The worldwide market is undergoing an exponential surge in data output. And, businesses are realising the value of leveraging data analytics to make smarter choices. However, specific skills and procedures must be complied with in order to become a data analyst.
Notably, big data analytics firms are flourishing, with a compound annual growth rate of nearly 30% expected in the upcoming years. The market’s entire revenue in 2019 was set at $15 billion. However, it is predicted to grow further by 2025, with sales exceeding $68 billion. This tremendous growth reflects the significantly growing requirement for qualified data analysts, making 2023 an ideal period to begin a profession as a data analyst.
Once you begin your journey to become a data analyst, remember that your success is a testimonial to your effort and the growing relevance of information in everyday life.
So, let’s proceed with this fascinating journey towards a data-driven future where your ability to analyse can make a huge difference.
Unveiling Mysteries: A Thorough Guide to Pursuing a Data Analyst Career
Isn’t it impressive how information capacity can empower decision making and tackle complex questions? In our tech-driven world, the role of a data analyst has never been more vital, with so many tech transformations taking place globally.
These unsung professionals operate behind the scenes across myriads of fields like healthcare, marketing, finance, advertising, and sports, effectively transforming raw data into actionable insights.
If you wish to become a data analyst, then here is a step-by-step guide you can go through to navigate this path.
-
Understanding the Role
A data analyst is a professional who obtains, analyses, cleans and evaluates data to help businesses make decisions based on compiled datasets. Their significance spans several areas, including telecommuting, medical care, financial services, and innovation.
A data analyst’s primary tasks include the following:
- Data collection and organisation from multiple sources
- Data cleaning and preparation for analysis
- Using analytical methods and tools to analyse data
- Identifying data trends, patterns, and oddities
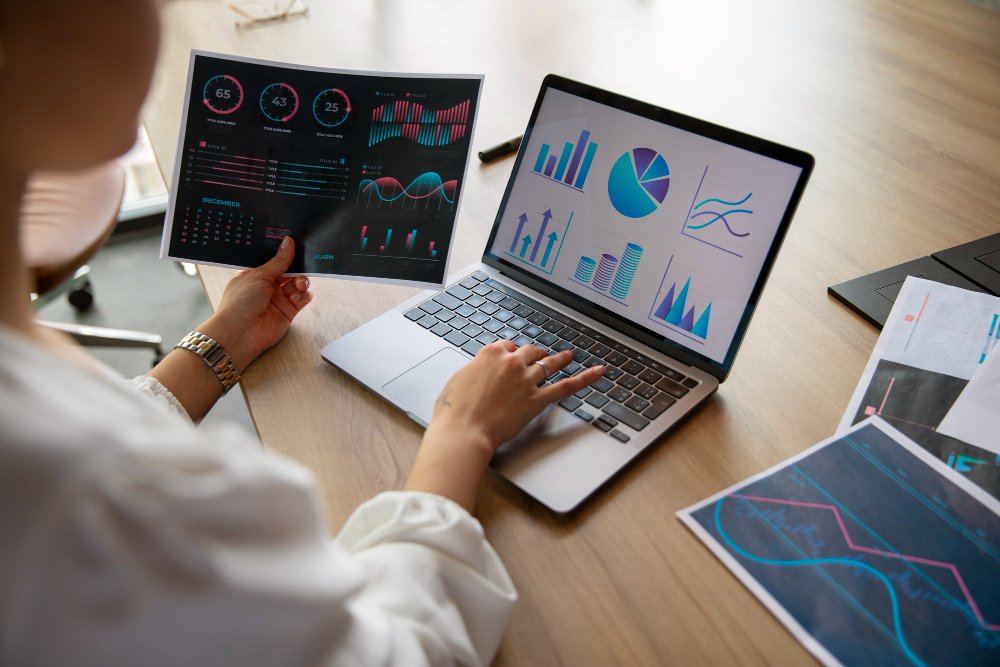
- Creating visual representations of discoveries
- Providing stakeholders with ideas and suggestions
2. Develop Essential Skills
To be a successful data analyst, you must master a variety of technical and soft skills. The following are the important abilities you should concentrate on:
- Data Processing and Cleaning: Discover how to clean, preprocess, and modify data before analysing it. This includes coping with values that are unavailable, anomalies, and inconsistencies in data.
- Data Visualisation: Use tools such as Matplotlib, Python, or ggplot2 (R) to produce relevant and useful graphical and visual representations of information.
- Statistical Analysis: Gain skills in analysing data using statistical methods such as testing hypotheses, regression evaluation, and statistical analysis.
- Machine Learning Fundamentals: Learn the fundamentals of machine learning to deploy prediction and classification methods.
- Structured Thinking and Solving Challenges: Develop excellent analytical and critical thinking abilities to approach complicated challenges and obtain practical insights from data.
3. Gain Practical Experience
To demonstrate your abilities, work on individual or cooperative data analysis projects. Make a portfolio demonstrating your ability to work with practical data and deliver insights. Look for internships or entry-level jobs that enable you to use your talents professionally. These opportunities provide substantial exposure and connection.
4. Constructing Your Portfolio
Once you’ve developed your data abilities, the next thing to do is to put it to use by compiling a portfolio of data tasks. These initiatives will show prospective employers your experience and skill in dealing with current data challenges.
Here are some pointers for developing a convincing data analytics portfolio:
- Select projects that correspond to your interests and professional objectives.
- Concentrate on projects that show a wide range of data abilities and methodologies.
- Document your project’s procedure, including problems encountered, solutions executed, and learnings acquired.
5. Engaging in Networking and Becoming Part of Data Science Communities
Attending online data science communities can assist you in building a network, acquiring knowledge from qualified experts, and demonstrating your abilities through challenges and collaborative endeavours.
Engage in data analytics meetings, conferences, and seminars to remain up to date on the latest developments and connect with like-minded people.
6. Preparing for Job Interviews
It is essential to prepare for job interviews while applying for data analyst roles by:
- Practising answers to common data analytics interview questions
- Refreshing your technical knowledge and notions
- Exercising problem-solving and coding skills
Keeping updated with the latest data analysis technology and tools and constantly strengthening your abilities through practice assignments and practical expertise are essential for success. By doing so, you can construct a strong portfolio of work and establish yourself as an extremely skilled and desired data specialist.
Final Words
Data analytics will be more than just a profession post 2023. The big data analytics sector is expanding and qualified data analysts are in demand.
We hope that through this article, you’ve learned about the profession of a data analyst, how to become one, the required skills, enrolling in a data analytics course, the importance of practical knowledge, and the need to establish a strong portfolio.
In case we have triggered your search for the right data analytics course, check out the postgraduate programme in data science and analytics from Imarticus. This programme provides hands-on learning and practical insights into how analytics and data science affect real-world enterprises.