Last Updated on 3 months ago by Imarticus Learning
Financial risk is rarely obvious at first. It shows up through small changes in interest rates, market behaviour, credit conditions, or model assumptions. Over time, these small changes compound. The FRM Exam exists to test whether someone can recognise and connect these signals before they turn into larger problems.
FRM focuses on how risk behaves in real systems. Questions are built around interpretation, probability, and context rather than isolated formulas. A single scenario may touch markets, data, and judgment at the same time, reflecting how decisions are made inside financial institutions.
What draws professionals to FRM is its relevance. Banks, funds, and regulated firms rely on risk teams to translate uncertainty into informed action. The exam mirrors this reality by testing applied understanding under time pressure.
Here is a quick overview of what this journey entails for candidates targeting a solid career in risk management:
→ FRM is a globally recognised certification focused specifically on financial risk management in regulated and market-driven environments.
→ FRM exams are structured across two papers that move from risk fundamentals to real-world application and judgment.
→The exam difficulty lies in interpreting risk scenarios under time pressure rather than in advanced calculations.
→ The exam dates are scheduled in fixed windows each year, making it possible to plan preparation alongside work or studies.
→ The FRM pass rate varies by attempt, which is why balanced preparation and mock practice matter more than targeting a fixed score.
This guide breaks down the FRM Exam in a clear, practical way. It covers structure, difficulty, pass rate logic, exam dates, and preparation strategy so you can follow the exam journey with clarity from start to finish.
An Overview of What is FRM
To understand the FRM Exam clearly, it helps to first step back and understand what is FRM and the role it plays in modern finance. FRM stands for Financial Risk Manager, a professional designation created to formalise how financial risk is identified, measured, and managed across institutions.
The FRM course as a discipline focuses on uncertainty. It looks at how market movements, credit events, liquidity pressure, operational failures, and regulatory changes affect financial systems. This perspective goes beyond valuation or accounting and centres on how decisions hold up when conditions change unexpectedly.
What FRM Covers at Its Core
FRM focuses on variability and how financial systems react when conditions shift. The framework looks at both everyday risks and extreme scenarios that stress models and decision-making.
Key risk areas include:
- Market movements and volatility impact
- Credit events and default risk
- Liquidity pressure during stressed periods
- Operational failures and process risk
- Regulatory and compliance-driven risk
These areas are not studied in isolation. FRM connects them through impact and response.
How FRM Thinking Applies in Real Environments
FRM concepts mirror how risk teams function inside financial organisations rather than how topics are taught in classrooms.
| Risk Focus | Practical Use in Institutions |
| Market Risk | Monitoring exposure during volatile market moves |
| Credit Risk | Assessing default probability and capital adequacy |
| Liquidity Risk | Managing funding gaps in stressed conditions |
| Operational Risk | Identifying process breakdowns and loss events |
| Regulatory Risk | Aligning decisions with compliance frameworks |
This applied orientation explains the relevance of the FRM designation in professional settings.
How This Connects Directly to the FRM Exam
FRM is structured as an assessment of this mindset. Instead of testing an isolated theory, it evaluates how well candidates connect ideas such as probability, financial instruments, decision analysis & risk modelling under time constraints.
The exam typically tests:
- Interpretation over memorisation
- Context-driven decision making
- Understanding of model assumptions
- Ability to evaluate downside outcomes
This is why the exam feels different even at the introductory level. The video below goes a layer deeper in explaining the FRM comprehensively:
How the FRM Exam Is Structured and Why It Matters
Before engaging with preparation plans or exam dates, it helps to understand how the FRM course structure itself is divided and why that division exists.
Two-Part Framework
The FRM Exam has two sequential levels.
| Level | Focus Area | Nature of Testing |
| Part I | Foundations of risk | Concepts, tools, and quantitative logic |
| Part II | Application of risk | Case-based and practical scenarios |
Part I focuses on the building blocks. Quantitative analysis, probability, financial markets, and valuation techniques form the spine of this level.
Part II moves away from tools and towards judgment. Market risk, credit risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, and enterprise risk are tested through applied questions.
This separation explains a common observation. Candidates often feel confident about one level and unsettled by the other. The skills tested are related, but the thinking style shifts meaningfully. Below, I have captured a snapshot of the exam details to help you understand the testing aspects of the certification more clearly:
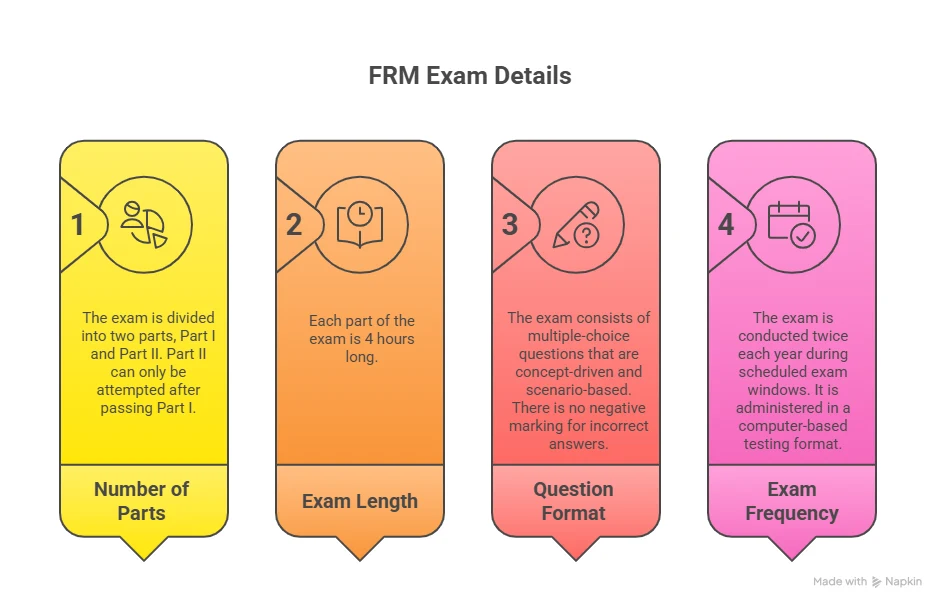
Why the FRM Exam Difficulty Is Often Misunderstood
When people discuss the exam difficulty of FRM, they often compress several factors into one vague idea. That oversimplification causes confusion.
Difficulty in the FRM certification comes from three independent sources.
1. Concept Density
Each topic draws from multiple financial disciplines. Statistics blends with economics. Derivatives connect to risk measurement. Accounting assumptions influence model outcomes.
None of the concepts is obscure, but many rely on layered understanding. Missing a foundational idea often means missing the entire question.
2. Time Pressure
Each part of the FRM Exam has a fixed number of questions within a limited window. The challenge is not just knowing the content, but processing it quickly.
Many questions are designed so that even a well-prepared candidate must choose between speed and precision.
3. Interpretation Over Calculation
A common misconception is that the FRM program is calculation-heavy by default. The numbers are rarely difficult on their own. The challenge lies in interpretation.
Small changes in assumptions can shift answers. Reading carefully matters as much as numerical accuracy.
Did You Know?
The growth of stress testing frameworks after the global financial crisis increased demand for certified risk professionals. (Source: Bank for International Settlements)
Understanding FRM Passing Marks Without Chasing Cutoffs
While GARP does not publish fixed passing marks. Instead, results are reported using quartiles.
This creates uncertainty for candidates who want a simple benchmark. The absence of a fixed score is intentional. It allows the exam to adjust for difficulty variations across attempts.
What matters more than a numerical target is relative performance. The FRM passing marks are evaluated in aggregate, based on how a candidate performs across topics rather than in isolation.
This explains why strong candidates sometimes fail, and borderline candidates pass. Score balance matters.
Reading the FRM Pass Rate More Carefully
The FRM pass rate is often quoted without context. That statistic tells only part of the story. Historically, the pass percentages have hovered between 35-60% across both parts. (Source: FRM Historical Pass Rate)
Pass rates fluctuate by exam window, but historically:
- Part I tends to have lower pass rates than Part II
- Candidates who attempt both parts together often struggle more
- Repeat candidates show higher success trends
The key nuance is this. Pass rate reflects candidate preparedness, not just exam toughness. High enrolment periods often coincide with lower averages.
FRM Exam Dates and Cycle Planning
The FRM Exam is offered twice to three times a year, in May, August, and November. Typically, exam windows fall around late spring and late autumn. Exact exam dates are announced well in advance to allow for preparation planning.
Why Dates Matter Strategically
Dates influence preparation rhythm more than most people realise.
- First-time candidates often underestimate the time needed for concept absorption.
- Working professionals benefit from longer timelines
- Registration windows affect motivation curves
The Mental Models the FRM Exam Rewards
The exam does not reward memorisation. It rewards frameworks.
Here are the mental habits that align well with exam expectations:
- Thinking in distributions, not point estimates
- Evaluating downside before upside
- Recognising model limitations
- Questioning assumptions
These habits explain why some candidates with strong academic backgrounds struggle. Familiarity with finance theory does not automatically translate into risk reasoning. The following infographic gives you an overview of the exam cycle timelines to shape your preparation with better clarity:
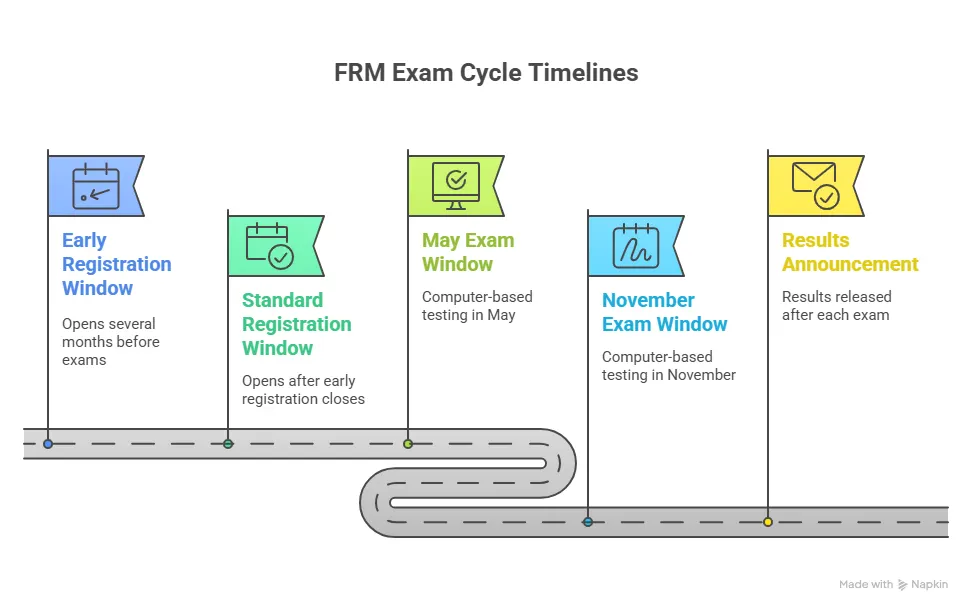
A Closer Look at Question Design
Most FRM questions share a common shape.
- A short scenario
- One key risk variable
- Multiple plausible outcomes
The wrong options often reflect mistakes in reasoning rather than math. This design tests understanding depth.
Candidates who rush calculations without reflecting on context often eliminate correct answers by accident.
Preparation Is a Process, Not Just Coverage
When people discuss FRM preparation strategy, they often focus on materials. Books, videos, question banks, and revision notes all matter.
But preparation quality is shaped more by sequence than quantity.
Effective preparation usually follows this logic:
- Concept familiarisation
- Framework building
- Question exposure
- Error analysis
Think of an FRM question like choosing a route while driving. You are given a brief situation, one key change such as traffic or weather, and several routes that all seem possible. The right choice depends on noticing that one detail. The wrong options come from ignoring context, not from misreading the map.
Preparation works the same way. First, you learn how the area is laid out, then you understand how routes behave in real conditions, and only after that does regular driving make sense. Skipping these steps and jumping straight into practice often leads to wrong turns, even when the basics are known.
Why Mock Tests Behave Differently in FRM
A FRM mock test serves a purpose beyond score prediction. Mock scores rarely map directly to final results.
Mocks are diagnostic tools. They show:
- Weak topic clusters
- Time mismanagement patterns
- Reading errors
High mock performance without reflection often leads to repeated mistakes. Lower scores accompanied by deep review tend to correlate with stronger outcomes.
Did You Know?
Risk management roles expanded globally after the 2008 financial crisis, triggering sustained demand for professional risk credentials.
Mapping Preparation Around the FRM Exam Dates
The FRM Exam is offered in fixed windows. These exam dates allow enough notice to plan, yet many candidates delay meaningful preparation until registration feels real.
A practical preparation window usually spans four to six months for one part. Shorter timelines increase cognitive load, longer ones risk stagnation.
How Candidates Typically Structure Time
| Phase | Duration | Purpose |
| Concept exposure | 6 to 8 weeks | Build familiarity |
| Application phase | 6 weeks | Solve mixed questions |
| Consolidation | 3 to 4 weeks | Strengthen weak areas |
This structure aligns learning with memory retention. It also allows flexibility if work or personal commitments intervene.
Reading for Risk Thinking, Not Completion
Study materials often encourage linear reading. That habit creates the illusion of progress.
The FRM Exam tests the application. Reading must serve interpretation, not recall.
Effective reading habits include:
- Pausing after each concept to ask how it alters risk exposure
- Noting assumptions behind formulas
- Linking models to real market behaviour
These pauses feel slow, yet they reduce future revision time.
The Role of Examples in Risk Learning
Risk management becomes clearer when abstract ideas meet ordinary situations.
For example, Value at Risk resembles household budgeting uncertainty. One may estimate monthly expenses, but rare breakdowns still occur. That tail risk is the focus.
Such analogies help anchor formulas into intuition. The FRM Exam rewards this internalisation.
Handling Setbacks and Failed Attempts
Failure in the FRM Exam does not end progression. Many charterholders pass after an initial setback.
The key difference lies in how the failure is processed.
Productive responses involve:
- Isolating weak learning segments
- Adjusting question practice volume
- Refining time allocation
Repeating the same approach rarely changes outcomes.
Cognitive Load and the Exam Difficulty Curve
The exam difficulty feels higher near the end of preparation. This is normal.
As understanding improves, candidates notice nuance. Questions feel trickier, not because they are harder, but because awareness has grown.
This awareness phase often precedes stabilisation. Recognising this pattern prevents premature discouragement.
Who Is Eligible for the FRM Exam
The FRM Exam follows an open-entry approach. There are no formal educational prerequisites required to register. This design allows candidates from varied backgrounds to enter the ecosystem and test their readiness for risk roles.
That openness often surprises people as to how the FRM is the best career option for risk professionals. Engineering graduates, commerce students, MBA candidates, working professionals, and even career switchers regularly appear in FRM candidate pools.
While anyone can attempt the FRM Exam, earning the charter eventually requires two years of relevant work experience in risk-related roles. This experience component is evaluated separately after clearing both exam parts.
FRM Exam Eligibility Overview
| Eligibility Aspect | Requirement | Important Notes |
| Educational Qualification | No formal requirement | Candidates can register for the exam regardless of their degree or academic background |
| Age Limit | No age restriction | Open to students, graduates, and working professionals |
| Professional Background | Not mandatory to attempt the exam | Candidates from engineering, commerce, finance, management, or career transitions are eligible |
| Number of Exam Parts | Two parts (Part I and Part II) | Part II can be attempted only after clearing Part I |
| Work Experience (For Charter) | 2 years of relevant risk-related work | Required only after clearing both exam parts |
| Accepted Work Experience Areas | Risk management, trading, treasury, analytics, audit, compliance, model validation | Experience is reviewed by GARP during the charter application |
| Time Limit for Experience Submission | Within 5 years of passing Part II | Failure to submit within this period requires retaking the exam |
How Eligibility Works in Practice
- Anyone can register and attempt the FRM Exam without prior approval.
- The certification title “FRM” is awarded only after both exam parts are cleared, and work experience is approved.
- Work experience can be completed before, during, or after the exams, giving flexibility to students and early-career candidates.
This open eligibility structure is what makes FRM accessible to a wide range of candidates while maintaining professional rigour at the certification stage.
Cost Structure and Financial Commitment
The FRM Exam follows a structured fee model, where the overall cost depends largely on when a candidate registers and which exam window they choose, making timing a meaningful factor in the total financial commitment.
Typical cost components include:
- One-time enrollment fee
- Exam registration fee per part
- Optional study materials and mock tests
Here is a detailed breakdown of the financial commitment required to attempt the FRM Exam. These are the standard costs (in USD) as defined by GARP (unless otherwise noted).
| Cost Component | What It Covers | Typical Amount |
| One-time Enrollment Fee | Charged once when you register for your first attempt at Part I (only for “new” candidates) | $400 |
| Exam Registration Fee (Per Part / Attempt) | Fee per exam sitting. Timing (early or standard) affects cost | Early registration: $600Standard registration: $800 |
| Part II Exam Fee (Per Part / Attempt) | For Level II of FRM, the same fee structure applies | Early: $600, Standard: $800 |
| Official Study Materials (Optional/Part-dependent) | Official curriculum books or online resources (not always included) | ~ $300 per Part (if purchased) |
| Approved Calculator (Optional but often required) | For calculation-heavy quantitative/risk questions during the exam | Typically between $34 – 56, depending on model (e.g. TI BA II Plus, HP12C) |
| Other Potential Costs | Retake fees, deferral/rescheduling fees, travel & lodging (if exams held outside home city), study-material bundles, third-party prep courses, etc. | Varies; some sources estimate the total cost (all inclusive) from $2,150 to 3,650+ for both Parts together. |
(Source: GARP FRM Exam Fees)
Financial Planning: What to Budget For
- If registering early for both parts and doing self-study (minimal extras), expect to pay roughly $1,600–1,800 (400 + 600 + 600 + maybe some misc like a calculator).
- If you include official study material for both Parts, a preferred calculator, and allow for one retake or deferral, the total outlay can increase to $2,500–3,000 or more.
- For candidates in India (or other countries), currency conversion + possible extra costs (travel, time off, study material shipping) should be factored in along with the USD base fee.
Registration Timing Matters: Early vs Standard
- Early registration gives a $200 savings per part (600 vs 800).
- Since there are two parts (Part I and Part II), registering early for both can save $400 total compared to standard fees.
- Delaying your decision or waiting until closer to exam dates increases cost. Smart financial planning recommends deciding early to reduce fees and to avoid last-minute stress.
What GARP’s Fees Cover And What They Do Not
- The enrollment fee and registration fee cover administrative processing and official examination participation.
- Study materials, approved calculators and prep courses are not included by default. These are optional but often essential, and thus add to the real cost.
- There is no refund for enrollment or registration fees after payment.
- If you need to switch exam months (deferral), there may be additional fees.
From a planning standpoint, early registration often reduces total cost. Delayed decisions tend to increase financial pressure as preparation intensifies closer to FRM exam dates.
Salary Outcomes After Clearing the FRM Exam
FRM salary questions rarely have universal answers, yet trends provide useful direction.
According to GARP’s published compensation insights and role surveys, FRM charterholders work in areas such as market risk, credit risk, treasury, model validation, and enterprise risk.
The reported salary ranges naturally differ depending on where someone works and the kind of risk role they take on. That said, global surveys published by GARP consistently show that mid-career FRM professionals are paid in line with roles that carry direct responsibility for managing financial risk within institutions.
Typical Roles and Salary Ranges After Clearing the FRM Exam
| Role | Common Employers | Estimated Annual Salary Range* |
| Market Risk Analyst | Investment banks, trading firms, asset managers | $80,000 – 140,000 |
| Credit Risk Analyst | Banks, NBFCs, rating agencies, fintech lenders | $70,000 – 130,000 |
| Treasury & Liquidity Risk Analyst | Banks, corporate treasuries, and large institutions | $75,000 – 135,000 |
| Model Validation Analyst | Banks, risk consulting firms, and regulators | $90,000 – 160,000 |
| Enterprise Risk Analyst | Banks, insurers, large corporates | $85,000 – 150,000 |
| Operational Risk Analyst | Banks, consulting firms, compliance teams | $65,000 – 120,000 |
| Risk Analytics / Quant Risk Analyst | Investment banks, hedge funds, fintech firms | $95,000 – 180,000 |
| Compliance & Regulatory Risk Analyst | Banks, financial institutions, and regulators | $70,000 – 125,000 |
(Sources: Glassdoor, PayScale, Robert Half Salary Guide)
The FRM Exam signals capability rather than guaranteeing outcomes. FRM Salary in India progression often reflects how candidates apply that signal in practice.
Let’s have a look at a broader perspective on the various roles you will be eligible for after the certification, all of which have tremendous potential to enable you for global risk roles:
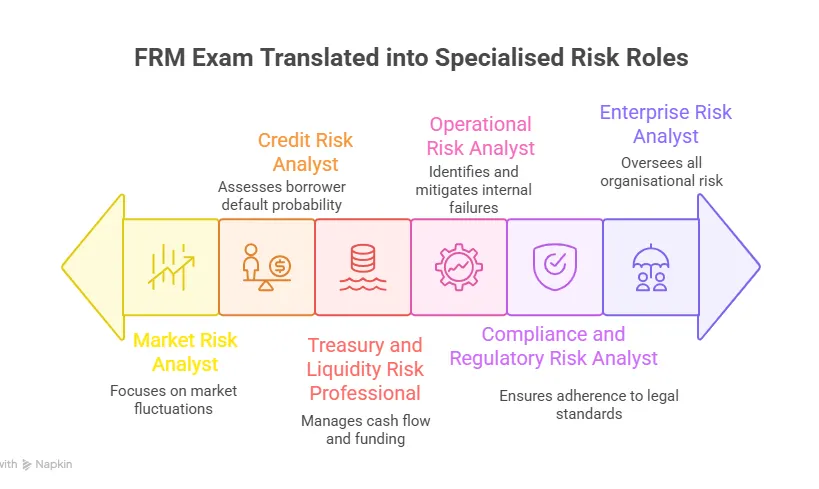
The Long-Term Value of the FRM Exam
Risk does not disappear in stable capital markets. It becomes invisible until it matters. This reality keeps demand for structured risk thinking alive.
The FRM Exam stays relevant because it evolves. Curriculum updates reflect financial innovation, regulatory change, and systemic shocks.
Long-term value comes from skill durability rather than pedigree alone.
To break down how FRM-aligned skills translate into different risk roles, I have added a video that explains the various career pathways FRM unlocks and the remuneration each of them offers, enabling you to be able to command top career avenues as a global standard risk professional:
Why Choose Imarticus Learning for Your FRM Exam Preparation
Students often require exploring FRM coaching in India to prepare smart for the exams. Opting to prepare for the FRM course with Imarticus Learning brings several advantages, from structured curriculum design to real-world-ready training. Here are the key USPs that make it a solid fit for aspiring risk professionals:
Comprehensive & GARP-Aligned Curriculum
- Imarticus offers the full FRM syllabus covering both Part I and Part II, aligning exactly with the requirements set by GARP.
- Coverage includes foundational quantitative methods, financial markets & products, valuation & risk models, as well as advanced topics like market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and current topics including ESG, fintech, and more.
Live Online Classes + Session Recordings + Flexibility.
- The program duration is around 8–9 months, delivered via live online sessions; ideal for working professionals or busy students.
- With access to session recordings, learners can revisit classes at their own pace, an important benefit when balancing work or other commitments.
Practical, Application-Focused Learning
- Imarticus doesn’t just teach theory; the course includes case studies, simulation exercises, and real-world risk scenarios, preparing students to apply concepts, not just memorise them.
- This practice-based approach helps bridge the gap between academic concepts and what risk professionals actually do in banks, funds, or financial institutions.
Extensive Mock Tests and Question Bank Support
- As part of exam readiness, Imarticus provides mock tests, formula/mind-map guides, and a robust question bank, all reflecting the standard and rigour of the FRM Exam.
- Such resources help build exam stamina, enhance speed and accuracy, and give a sense of real exam pressure, a critical element in “how to clear FRM exam.”
Strong Career Support and Industry-Relevant Placement Edge
- Imarticus is associated with many global banks, financial institutions, and firms, offering participants a pathway to relevant roles in risk management, treasury, asset management, and more.
- For professionals seeking to turn certification into a career advantage, this network + structured prep + curriculum alignment can make a meaningful difference.
FAQs About the FRM Exam
This section answers the most frequently asked questions around the FRM Exam, covering eligibility, difficulty, pass rate, exam structure, preparation approach, and career outcomes. It is designed to clarify practical doubts and help readers understand how the exam works before and during their preparation journey.
What is the FRM Exam?
The FRM Exam is a globally recognised certification assessment focused on financial risk management. It tests how candidates understand, measure, and respond to different forms of risk across markets and institutions. The exam is divided into two parts and is administered by the Global Association of Risk Professionals. The structure of the exam is designed to reflect real-world risk thinking rather than academic theory alone.
Is CFA better than FRM?
Whether CFA is better than FRM depends on career intent. FRM specialises in risk roles such as market risk, credit risk, and enterprise risk. The CFA program focuses more broadly on investment analysis and portfolio management. Professionals working in risk-heavy functions often choose the FRM because it aligns directly with their responsibilities.
Who is eligible for the FRM exam?
Anyone can register for the FRM Exam without prior qualifications. Eligibility to earn the FRM designation requires passing both parts of the exam and completing two years of relevant work experience. This open eligibility model allows students, professionals, and career switchers to test readiness before committing long-term. Imarticus Learning helps candidates from varied backgrounds build the required exam-ready foundation over time.
Which is harder, CFA or FRM?
Difficulty is experienced differently. The FRM exam difficulty comes from dense concepts, probabilistic thinking, and interpretation under time pressure. CFA difficulty comes from breadth and endurance across levels. Candidates often find the FRM exam more intense during preparation phases, especially in quantitative topics.
What is the FRM salary?
The FRM salary varies by geography, experience, and role. According to official GARP salary surveys, entry-level early-career FRM professionals earn around $60,000–90,000 per year, mid-career roles such as market risk or credit risk analysts earn about $90,000–150,000, and senior risk, model validation, or enterprise risk roles often range between $150,000–250,000+ annually, depending on geography and institution size. In India, FRM-qualified professionals commonly earn ₹10–25 LPA.
Is FRM tougher than MBA?
The FRM Exam tests technical depth, while an MBA tests managerial breadth. FRM exam difficulty arises from analytical rigour and applied risk logic. MBA programs vary widely in structure and assessment style. The two paths serve different professional needs and often complement each other rather than compete directly. Imarticus Learning helps bridge the gap between technical finance concepts and practical application, allowing the two paths to complement each other.
Is FRM maths heavy?
The FRM Exam is not maths-heavy in the traditional sense. It uses mathematics to explain risk relationships, probability, and model behaviour, but the level is mostly practical. The focus is on understanding what numbers mean and how they change under different scenarios rather than on complex calculations or advanced mathematics. Many candidates find that structured learning support with Imarticus Learning helps clarify these quantitative concepts by linking formulas directly to real risk situations.
Is FRM costly?
The FRM Exam involves a structured cost, including a one-time enrollment fee of USD 400 and exam fees of USD 600 (early) or USD 800 (standard) per part, as set by GARP. When accounting for study materials and preparation resources, the total cost for both parts typically ranges between USD 1,600 and USD 3,000, depending on registration timing and preparation choices.
What if I fail FRM?
Failing an attempt at the FRM Exam does not block future attempts. Candidates are allowed to retake any part without penalty, paying only the exam registration fee again. Many successful FRM charterholders clear one or both parts after a reattempt, often by refining their preparation strategy and exam execution. Imarticus Learning helps candidates identify gaps and improve exam execution without starting over from scratch.
How many papers are in FRM?
The FRM Exam consists of two papers, known as Part I and Part II. Part I focuses on foundational risk concepts and quantitative tools, while Part II covers applied risk areas such as market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk. Part II can be taken only after clearing Part I.
Bringing the FRM Exam Journey Into Focus
The FRM Exam brings structure to how financial risk is understood and managed. Across its two parts, it tests concepts, judgment, and the ability to interpret uncertainty under pressure. Its difficulty largely depends on how well candidates connect ideas, manage time, and apply frameworks rather than memorise formulas.
Exam dates, pass rates, mock tests, and preparation strategy all play a role, but they work best when approached as part of a single, well-paced plan.
What stands out about the FRM Exam is its relevance. The skills it tests show up in real roles across market risk, credit risk, treasury, and regulatory teams. Preparation becomes more effective when learning mirrors that reality, steady, focused, and grounded in context.
For learners who value guided timelines, curated materials, and regular feedback without unnecessary complexity, Imarticus Learning offers the FRM course prep guided by expert mentors with patience and disciplined preparation, approached thoughtfully.


This info is invaluable. Where can I find out more?