often provide anonymised templates. Use them as a reference to familiarise yourself with industry norms.
From Theory to Trade Desk
Many professionals treat the ISDA Master Agreement as a legal checkbox. However, the difference between a well-negotiated clause and a standard one could mean a loss buffer or a lawsuit. If you’re prepping for front-office or middle-office roles, now is the time to move from passive reading to active application.
- Start reading real agreements.
- Dissect clauses.
- Ask your seniors how these documents played out in crisis scenarios.
This isn’t about rote learning—it’s about strategic thinking.
ISDA Agreement Key Elements at a Glance
| Component | Purpose / Function | |
| Master Agreement | Defines overarching legal terms for all trades | |
| Schedule | Customises general terms for specific counterparties | |
| CSA | Outlines collateral requirements, thresholds, and margin rules | |
| Confirmations | Captures specific trade details under the master contract | |
| Termination Provisions | Sets events and rules for early closure and valuation | |
Launch Your Finance Career with the Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional (CIBOP™) Programme
Imarticus Learning’s Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional (CIBOP™) programme is a career-defining choice for finance graduates with up to three years of work experience.
Recognised as the Best Education Provider in Finance at the 30th Elets World Education Summit 2024, this investment banking course has shaped countless careers over the past decade by combining job-assured outcomes with practical, industry-aligned learning.
Through practical hands-on training delivered by experienced teaching faculty, Imarticus Learning provides students with an interactive educational movement. This investment banking course focuses intensively on skills necessary for operational roles at securities institutions, wealth management, and asset management organisations.
Students develop an understanding of the industry dynamics through a combination of case studies, classroom exercises, projects, and interactive puzzles, which reveal how it operates. The 100% job assurance model stands as Imarticus’ differentiating factor. An integral component of this programme is at least seven exclusive meetings that connect students with premier investment banking companies.
Students enrol in comprehensive career support activities combined with technical education at Imarticus learning, which includes soft skills instruction, along with curriculum vitae creation assistance and practice interview preparation to maximise their readiness for employment.
Enrol in the Certified Investment Banking Operations Professional (CIBOP™) programme by Imarticus Learning today and secure your future in the world of investment banking.
FAQs
Q1. What is an ISDA agreement used for?
It standardises the legal terms for over-the-counter derivatives between two parties.
Q2. How is the ISDA agreement structure organised?
It typically includes a Master Agreement, Schedule, CSA, and trade confirmations.
Q3. Can you share an ISDA agreement example?
Yes. A standard interest rate swap between a bank and corporate borrower would fall under a signed ISDA Master Agreement, with specific terms customised in the Schedule.
Q4. What does a Credit Support Annexe do?
It outlines collateral arrangements between counterparties to manage credit risk.
Q5. Is ISDA only for banks?
No. Hedge funds, corporates, insurance firms, and even government bodies use it.
Q6. Do all trades require a new agreement?
No. Once an ISDA Master Agreement is in place, you can add individual trades via confirmations.