Last updated on April 8th, 2024 at 04:31 am
Last Updated on 2 years ago by Imarticus Learning
Data security and privacy are most important than ever in the technology-driven society we live in today because of the explosion in the volume of data being created and exchanged.
The preventative steps taken to stop illegal access, theft, or damage to electronic data are data security. In contrast, privacy entails preventing the collection, use, or sharing of someone’s personal information without that person’s agreement.
Both data security and privacy are crucial for both individuals and companies since a breach of either may have serious repercussions, such as monetary loss, legal liability, reputational harm, and loss of confidence.
This blog will discuss the importance of data security and privacy for individuals and corporations. We will examine the dangers and repercussions of data breaches, discuss best practices for data protection, and offer advice on negotiating the complicated regulatory environment around data privacy.
What are data security and privacy?
The process of protecting data against illegal access, use, alteration, disclosure, or destruction is known as data security. Data security in cloud computing seeks to thwart hostile actions that might jeopardize the integrity and confidentiality of data, including data breaches, cyberattacks, fraud, and identity theft.
Customers used financial applications a trillion times in 2019, and Forbes predicted that number would increase considerably in 2020.
Individuals and organizations have the right to determine how their data is gathered, utilized, shared, and preserved. Data privacy goals are respected for data ownership, permission, openness, and responsibility. Complying with the rules and regulations that control data protection is another aspect of maintaining data privacy.
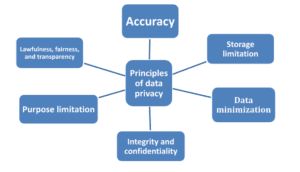
The General Data Protection Regulation GDPR Compliance of the European Union outlines the six data privacy principles. These principles are:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality
Why are data privacy and security crucial for individuals?
You produce and consume a lot of data daily in the digital age. Additionally, you keep your data on external devices like your laptop or smartphone and cloud services. Your information is important to you and others who might wish to utilize it for their gain. For instance, hackers could seek to steal your information to access your accounts, pass themselves off as you, or sell it on the dark web.
If your data is not private and secure, you risk suffering catastrophic repercussions like:
- Identity theft: If your identity is stolen, someone else may use it to defraud people or commit crimes in your name.
- Financial loss: If someone gains access to your credit cards or bank accounts, they may withdraw money or make illicit transactions.
- Reputational harm or blackmail: If someone posts private or humiliating information about you online, it might hurt your reputation.
- Loss of trust: When someone misuses your data without your knowledge or consent, they undermine your trust in online services or platforms.
- Loss of freedom: If someone restricts your online access to information or services based on your data profile, they may do so to the detriment of your freedom.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Small Businesses
October is recognized worldwide as Cybersecurity Awareness Month (CSAM).
As a result, in the digital era, an individual who values data security and privacy rights:
- You must know how internet companies acquire, utilize, share, and keep your data.
- Be cautious about the data you disclose online and with whom you share it.
- Use encryption software and strong passwords to prevent unwanted access to your data.
- You should frequently upgrade your software and hardware to address any security flaws.
- You should check your privacy preferences and settings across various platforms and services to ensure they align with your expectations.
The Importance of Data Privacy for Businesses
In the digital era, information security has grown more crucial for enterprises. Protecting consumer and employee personal information is essential for businesses, given the rise in data breaches and cyberattacks. Failure to do so may result in money, legal responsibilities, and reputation losses.
The effect it may have on a company’s reputation is the reason why data privacy is vital for enterprises. A data leak may significantly damage a company’s reputation and erode consumer and stakeholder confidence. This may result in a drop in revenue, trouble finding new clients, and harm the company’s reputation.
Additionally, organizations are required by law to safeguard customer information under several privacy regulations. Heavy fines, legal action, and other penalties for breaking these rules may be imposed.
Businesses may suffer serious financial consequences as a result of data breaches. Investigations, legal expenses, and consumer notification can all significantly add to the rehabilitation cost. Additionally, corporate losses brought on by reputational harm might result in large revenue losses.
The Final Words
Data security and privacy are crucial for individuals and enterprises in the digital era. Numerous advantages have resulted from the ever-increasing use of technology, but it has also introduced new dangers and difficulties, particularly when safeguarding sensitive data.
People may defend themselves against identity theft, fraud, and other cybercrimes by implementing efficient data security and privacy safeguards, and organizations can protect their reputation, clients, and financial stability. Maintaining vigilance and proactively securing sensitive data as the digital environment changes are critical.
The PG Program in Cybersecurity, developed by Imarticus Learning in partnership with industry leaders, seeks to provide future cybersecurity professionals with the finest learning experience possible. You will graduate from this comprehensive 6-month program with the abilities and know-how needed to succeed in positions like cybersecurity analyst, penetration tester, incident handler, and SOC team member.

